For the reaction, N2(g)+3H2(g)⇔2NH3(g)+heat the equilibrium shifts in forward direction-Solution in Bengali
By increasing the concentration of NH3(g)
By increasing pressure and decreasing temperature
by decreasing the concentration of N2(g) and H2(g)
By decreasing the pressure
The reaction is exothermic and it is associated with decrease in volume. So, according to Le Chatelier's principle, increase in pressure at constant temperature or decrease in temperature will make the equilibrium shift to the right.
Similar Questions
For the reversible reaction
N2(g)+3H2(g)⇔2NH3(g)+Heat
The equilibrium shifts in forward directions.
View SolutionFor the reversible reaction N_2(g)+3H_2(g) iff 2NH_3(g) +heat The equilibrium shifts in forward direction
View SolutionWhen He(g) is added in the following equilibrium at constant volume
N2(g)+3H2(g)⇔2NH3(g)
Then select the correct statement.
View SolutionExamine the chemical equation given below and write the forward and backward reaction N2(g)+3H2(g)↔2NH3(g)
View SolutionN_2(g)+3H_2(g)harr2NH_3(g)+Heat Which is the endothermic reaction in this? Forward reaction/Bakward reaction.
View SolutionN_2(g)+3H_2(g)harr2NH_3(g)+heat : What change in pressure is required for the maximum yield of the product?
View SolutionN_2(g)+3H_2(g)harr2NH_3(g)+heat : What is the change in conce-natration required for increasing the rate of the forward reaction?
View SolutionThe graph for the reaction N2(g)+3H2(g)↔2NH3(g)+heat is given below.
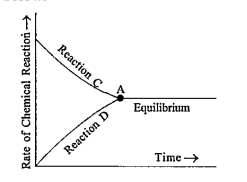 Indentify and write the reactions C and D
Indentify and write the reactions C and D
View Solution

