A student is performing an experiment with two triangular glass prisms. He places the first glass prism on its base. The second glass prism is placed upside down behind the first glass prism. When a beam of white light is allowed to fall on the first glass prism, then a patch of ordinary white light is obtained on a screen placed behind the second glass prism.
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the above· arrangement of two glass prisms and the light passing through them.
(b) What is the function-of (i) first prism, and (ii) second prism, in this arrangement?
Step-by-Step Solution
1. Draw the First Prism:
- Start by drawing a triangular prism on its base. Label it as Prism 1.
2. Draw the Second Prism:
- Draw another triangular prism upside down behind the first prism. Label it as Prism 2.
3. Incident Ray:
- Draw a straight line representing a beam of white light (incident ray) approaching the first prism at an angle.
4. Refraction at the First Prism:
- As the incident ray enters Prism 1, draw the refracted rays dispersing into a spectrum of colors (red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet). This shows the dispersion of light.
5. Emerging Rays from the First Prism:
- Draw the dispersed rays exiting Prism 1, spreading out into the colors of the spectrum.
6. Entering the Second Prism:
- Draw the dispersed rays entering Prism 2. Since Prism 2 is inverted, the rays will be directed towards the base of the prism.
7. Refraction at the Second Prism:
- As the rays pass through Prism 2, they will converge back together. Draw the converging rays emerging from Prism 2.
8. Screen:
- Finally, draw a screen behind Prism 2 where the converged light forms a patch of ordinary white light.
(b) Functions of the Prisms:
1. Function of the First Prism:
- The first prism (Prism 1) acts as a dispersing prism. Its function is to separate the white light into its constituent colors (spectrum) due to refraction.
2. Function of the Second Prism:
- The second prism (Prism 2) acts as a converging prism. Its function is to recombine the dispersed colors back into a single beam of white light.
- Start by drawing a triangular prism on its base. Label it as Prism 1.
- Draw another triangular prism upside down behind the first prism. Label it as Prism 2.
- Draw a straight line representing a beam of white light (incident ray) approaching the first prism at an angle.
- As the incident ray enters Prism 1, draw the refracted rays dispersing into a spectrum of colors (red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet). This shows the dispersion of light.
- Draw the dispersed rays exiting Prism 1, spreading out into the colors of the spectrum.
- Draw the dispersed rays entering Prism 2. Since Prism 2 is inverted, the rays will be directed towards the base of the prism.
- As the rays pass through Prism 2, they will converge back together. Draw the converging rays emerging from Prism 2.
- Finally, draw a screen behind Prism 2 where the converged light forms a patch of ordinary white light.
- The first prism (Prism 1) acts as a dispersing prism. Its function is to separate the white light into its constituent colors (spectrum) due to refraction.
- The second prism (Prism 2) acts as a converging prism. Its function is to recombine the dispersed colors back into a single beam of white light.
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Two students perform experiments on series and parallel combinations of two given resistors R1andR2 and plot the following V - I graphs [Fig. 5.24.]. Which of the graphs is/are correctly labeled in terms of the words 'series' and 'parallel'? Justify your answer.
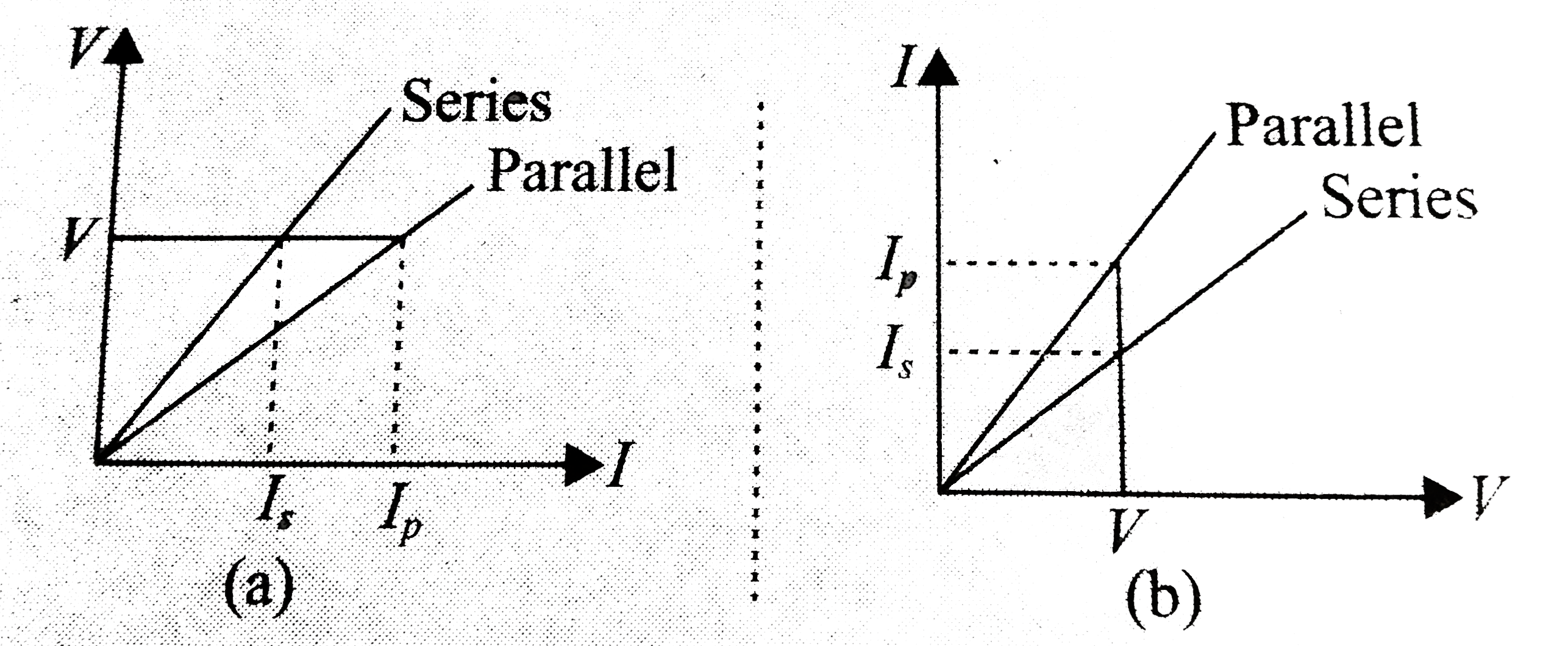
View SolutionDraw the pattern of magnetic field lines of a current carrying solenoid What does the pattern of field lines inside the solenoid indicate? Write one application of magnetic field of current carrying solenoid.
View SolutionA student performs an experiment to study the magnetic effect of current around a current-carrying straight conductor. He reports that:
(i) the direction of deflection of the north pole of a compass needle kept at a given point near the conductor remains unaffected even when the terminals of the battery sending the current in the wire are interchanged.
(ii) For a given battery current, the degree of deflection of a N-pole decreases when the compass is kept at a point farther away from the conductor.
Which of the above observations is correct and why?
View SolutionDispersion Of White Light By A Glass Prism
View SolutionA beam of white light is incident on a hollow prism of glass. Then
View SolutionA beam of white light is shone onto a glass prism. The light cannot be :
View SolutionA beam of white light falls on a glass prism. The colour of light which undergoes the least bending on passing through the glass prism is :
View Solutionएक सामग्री पारदर्शी माध्यम में रखा काँच का प्रिज्म प्रकाश-किरण को विवचित करेगा:
View Solution…..................... light is deviated the maximum in the spectrum of white light obtained with a glass prism.
View Solution…......................... light is deviated the least in the spectrum of white light obtained with a glass prism.
View SolutionHow will you use two identical glass prisms so that a narrow beam of white light incident on one prism emerges out of the second prism as white light? draw and label the ray diagram
View Solution…..................... light is deviated the maximum in the spectrum of white light obtained with a glass prism.
View Solution"…........................." light is deviated the least in the spectrum of white light obtained with a glass prism.
View Solutionजब श्वेत प्रकाश काँच के प्रिज्म में से गुजरता है, तो प्रिज्म के आधार की ओर अधिकतम झुकी प्रकाश किरण का रंग होता है -
View SolutionWhen white light passes through a glass prism
View Solution