A : A person on a frictionless surface can get away from it by blowing air out of his mouth
R : For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
If both Assertion & Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
If both Assertion & Reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
If Assertion is true statement but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false statements
To solve the problem, let's break down the assertion and reason provided in the question:
Assertion (A): A person on a frictionless surface can get away from it by blowing air out of his mouth.
Reason (R): For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
1. Understanding the Situation:
- We have a person on a frictionless surface. This means there is no frictional force acting against the person’s movement.
Hint: Consider what happens when there is no friction. How does that affect movement?
2. Action of Blowing Air:
- When the person blows air out of their mouth, they exert a force on the air particles in the direction they are blowing.
Hint: Think about how pushing something away can affect your own position.
3. Applying Newton's Third Law:
- According to Newton's Third Law of Motion, for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Therefore, when the person blows air forward, the air exerts an equal and opposite force backward on the person.
Hint: Remember that forces always come in pairs. What happens to the person when they push the air?
4. Resulting Motion:
- The backward force exerted by the air on the person will cause the person to accelerate in the opposite direction (backward) due to the absence of friction.
Hint: Consider how acceleration is related to force and mass (Newton's second law).
5. Conclusion:
- Since the person experiences a force in the backward direction due to the air being blown out, they will indeed move away from their original position on the frictionless surface. Thus, the assertion is correct.
- The reason provided (Newton's Third Law) correctly explains why the assertion is true.
Final Answer:
Both the assertion (A) and the reason (R) are correct, and the reason explains the assertion correctly.
Summary:
- Assertion (A) is true because the person can move on a frictionless surface by blowing air.
- Reason (R) is true as it describes Newton's Third Law, which explains the action-reaction pair involved in this scenario.
- We have a person on a frictionless surface. This means there is no frictional force acting against the person’s movement.
Hint: Consider what happens when there is no friction. How does that affect movement?
- When the person blows air out of their mouth, they exert a force on the air particles in the direction they are blowing.
Hint: Think about how pushing something away can affect your own position.
- According to Newton's Third Law of Motion, for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Therefore, when the person blows air forward, the air exerts an equal and opposite force backward on the person.
Hint: Remember that forces always come in pairs. What happens to the person when they push the air?
- The backward force exerted by the air on the person will cause the person to accelerate in the opposite direction (backward) due to the absence of friction.
Hint: Consider how acceleration is related to force and mass (Newton's second law).
- Since the person experiences a force in the backward direction due to the air being blown out, they will indeed move away from their original position on the frictionless surface. Thus, the assertion is correct.
- The reason provided (Newton's Third Law) correctly explains why the assertion is true.
Both the assertion (A) and the reason (R) are correct, and the reason explains the assertion correctly.
- Assertion (A) is true because the person can move on a frictionless surface by blowing air.
- Reason (R) is true as it describes Newton's Third Law, which explains the action-reaction pair involved in this scenario.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- LAWS OF MOTIONBOOK - AAKASH INSTITUTECHAPTER - LAWS OF MOTIONEXERCISE - Assignment (SECTION-C)
63 Videos
- KINETIC THEORYBOOK - AAKASH INSTITUTECHAPTER - KINETIC THEORYEXERCISE - EXERCISE (ASSIGNMENT) SECTION - D Assertion - Reason Type Questions
10 Videos
- MAGNETISM AND MATTER BOOK - AAKASH INSTITUTECHAPTER - MAGNETISM AND MATTER EXERCISE - ASSIGNMENT (SECTION D)
26 Videos
Similar Questions
Newton established that a force never occurs singly in nature Forces always occur in pairs as a result of mutual interaction between to bodies According to Newton s third law to every action there is always an equal and opposite reaction The force of action and reaction may appear due to actual physical contact of the two bodies or even from a distance The law is applicable whether the bodies are at rest or they are in motion. Read the above passage and answer the following questions
(i) It is difficult to walk on sand or ice Why?
(ii) What does the law imply in day to day life ?
View SolutionA : According to Newton's third law of motion for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
R : There is no time lag between action and reaction.
View Solution
Knowledge Check
Assertion:A table cloth can be pulled from a table without dislodging the dishes.
Reason: To every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.AIf both assertion and reason are ture and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.BIf both assertion and reason are ture but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.CIf assertion is ture but reason is false.DIf both assertion and reason are false.To every action there is an equal and opposite reaction which law of motion is this?
AFirstBSecondCThirdDNone of these.Consider the following statements :
Assertion (A) : A table cloth can be pulled from a table without dislodging the dishes .
Reason (R ) : To every action there is an equal and opposite reaction of these statements .Aboth A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of ABBoth A and R are true but R is not the correc explanation of ACA is true but R is falseDA is false but R is true
STATEMENT-1: A cloth covers a table. Some dishes are kept on it. The cloth can be pulled out without dislodging the dishes from the table.
STATEMENT-2: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
View SolutionStatement -1 : Aeroplanes always fly at low altitudes.
Statement -2 : Ac cording to Newton's third law of motion, for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
View SolutionIn each of the following questions a statements of Assertion is given followed by the corresponding statements of Reason of the statements, mark the correct answer.
Assertion (A) In order to swim, a person pushes the water backwards.
Reason (R) To every action there is an equal and opposite reaction,
View SolutionA block of mss m is placed on a level frictionless table. The block is attached to a horizontally aligned spring fixed with its other end and is vibrating in a horizontal with the pariod T. Suddenly at the instant of time when the spring comes to the position of euilibrium and becomes unstretched the block disconnects form the spring and continues sliding across the frictionless surface away from the until it encounters loop of radius R. What must be the amplitude of vibrations of the block s on the spring in order for the block to complets one loop without falling down?
_E01_049_Q01.png)
View SolutionTwo persons, A of mass 60kg and B of mass 40kg, are standing on a horizontal platform of mass 50kg. The platform is supported on wheels on a horizontal frictionless surface and is initially at rest. Consider the following situations.
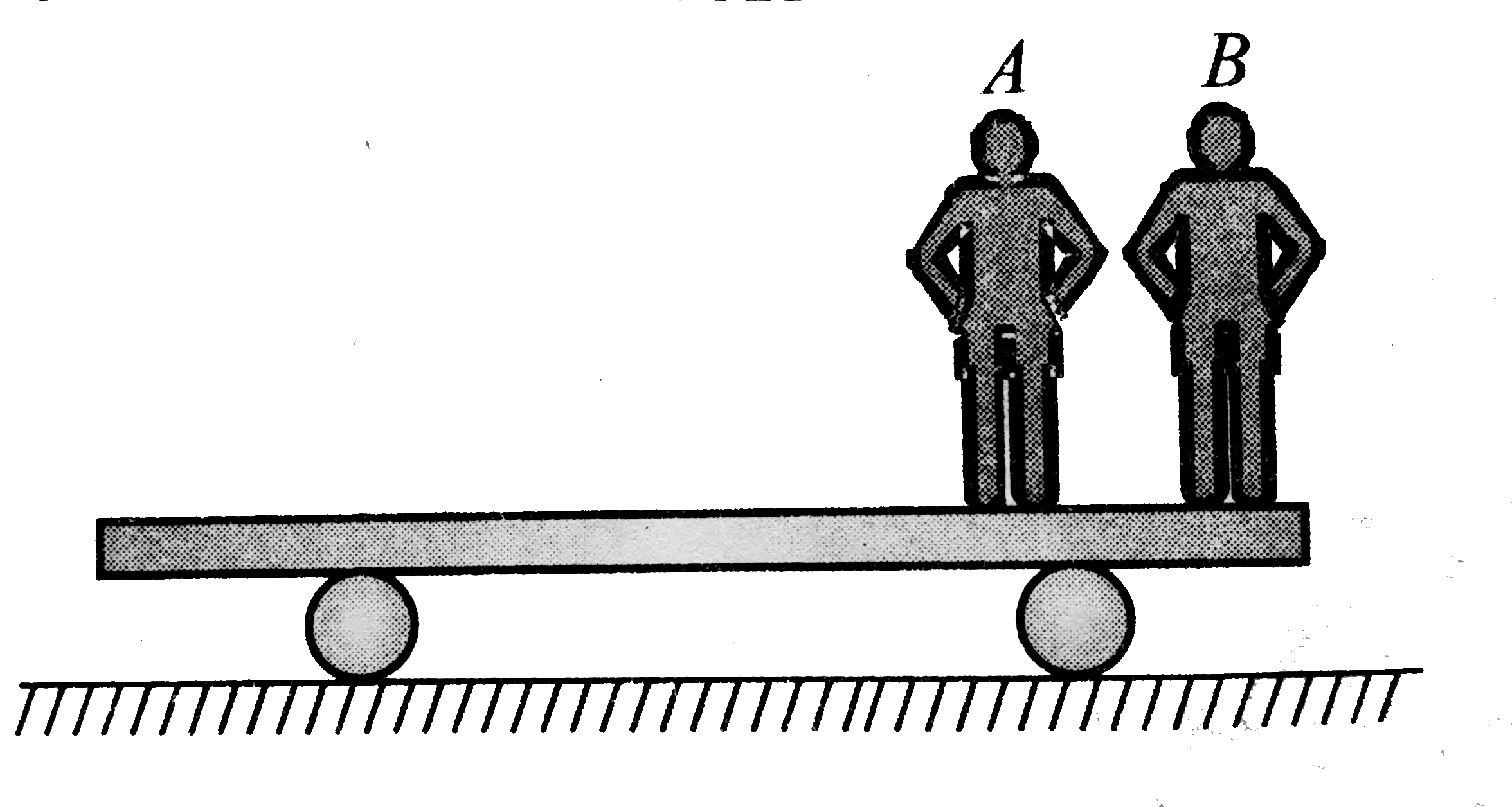
(i) Both A and B jump from the platform simultaneously and in the same horizontal direction.
(ii) A jumps first in a horizontal direction and after a few seconds B also jumps in the same direction. In both the situations above, just after the jump, the person (A or B) moves away from the platform with a speed of 3m/s relative to the platform and along the horizontal.
Final speed of the platform in situation (ii), i.e., just after B has jumped, will be nearly
View Solution

