For a series of indicators the following colours and pH range over which colour change takes place are as follows :
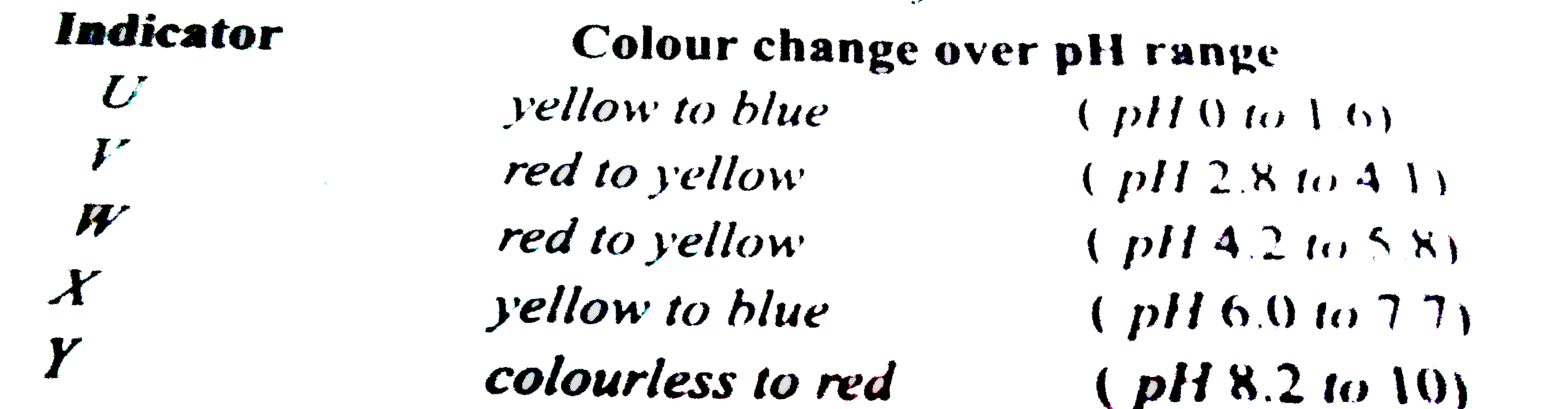
Indicator U could be used to distinguish between 0.1 M and 0.01 M solution of sulphuric acid :
(a) True
(b) False
The correct Answer is:B
Topper's Solved these Questions
- VOLUMETRIC ANALYSISBOOK - OP TANDONCHAPTER - VOLUMETRIC ANALYSISEXERCISE - Passage 3
5 Videos
- VOLUMETRIC ANALYSISBOOK - OP TANDONCHAPTER - VOLUMETRIC ANALYSISEXERCISE - Passage 4
5 Videos
- VOLUMETRIC ANALYSISBOOK - OP TANDONCHAPTER - VOLUMETRIC ANALYSISEXERCISE - Passage 1
5 Videos
- THE COLLOIDAL STATEBOOK - OP TANDONCHAPTER - THE COLLOIDAL STATEEXERCISE - Self Assessment
21 Videos
Similar Questions
Chemists work with standardised solution, a solution whose concentration is known. The requirements to standardise the solution are :
1. the volume of the solution.
2. the number of moles of solute in that volume.
A primary standard solution is used in determining the molarity of a solution. To find the molarity of HCl, 0.317 g of Na2CO3, the primary standard dissolved in water, is used in titrating the solution of HCl. 22.9 mL of acid are required to neutralise the sodium carbonate. This is the needed volume (first requirement). The stoichiometric equation is used to know the second requirement.
2HCl(aq.)+Na2CO3(aq.)→2NaCl+H2O+CO2↑⏐
What is the molarity of HCl in the above case ?
View Solution0.5 g bleaching powder was suspended in water and excess KI is added. On acidifying with dil. H2SO4,I2 was liberated which required 50 mL of N/10 hypo (Na2S2O3.5H2O) in presence of starch. The reactions involved are :
I. CaOCl2+H2SO4→CaSO4→CaSO4+H2O+Cl2
II. 2KI+Cl2→2KCl+I2
III. 2Na2S2O3+I2→Na2S4O6+2NaI
In the reaction (I), which one is reduced ?
View SolutionPyrolusite, MnO2, is the main ore from which manganese is produced. The manganese content of the ore may be determined by reducing the MnO2 under acetic conditions to Mn2+ with the oxalate ion, C2O2−4, the oxalate ion being oxidised to carbon dioxide during the reaction. The analytical determination is carried out by adding a known excess volume of oxalate solution to a suspension of the pyrolusite and digesting the mixture on a hot water bath until all the MnO2 has been reduced. The excess, unreacted oxalate solution is then titrated with standardised potassium permanganate, KMnO4 solution after which the manganese content of the ore can be calculated.
A student prepared a standard solution of sodium oxalate by weighing 3.2 g of the dry anhydrous salt, dissolving it in distilled water and making the solution up to 500 mL. 25 mL of the oxalate solution required 24.76 mL of KMnO4 solution.
What is the equivalent mass of MnO2 in the present titration ?
View SolutionDispersed phase and dispersion medium in butter are respectively :
View SolutionFor a series of indicators, the colour and pH range over which colour change takes place are as follows:
IndicatorColour change over pH rangeUYellow to blue pH 0.0 to 1.6VRed to yellow pH 2.8 to 4.1WRed to yellow pH 4.2 to 5.8XYellow to blue pH 6.0 to 7.7YColourless to red pH 8.2 to 10.0
Which of the followinfg statements is correct ?
View SolutionK_(b) of an acid-base indicator H In is 10^(-9) . The pH at which its 10^(-3) (M) solution shows the colour change
View SolutionAcid base indicators are either weak organic acids or weak organic bases. Indicator change colour in dilute solution when the hydronium ion concentration reaches a particular value. For example, phenopthalein is a colour less substance in any aqueous solution with a pH less than 8.3 in between the pH range 8.3 to 10 , transaction of colour (colourless to pink) takes place and if pH of solution is greater than 10 , then solution colour is dark pin. Considering an acid indicator HIn, base In^(-) can be represented as : HIn hArr H^(+) + In^(-) acidic form basic form pH of solution can be computed as : pH = pK_(In) + "log" ([In^(-)])/([HIn]) In general, transition of colour takes place in between the pH range pK_(In) +-1 An indicator is a weak acid and pH range is 4.0 to 6.0 . If indicator is 50% ionized in a given solution then what is ionization consatant of the acid?
View SolutionAcid base indicators are either weak organic acids or weak organic bases. Indicator change colour in dilute solution when the hydronium ion concentration reaches a particular value. For example, phenopthalein is a colour less substance in any aqueous solution with a pH less than 8.3 in between the pH range 8.3 to 10 , transaction of colour (colourless to pink) takes place and if pH of solution is greater than 10 , then solution colour is dark pin. Considering an acid indicator HIn, base In^(-) can be represented as : HIn hArr H^(+) + In^(-) acidic form basic form pH of solution can be computed as : pH = pK_(In) + "log" ([In^(-)])/([HIn]) In general, transition of colour takes place in between the pH range pK_(In) +-1 The ionization constant of an indicator is 5 xx 10^(-5) at 25^(0)C . Its acid form is deep orange while its basic is yellow colour in aqeous solution. which of the following statement is true for this indicator
View SolutionAcid base indicators are either weak organic acids or weak organic bases. Indicator change colour in dilute solution when the hydronium ion concentration reaches a particular value. For example, phenopthalein is a colour less substance in any aqueous solution with a pH less than 8.3 in between the pH range 8.3 to 10, transaction of colour (colourless to pink) takes place and if pH of solution is greater than 10, then solution colour is dark pin. Considering an acid indicator HIn, base In− can be represented as :
HIn⇔H++In−
acidic form basic form pH of solution can be computed as :
pH=pKIn+log[In−][HIn]
In general, transition of colour takes place in between the pH range pKIn±1
If an indicator is to be used in an acid base titration having an equivalence point in pH range 8 to 10, the indicator must
View SolutionFor a series of indicators the following colours and pH range over which colour change takes place are as follows : Indicator V could be used to find the equivalence point for 0.1 M acetic acid and 0.1 M ammonium hydroxide solution : (a) True (b) False
View SolutionFor a series of indicators the following colours and pH range over which colour change takes place are as follows :
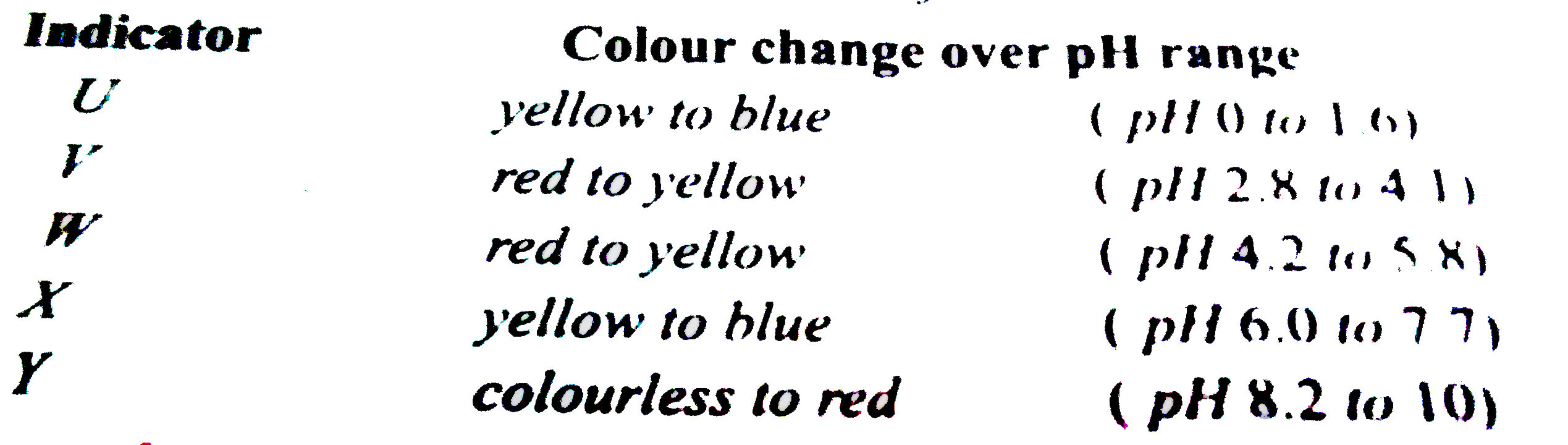
Indicator Y could be used to distinguish between the solutions of ammonium chloride and sodium acetate solution :
(a) True
(b) False
View SolutionFor a series of indicators the following colours and pH range over which colour change takes place are as follows : Indicator X could be used to distinguish between the solution of ammonium chloride and sodium acetate solution : (a) True (b) False
View SolutionFor a series of indicators the following colours and pH range over which colour change takes place are as follows :
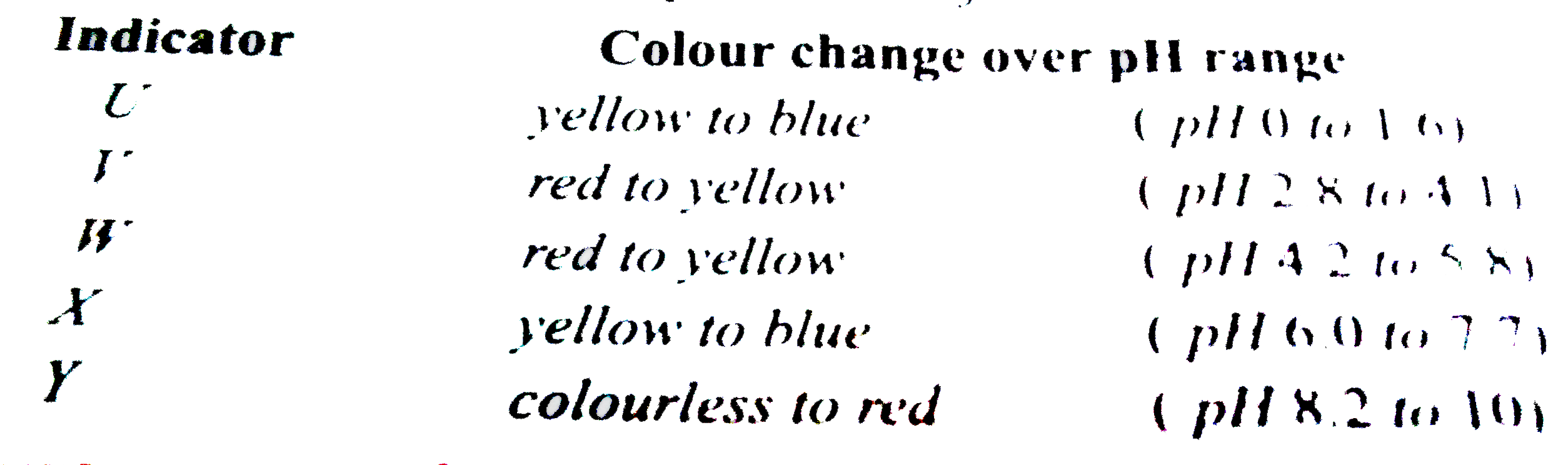
Indicator W would be suitable for use in the determination of the concentration of acetic acid in white vinegar by base titration :
(a) True
(b) False
View SolutionpH at which an acidic indicator with Kin=1×10−5 changes colour when the indicator is 1×10−3 M is
View SolutionThe indicator that shows colour changes in the entire pH range is
View Solution

