How many of the following groups are ortho,para directing and ring activating?
−NO2,−CN,−CH3,−OH,−NH2,
−OR,−X,−CHO,−NHR
The correct Answer is:5
To determine how many of the given groups are ortho, para directing and ring activating, we will analyze each group one by one based on their electronic effects on the aromatic ring.
1. Identify the Groups: We have the following groups to analyze:
- -NO₂ (Nitro group)
- -CN (Cyanide group)
- -CH₃ (Methyl group)
- -OH (Hydroxyl group)
- -NH₂ (Amino group)
- -OR (Alkoxy group)
- -X (Halogen)
- -CHO (Aldehyde group)
- -NHR (Amino group with R)
2. Analyze Each Group:
- -NO₂: This is a strong electron-withdrawing group due to its -I (inductive) and -M (mesomeric) effects. It decreases electron density on the ring, making it meta-directing and ring deactivating.
- -CN: Similar to -NO₂, the cyanide group is also electron-withdrawing and meta-directing. It pulls electron density away from the ring.
- -CH₃: The methyl group is an electron-donating group via hyperconjugation (+H effect). It increases electron density at the ortho and para positions, making it ortho-para directing and ring activating.
- -OH: The hydroxyl group donates electron density to the ring through resonance (+R effect), increasing electron density at ortho and para positions. Thus, it is ortho-para directing and ring activating.
- -NH₂: The amino group also donates electron density through resonance (+R effect), making it ortho-para directing and ring activating.
- -OR: Alkoxy groups are similar to -OH in that they donate electron density to the ring. Therefore, they are ortho-para directing and ring activating.
- -X (Halogens): Halogens have a -I effect (electron-withdrawing) but also a +R effect (electron-donating). However, the -I effect is stronger, making them ortho-para directing but ring deactivating.
- -CHO: The aldehyde group is an electron-withdrawing group (-I effect), making it meta-directing and ring deactivating.
- -NHR: Similar to -NH₂, the NHR group donates electron density through resonance (+R effect), making it ortho-para directing and ring activating.
3. Count the Groups:
- The groups that are ortho-para directing and ring activating are:
- -CH₃
- -OH
- -NH₂
- -OR
- -NHR
- Total: 5 groups.
Final Answer:
Out of the given groups, 5 groups are ortho, para directing and ring activating.
- -NO₂ (Nitro group)
- -CN (Cyanide group)
- -CH₃ (Methyl group)
- -OH (Hydroxyl group)
- -NH₂ (Amino group)
- -OR (Alkoxy group)
- -X (Halogen)
- -CHO (Aldehyde group)
- -NHR (Amino group with R)
- -NO₂: This is a strong electron-withdrawing group due to its -I (inductive) and -M (mesomeric) effects. It decreases electron density on the ring, making it meta-directing and ring deactivating.
- -CN: Similar to -NO₂, the cyanide group is also electron-withdrawing and meta-directing. It pulls electron density away from the ring.
- -CH₃: The methyl group is an electron-donating group via hyperconjugation (+H effect). It increases electron density at the ortho and para positions, making it ortho-para directing and ring activating.
- -OH: The hydroxyl group donates electron density to the ring through resonance (+R effect), increasing electron density at ortho and para positions. Thus, it is ortho-para directing and ring activating.
- -NH₂: The amino group also donates electron density through resonance (+R effect), making it ortho-para directing and ring activating.
- -OR: Alkoxy groups are similar to -OH in that they donate electron density to the ring. Therefore, they are ortho-para directing and ring activating.
- -X (Halogens): Halogens have a -I effect (electron-withdrawing) but also a +R effect (electron-donating). However, the -I effect is stronger, making them ortho-para directing but ring deactivating.
- -CHO: The aldehyde group is an electron-withdrawing group (-I effect), making it meta-directing and ring deactivating.
- -NHR: Similar to -NH₂, the NHR group donates electron density through resonance (+R effect), making it ortho-para directing and ring activating.
- The groups that are ortho-para directing and ring activating are:
- -CH₃
- -OH
- -NH₂
- -OR
- -NHR
- Total: 5 groups.
Out of the given groups, 5 groups are ortho, para directing and ring activating.
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Classify the following groups as ortho, para or meta directing when present on benzene nucleus.
(i) −CH3,(ii)−NH2, (iii) −NO2, (iv)−COOH, (v) −OH, (vi) −SO3H,
(vii) −X(halogen),
(viii) OCH3, (ix) −CHO, (x) −CN
(B) Classify the following goups as activating or deactivating with respect to further electrophilic substitution of the aromatic ring.
(i) −NH2 (ii) −NO2 (iii) −SO3H, (iv) −CH3 (v) −CI, (vi)−CN.
( C) For each of the following substituents indicate whether in donate electron or withdraw electron.
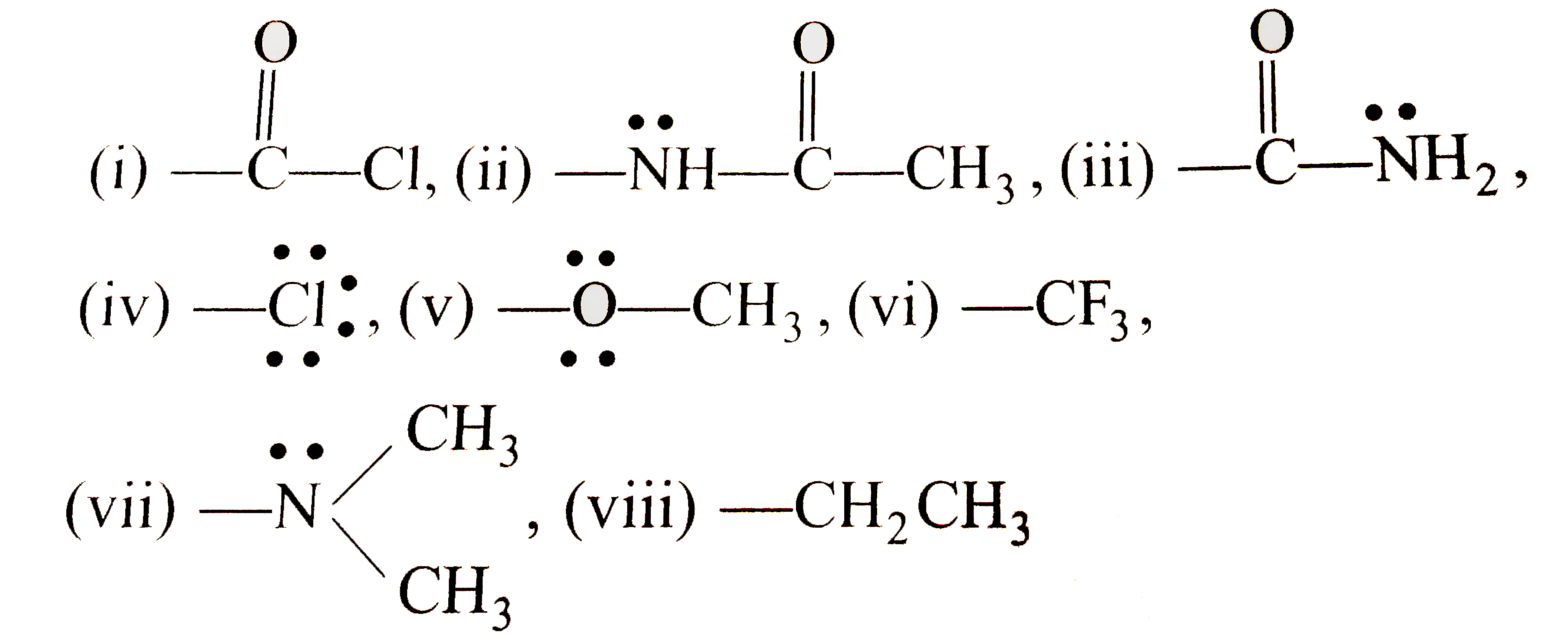
View SolutionWhy is −CH3 group ortho and para directing in toluene ?
View SolutionSelect the principal functional group when the following groups are present in the molecule :
(a) −OH,−COOH,−NO2
(b) −OCH3,OH,−Cl
(c) −CHO,−CN,−OH
(d) −Cl,−CONH2,−CHO
View SolutionWhich of the following are meta directors ?
−NO2,−SO3H,−Cl,−OH,−NH2,−CHO
View SolutionSelect the principal functional group when the following groups are present in the molecule:
(a) −OH,−COOH,−NO2
(b) −NO2,−NH2,−CONH2
(C ) −Br,−CH3,−CHO
(d) Cl,−CH3,−OH.
View SolutionRank the following group in order of decreasing priority for R,S configuration.
(a)−DF,−NH2,−CH3,−OH
(b) −CH3,−CH2CH3,−CH2CH2CH3,−(CH2)3CH3
( c) −NH2,−CH2NH2,−CH3,−CH2NHCH3 (d)−COOH,−CH2OH,−H,−CHO
( e) −Cl,−CH3,−SH,−OH
(f) −C≡CH,−CH(CH3)2,−CH2CH3,−CH=CH2
View SolutionHow many of the following ligands are chelating ligands?
DMG,H2O,C2O2−4,CH3NH2,en,CN−,NH2CH2COO−,NH3
View SolutionHow many of the following compounds cleave diborane symmetrically?
CH3NH2,(CH3)2NH,(CH3)3N,CO(CH3)2O,NH3
View Solutionनिम्नलिखित में से कितने समूह ऑर्थो, पैरा निर्देशक और वलय सक्रियक है ?
−NO2,−CN,−CH3,−OH,−NH2,−OR,−X,−CHO,−NH−R
View SolutionReaction of aniline with acetic anhydride in presence of pyridine yields acetic acid and product 'X'.
What is the total number of groups from the following, present in the compound 'X' ?
−NO2−NH−CO−−NH2−COOH−CH3−N=N−−CH2CH3−C6H5−OH
View Solution

