Rate of decarboxylation of following carboxylic acid with sodalime will be in order
CH3COOHNaOH+CaO−−−−−−−→r1
CH3CH2COOHNaOH+CaO−−−−−−−→r2
CH3−CH3∣CH−COOHNaOH+CaO−−−−−−−→r3
r1>r2>r3
r3>r2>r1
r2>r3>r1
r1>r3>r2
The correct Answer is:A
To determine the rate of decarboxylation of the given carboxylic acids with sodalime (a mixture of sodium hydroxide and calcium oxide), we will analyze the stability of the carbanions formed during the decarboxylation process.
1. Identify the Carboxylic Acids:
- The three carboxylic acids are:
- R1: Acetic acid (CH₃COOH)
- R2: Propanoic acid (CH₃CH₂COOH)
- R3: Isobutyric acid (CH₃(CH₃)C(COOH)H)
2. Understand the Decarboxylation Mechanism:
- Decarboxylation involves the removal of CO₂ from the carboxylic acid, which can be facilitated by the presence of strong bases like NaOH in sodalime.
- The hydroxide ion (OH⁻) abstracts a hydrogen atom from the carboxylic acid, forming a carbanion (RCH₂COO⁻).
3. Formation of Carbanions:
- For R1 (Acetic acid): The carbanion formed is CH₃⁻.
- For R2 (Propanoic acid): The carbanion formed is CH₃CH₂⁻.
- For R3 (Isobutyric acid): The carbanion formed is (CH₃)₂C⁻.
4. Stability of Carbanions:
- The stability of carbanions decreases with increasing substitution:
- CH₃⁻ (1° carbanion) is the most stable.
- CH₃CH₂⁻ (2° carbanion) is less stable than CH₃⁻.
- (CH₃)₂C⁻ (3° carbanion) is the least stable due to the destabilizing inductive effect of the two methyl groups.
5. Rate of Decarboxylation:
- The rate of decarboxylation is directly related to the stability of the carbanion formed:
- R1 (Acetic acid) will decarboxylate the fastest due to the stability of CH₃⁻.
- R2 (Propanoic acid) will decarboxylate next as CH₃CH₂⁻ is less stable than CH₃⁻.
- R3 (Isobutyric acid) will decarboxylate the slowest due to the instability of (CH₃)₂C⁻.
6. Conclusion:
- The order of decarboxylation rates is:
- R1 > R2 > R3
Final Answer:
The rate of decarboxylation of the given carboxylic acids with sodalime will be in the order:
R1 (CH₃COOH) > R2 (CH₃CH₂COOH) > R3 ((CH₃)₂C(COOH)H).
---
- The three carboxylic acids are:
- R1: Acetic acid (CH₃COOH)
- R2: Propanoic acid (CH₃CH₂COOH)
- R3: Isobutyric acid (CH₃(CH₃)C(COOH)H)
- Decarboxylation involves the removal of CO₂ from the carboxylic acid, which can be facilitated by the presence of strong bases like NaOH in sodalime.
- The hydroxide ion (OH⁻) abstracts a hydrogen atom from the carboxylic acid, forming a carbanion (RCH₂COO⁻).
- For R1 (Acetic acid): The carbanion formed is CH₃⁻.
- For R2 (Propanoic acid): The carbanion formed is CH₃CH₂⁻.
- For R3 (Isobutyric acid): The carbanion formed is (CH₃)₂C⁻.
- The stability of carbanions decreases with increasing substitution:
- CH₃⁻ (1° carbanion) is the most stable.
- CH₃CH₂⁻ (2° carbanion) is less stable than CH₃⁻.
- (CH₃)₂C⁻ (3° carbanion) is the least stable due to the destabilizing inductive effect of the two methyl groups.
- The rate of decarboxylation is directly related to the stability of the carbanion formed:
- R1 (Acetic acid) will decarboxylate the fastest due to the stability of CH₃⁻.
- R2 (Propanoic acid) will decarboxylate next as CH₃CH₂⁻ is less stable than CH₃⁻.
- R3 (Isobutyric acid) will decarboxylate the slowest due to the instability of (CH₃)₂C⁻.
- The order of decarboxylation rates is:
- R1 > R2 > R3
The rate of decarboxylation of the given carboxylic acids with sodalime will be in the order:
R1 (CH₃COOH) > R2 (CH₃CH₂COOH) > R3 ((CH₃)₂C(COOH)H).
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
H2C=CH−CH3∣C∣CH3−COOHNaOH−−−−→CaO/ΔXwill be
AH3C−CH=CH3∣C−CH3BH2C=CH−CH3∣C∣H−CH3CH3C−CH=CH3∣C−CH2OHDH3C=CH−CH3∣C∣CH3−COONaCH3−CH3∣C∣OH−CH3∣C∣NH2−CH3HNO2−−−→Δ?
A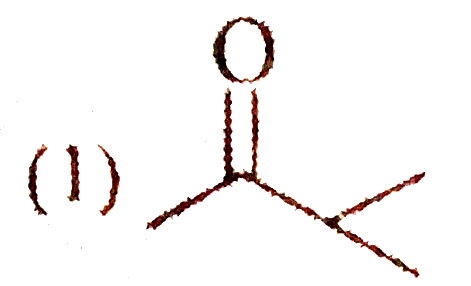 B
B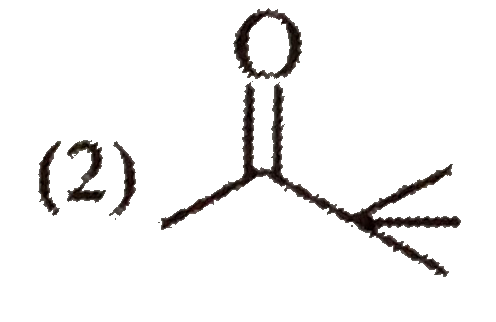 C
C D
D
CH3CH2CH2CH3AlCl3/HCl−−−−−−→Δ
ACH3CH=CHCH3BCH3CH2CH3CCH3CH2CH=CH2D(CH3)3CH
CH3−CH3∣C∣CH3−O−CH2−CH3Cold and conc.−−−−−−−−→HI?
View SolutionXNaOH+CaO−−−−−−−→CH3−CH3∣C∣CH3−CH3
XKolbe's electrolysis−−−−−−−−−−→y 'y' is
View SolutionCH3−C∣COOHHCOOH∣CH−CH3KOH−−−−−−−→E≤ctrolysis Product:
View SolutionWhat will be the major product (A)
CH3−CH3∣CH−CH=CH2HBr−−→(A)
View SolutionCH3CH2CHONaOH,Δ−−−−−−−→(aldol)A,A is.
View Solution
