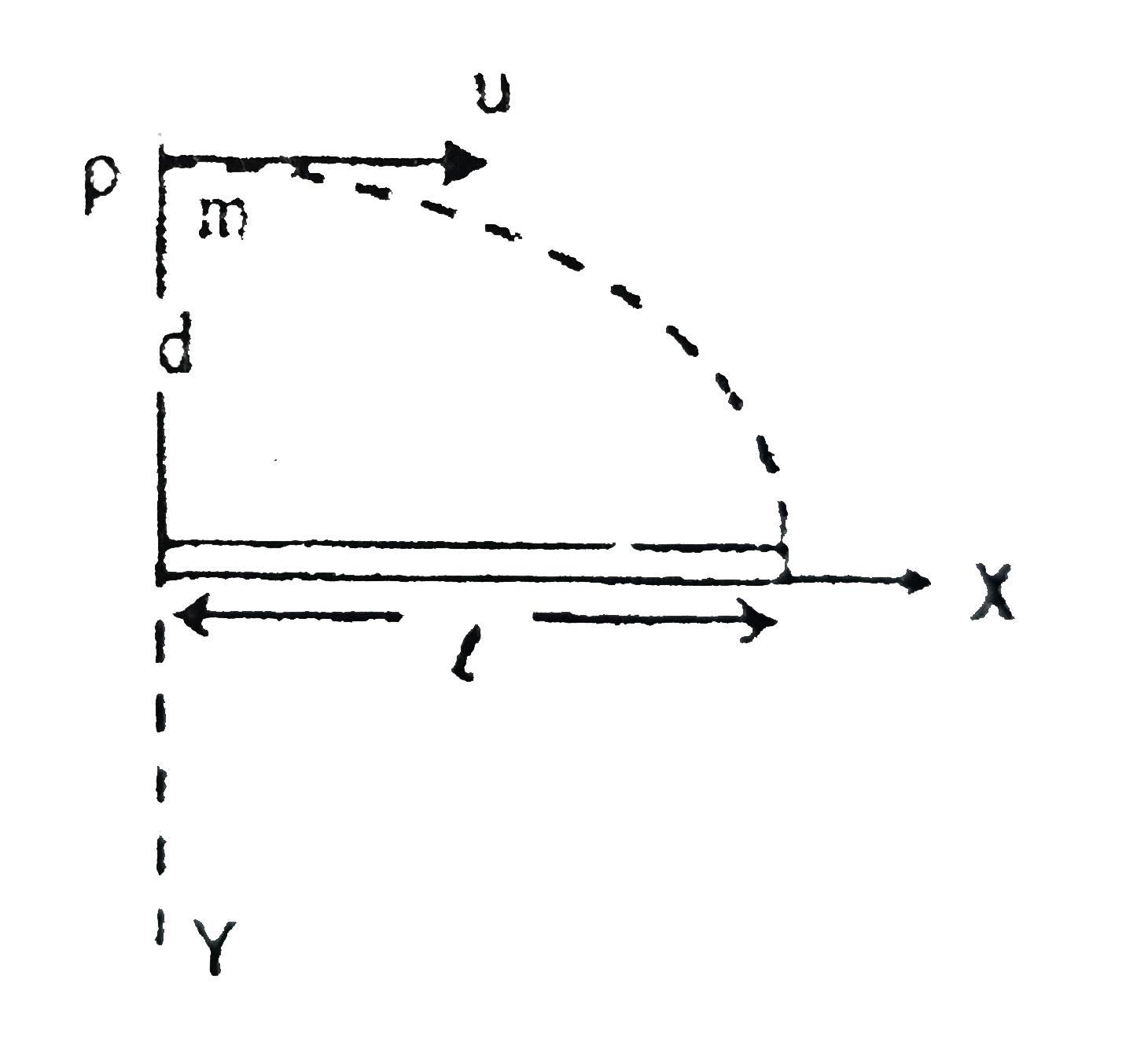
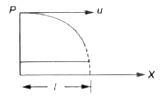
An electron is projected from a distance d and with initial velocity u parallel to a uniformly charged flat conducting plate as shown. It strikes the plate after travelling a distance l long the direction of projection. The surface charge density of the conducting plate is equal to

2dε0mu2el2
2dε0muel
dε0mu2el
dε0muel
For the motion of the electon along Y axis
d=12eEmt2 ...(1)
Where E is the electric field due to the charged plate given by
E=σε0 ...(2)
σ is the surface density of charge of the plate.
The time taken by the electron is
t=lu ...(3)
From (1), (2) and (3) we obtain,
d=12eσε0m(lu)2⇒σ=2dε0mu2el2
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ELECTROSTANTICSBOOK - FIITJEECHAPTER - ELECTROSTANTICSEXERCISE - EXERCISE
10 Videos
- ELECTROSTANTICSBOOK - FIITJEECHAPTER - ELECTROSTANTICSEXERCISE - ASSIGNMENT PROBLEMS (SUBJECTIVE) LEVEL - I
14 Videos
- ELECTROSTANTICSBOOK - FIITJEECHAPTER - ELECTROSTANTICSEXERCISE - SOLVED PROBLEMS (SUBJECTIVE)
10 Videos
- ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE & WAVE OPTICSBOOK - FIITJEECHAPTER - ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE & WAVE OPTICSEXERCISE - ASSIGNMENT PROBLEMS Objective : Level-II (MULTI CHOICE SINGLE CORRECT)
21 Videos
- ELECTROSTATICSBOOK - FIITJEECHAPTER - ELECTROSTATICSEXERCISE - Example
14 Videos
Similar Questions
What is the electric field intensity at any point on the axis of a charged rod of length 'L' and linear charge density λ? The point is separated from the nearer end by a.
View SolutionAn infinite number of charges each equal to q, are placed along the X-axis at x=1,x=2,x=4,x=8,…….. and so on.
(i) find the electric field at a point x=0 due to this set up of charges.
(ii) What will be the electric field if the above setup, the consecutive charges have opposite signs.
View SolutionFind the electric field on the axis of a charged disc.
View SolutionEnergy of electromagnetic waves is due to their
View SolutionAn infinite dielectric sheet having charge density σ has a hole of radius R in it. An electron is released on the axis of the hole at a distance √3R from the center. Find the speed with which it crosses the center of the hole.

View SolutionAn electron is projected as shown in fig. with kinetic energy K, at an angle theta=45^(@) between two charged plates. Ignore the gravity. At what distance from the starting point will the electron strike the lower plate?
View SolutionAn electric field E is produced between two parallel plates having a separation d as shown.
(a) With what minimum speed should an electron be projected from the lower plate in the direction of field so that it may reach the upper plate ?
(b) Suppose the electron is projected from the lower plate with the speed calculated in part (a). The direction of projection makes an angle of 60∘with the field. Find the maximum height reached by the electron.
(c ) After how much time , the electron again strikes the lower plate ?
(d) Horizontal distance travelled by the electron in time calculated in part (c).
Charge on electron : e ,mass of electron : m, consider only electric force.
View SolutionThe plates of small size of a parallel plate capacitor are charged as shown. The force on the charged particle of 'q' at a distance 'l' from the capacitor is : (Assume that the distance between the plates is d<<l)

View SolutionAn electron is projected as shown with speed u . If electron just fails to strike the upper plate, find range. (distance from starting point at which electron strike the lower plate again). Consider only electric force.
View SolutionAn electron (charge = e, mass = m) is projected horizontally into a uniform electric field produced between two oppositely charged parallel plates, as shown in figure. The charge density on both plates is +- sigma C//m^2 and separation between them is d. You have to assume that only electric force acts on the electron and there is no field outside the plates. Initial velocity of the electron is u, parallel to the plates along the line bisecting the gap between the plates. Length of plates is 2L and there is a screen perpendicular to them at a distance L. (i) Find s if the electron hits the screen at a point that is at same height as the upper plate. (ii) Final the angle q that the velocity of the electron makes with the screen while it strikes it.
View SolutionAn electron is projected from a distance d and with initial velocity u parallel to a uniformly charged flat conducting palte as shown. It strikes the plate after travelling a distance l along the direction of projection. The surface charge density of the conducting plate is equal to
View SolutionInto the region of space between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor there Ilies (a) an electron and (b) a negatively charged ion with a velocity directed parallel to the plates. Both the electron and the ion have rec.eived their initial kinetic energy by passing the same potential difference U_0 and the potental difference across the capacitor is U. The distance between the plates is d. Which of the two particles will travel a greater distance before hitting the positively charged plate if both fly into the capacitor at a point that is exactly in the middle of the distance between the plates?
View SolutionThree charged conducting plates are separated by small distances as shown in figure. The charges on the plates are shown. Find the ratio of charge on right surface and left surface of the middle plate.
View SolutionAn electron is projected from a distance d and with initial velocity u parallel to a uniformly charged flat conducting plate as shown. It strikes the plate after travelling a distance l along the direction of projection. The surface charge density of the conducting plate is equal to
View Solutionएक समान्तर प्लेट संधारित्र की प्रत्येक प्लेट का क्षेत्रफल A एवं प्लेटों के बीच की दूरीd हैं, इसे नियत धारा । से आवेशित किया गया है यदि A/2 क्षेत्रफल की एक समतल सतह प्लेटों के मध्य इनके समान्तर स्थित हो तो इस सतह से प्रवाहित विस्थापन धारा होगी
View Solutionएक इलेक्ट्रॉन d दूरी से u वेग से एकसमान आवेश के समान्तर प्रक्षेपित किया जाता है, जैसाकि चित्र में दखाया गया है। यह x-सीधा में l दूरी चलकर प्लेट से टकराता है। चालकीय प्लेट का आवेश पृष्ठ घनत्व बराबर है
View Solution

