A brown coloured mixture of two gases is obtained by the reduction of 6N nitric acid with metallic copper. Condeness to a blue liquid which on freezing at −30∘C gives a blue solid. The correct choice for blue liquid or solid is .
It is referred to as the anhydride of nitrous acid
It is an acidic oxide and hence dissolves in alaklies producing nitries.
It can also be prepared by the action of 50%HNO3 on arsenious oxide and then cooling to 250 K.
All of these
The correct Answer is:D
To solve the question step by step, we need to analyze the information given and the reactions involved:
Step 1: Identify the Reaction
The question states that a brown-colored mixture of gases is obtained by the reduction of 6N nitric acid (HNO3) with metallic copper (Cu). The relevant reaction can be summarized as follows:
Cu+4HNO3→Cu(NO3)2+2NO+2H2O
In this reaction, copper reacts with nitric acid to produce copper nitrate, nitrogen monoxide (NO), and water. The nitrogen monoxide can further react with oxygen to form nitrogen dioxide (NO2), contributing to the brown color of the gas mixture.
Step 2: Analyze the Gases Produced
The brown-colored mixture consists of nitrogen monoxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2). Both of these gases can condense into a blue liquid when cooled.
Step 3: Condensation to Blue Liquid
Upon cooling, the brown gas mixture condenses into a blue liquid. This blue liquid is likely to be dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4), which exists in equilibrium with nitrogen dioxide (NO2). The equilibrium can be represented as:
2NO2⇌N2O4
Step 4: Freezing Point of the Blue Liquid
The question states that this blue liquid freezes at -30°C to give a blue solid. The blue solid formed upon freezing is likely to be dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4), which has a freezing point around -11.2°C. However, the question indicates a blue solid at -30°C, which suggests that the solid might be a different nitrogen oxide, possibly nitrous oxide (N2O3), which can appear blue in color.
Step 5: Conclusion
Based on the analysis, the blue liquid is likely to be dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4), and the blue solid formed upon freezing is likely to be dinitrogen trioxide (N2O3).
Final Answer:
- The blue liquid is dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4).
- The blue solid is dinitrogen trioxide (N2O3).
The question states that a brown-colored mixture of gases is obtained by the reduction of 6N nitric acid (HNO3) with metallic copper (Cu). The relevant reaction can be summarized as follows:
The brown-colored mixture consists of nitrogen monoxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2). Both of these gases can condense into a blue liquid when cooled.
Upon cooling, the brown gas mixture condenses into a blue liquid. This blue liquid is likely to be dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4), which exists in equilibrium with nitrogen dioxide (NO2). The equilibrium can be represented as:
The question states that this blue liquid freezes at -30°C to give a blue solid. The blue solid formed upon freezing is likely to be dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4), which has a freezing point around -11.2°C. However, the question indicates a blue solid at -30°C, which suggests that the solid might be a different nitrogen oxide, possibly nitrous oxide (N2O3), which can appear blue in color.
Based on the analysis, the blue liquid is likely to be dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4), and the blue solid formed upon freezing is likely to be dinitrogen trioxide (N2O3).
- The blue liquid is dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4).
- The blue solid is dinitrogen trioxide (N2O3).
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
The table below gives the results of three titrations carried out with 0.200 M HCl to determine the molarity of a given NaOH solution using phenolphthalein as indicator. NaOH was taken in the burette and HCl was taken in a conical flask for the titrations
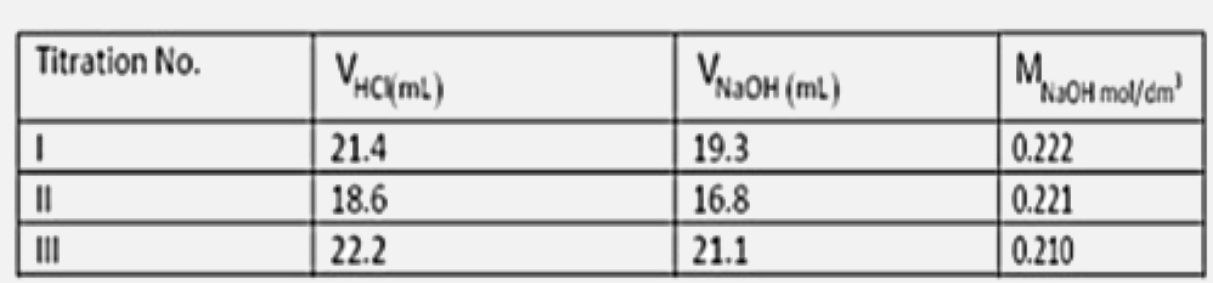
The actual molarity of the prepared NaOH solution was 0.220 mol dm−3. Which among the following could be the reason for the wrong value obtained in titration III?
View SolutionThe radial wave equation for hydrogen of radial nodes from nucleus are:
Ψ1s=116√4(1a0)3/2[(x−1)(x2−8x+12)]e−x/2
where, x=2r/a0,a0 = radius of first Bohr orbit
The minimum and maximum position of radial nodes from nucleus are:
View SolutionBlue liquid which is formed at −30∘C by mixing of two gases is.
View SolutionAlkali metals readily dissolve in liquid ammonia to give blue coloured solutions. The blue colour is believed to be due to
View SolutionThe metal that dissolves in liquid ammonia, giving a dark blue coloured solution is
View SolutionWhich blue liquid is obtained on reacting equimolar amounts of two gases at -30^@C ?
View SolutionA brown coloured mixture of two gases is obtained by the reduction of 6N nitric acid with metallic copper. The mixture on cooling condenses to a blue liquid which on freezing (-30^@ C) gives a blue solid.The correct choice for blue liquid or solid is :
View SolutionWhich blue liquid is obtained on reacting equimolar amounts of two gases at −30∘C?
View SolutionPure oxygen is colourless gas but liquid and solid O_(2) is pale blue or blue coloured, this is because
View SolutionBlue solid which is obtained on racting equimolar amounts of two gases at 245K is
View SolutionWhich blue liquid is obtained on reacting equi molar amounts of two gases at -30^@C ?
View SolutionThe alkali metals dissolve in liquid ammonia to give solutions which are blue in colour if dilute. The blue colour is believed to be due to______.
View SolutionGive reasons. (i )Solutions of alkali metals in liquid ammonia are blue in colour.
View SolutionAlkali metals dissolve in liquid ammonia to give blue coloured solutions. Why?
View SolutionBlue liquid which is formed at - 30^@ C by mixing of two gases is.
View Solution

