HO-CH2−CH2-CH =O (1)KCN−−−−−−−→(2)H⊕(3)H2O⊕(4)Δ(A), Product (A) is ,
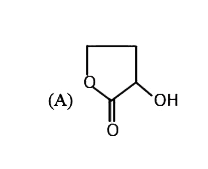
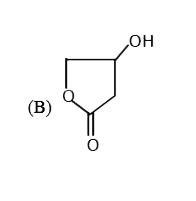
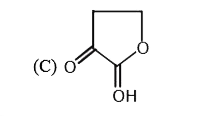
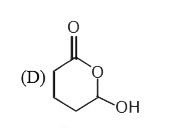
The correct Answer is:A
To solve the given question, we need to analyze the reaction step by step. The starting material is HO-CH₂-CH₂-CH=O, which is an aldehyde with a hydroxyl group. The reaction involves KCN (potassium cyanide) and H₂O (water) in the presence of H⁺ ions.
1. Identify the Starting Material:
The starting compound is HO-CH₂-CH₂-CH=O. This is a 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde.
2. Nucleophilic Attack by KCN:
The cyanide ion (CN⁻) from KCN acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde (C=O) group. This results in the formation of a tetrahedral intermediate.
Hint: Remember that nucleophiles attack electrophilic centers, such as carbonyl carbons.
3. Protonation of the Intermediate:
In the presence of H⁺ ions, one of the hydroxyl groups can be protonated, leading to the formation of an oxonium ion. This intermediate can then undergo hydrolysis.
Hint: Protonation increases the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon, making it more reactive.
4. Hydrolysis:
Water (H₂O) attacks the carbonyl carbon of the oxonium ion, leading to the formation of a new hydroxyl group and the conversion of the carbonyl to a hydroxyl.
Hint: Hydrolysis is a reaction where water is used to break bonds, often resulting in the formation of hydroxyl groups.
5. Formation of a 5-Membered Ring:
The lone pair on the oxygen can attack the carbonyl carbon, forming a 5-membered cyclic intermediate. This step is crucial as it stabilizes the structure.
Hint: Cyclic structures often form in reactions involving nucleophiles and electrophiles due to the stability of ring formations.
6. Deprotonation:
The nitrogen in the intermediate can accept a proton, leading to the formation of an amine group. This step is essential for the final product.
Hint: Deprotonation is a common step in organic reactions that helps stabilize charged intermediates.
7. Formation of the Final Product:
The leaving group (NH₃) departs, and we are left with a double bond between carbon and oxygen (C=O) along with a hydroxyl group (OH) on the adjacent carbon.
Hint: The leaving group is often a good nucleophile or a stable molecule that can depart without destabilizing the product.
8. Final Structure:
The final product A is a compound with a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (OH) adjacent to it, which corresponds to the structure of a 5-membered ring compound.
Conclusion:
The product A formed from the reaction is a 5-membered cyclic compound with a hydroxyl group and a carbonyl group.
Final Product:
The final product A is 5-hydroxy-2-oxopentanenitrile.
The starting compound is HO-CH₂-CH₂-CH=O. This is a 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde.
The cyanide ion (CN⁻) from KCN acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde (C=O) group. This results in the formation of a tetrahedral intermediate.
In the presence of H⁺ ions, one of the hydroxyl groups can be protonated, leading to the formation of an oxonium ion. This intermediate can then undergo hydrolysis.
Water (H₂O) attacks the carbonyl carbon of the oxonium ion, leading to the formation of a new hydroxyl group and the conversion of the carbonyl to a hydroxyl.
The lone pair on the oxygen can attack the carbonyl carbon, forming a 5-membered cyclic intermediate. This step is crucial as it stabilizes the structure.
The nitrogen in the intermediate can accept a proton, leading to the formation of an amine group. This step is essential for the final product.
The leaving group (NH₃) departs, and we are left with a double bond between carbon and oxygen (C=O) along with a hydroxyl group (OH) on the adjacent carbon.
The final product A is a compound with a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (OH) adjacent to it, which corresponds to the structure of a 5-membered ring compound.
The product A formed from the reaction is a 5-membered cyclic compound with a hydroxyl group and a carbonyl group.
The final product A is 5-hydroxy-2-oxopentanenitrile.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- CARBONL COMPOUNDSBook:MOTIONChapter:CARBONL COMPOUNDSExercise:EXERCISE -2 (LEVEL-II)
Explore 18 Videos
- CARBONL COMPOUNDSBook:MOTIONChapter:CARBONL COMPOUNDSExercise:EXERCISE - 3
Explore 10 Videos
- CARBONL COMPOUNDSBook:MOTIONChapter:CARBONL COMPOUNDSExercise:EXERCISE -1
Explore 40 Videos
- BIOMOLECULES & POLYMERSBook:MOTIONChapter:BIOMOLECULES & POLYMERSExercise:EXERCISE - 4 (LEVEL II)
Explore 17 Videos
- CARBOXYLIC ACIDBook:MOTIONChapter:CARBOXYLIC ACIDExercise:Exercise - 4 (LEVEL - 2 )
Explore 22 Videos
Similar Questions
Which one of the following is mixed ketone (Aliphatic & aromatic):
View SolutionPredict the product of the reaction of propanal with each of the following
(a) Lithium aluminum hydride
(b) Sodium borohydride
(c) Hydrogen(nickel catalyst)
(d) Methylmagnesium iodide, followed by dilute acid.
(e) Sodium acetylide, followed by dilute acid
(f) Phenyllithium, followed by dilute acid
(g) Methanol containing dissolved hydrogen chloride
(h) Ethylene glycol, p-toluenesulfonic acid, benzene
(i) Aniline (C6H5NH2)
(j) Dimethylamine, p-toluenesulfonic acid, benzene
(k) Hyderoxylamine
(l) Hydrazine
(m) Product of part(l) heated in triethylene glycol with sodium hydroxide
(n) p- Nitrophenylhydrazine
(o) Semicarbazide
(p) Ethylidenetriphenylphosphorane [(C6H5)3+P–¯¯¯..CHCH3] (q) Sodium cyanide with addition of sulfuric acid
(r) Chromic acid
View SolutionThe best method for the conversion of ethanol to ethanal is-
View SolutionWhich of the following pairs give positive Tollen's test ?
View SolutionThe IUPAC name of C6H5COCl is
View SolutionIn the given reaction,The main product will be: underset(H_(2)O //H^(oplus))overset(CH_(3)MgBr//Cu_(2)I_(2))(rarr)(Y)
View Solution2Ph-overset(O)overset(||)(C)-CH_(3)underset(H_(2)O)overset(Mg-Hg)to underset(Delta)overset(Conc.H_(2)SO_(4))to overset(KMnO_(4),H^(oplus))to The final product is
View SolutionH_(3)C-overset(O)overset("||")C-O-underset(Ph)underset(|)C=CH_(2)+H_(2)O overset(NaOH)underset(H_(3)^(oplus)O)rarrX+Y X and Y are:
View SolutionCH_(3)-underset(Br)underset(|)CH-CH_(2)-overset(O)overset(||)C-CH_(3)underset(Delta)overset(N_(2)H_(4),overset(Ө)OH)rarr product :
View Solution2Ph−O∣∣C−CH3Mg−Hg−−−−→H2OConc.H2SO4−−−−−−−→ΔKMnO4,H⊕−−−−−−−→
The final product is
View Solution(i). R-underset(OH)underset(|)(CH)-CH_(2)COOHunderset(Delta)overset(NaHCO_(3))toR-underset(OH)underset(|)(CH)-CH_(2)-H (ii). R-underset(NO_(3))underset(|)(CH)-CH_(2)COOHunderset(Delta)overset(NaHCO_(3))toR-underset(NO_(2))underset(|)(CH)-CH_(2)-H (iii) R-underset(O)underset(||)C-CH_(2)COOHoverset(Delta)rarrR-underset(O)underset(||)C-CH_(3)
View SolutionCh3−CH2−C≡CHR−−−→H3O⊕ Butanone, R is
View Solution3-Pentanol is produced by which of the following reactions?
1. CH3CH2BrMg−−→EtherCH3CH2OH−−−−−−−→H⊕−−→H2O
2.H≡CHNaNH2−−−−→CH3CH2CHO−−−−−−−−→H⊕−−→H2O
3.(CH3CH2)2COLiAlH4−−−→EtherH⊕−−→H2O
View SolutionCH_(3)-CH_(2)-O-underset(CH_(3))underset(|)(C)=CH_(2)overset(H_(3)O^(oplus))rarr Products are
View SolutionIn the following reaction H_(3)C - underset(CH_(3))underset(|)overset(CH_(3))overset(|)(C) - CH = CH_(2) overset(H_(2)O //H^(oplus))rarr underset("Major product")(A) + underset("Minor product")(B) The major product is
View Solution
