For shown situation draw a graph showing acceleration of A and B on y-axis and time on x-axis (g=10ms−2)
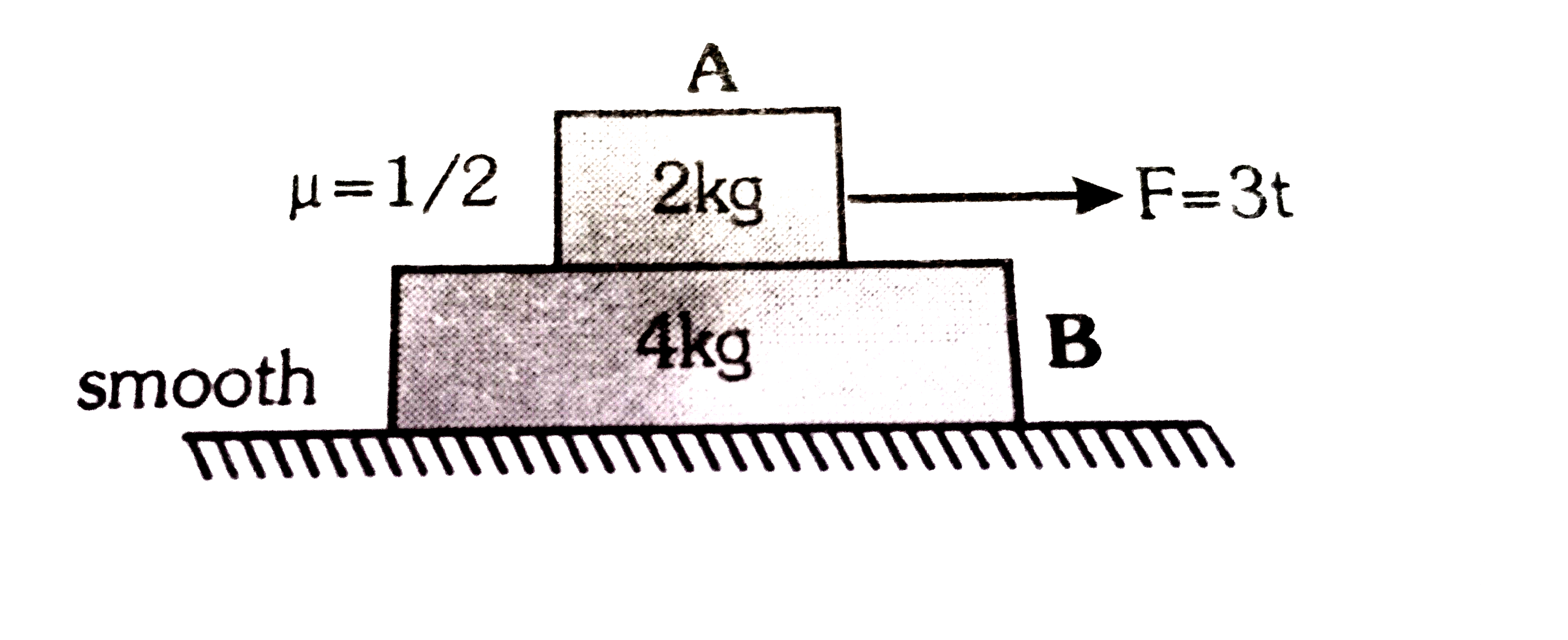
Limiting fricition between A&B,f1=μmAg=(12)(2)(10)=10N
Block B moves due to friction only. So maximum acceleration of
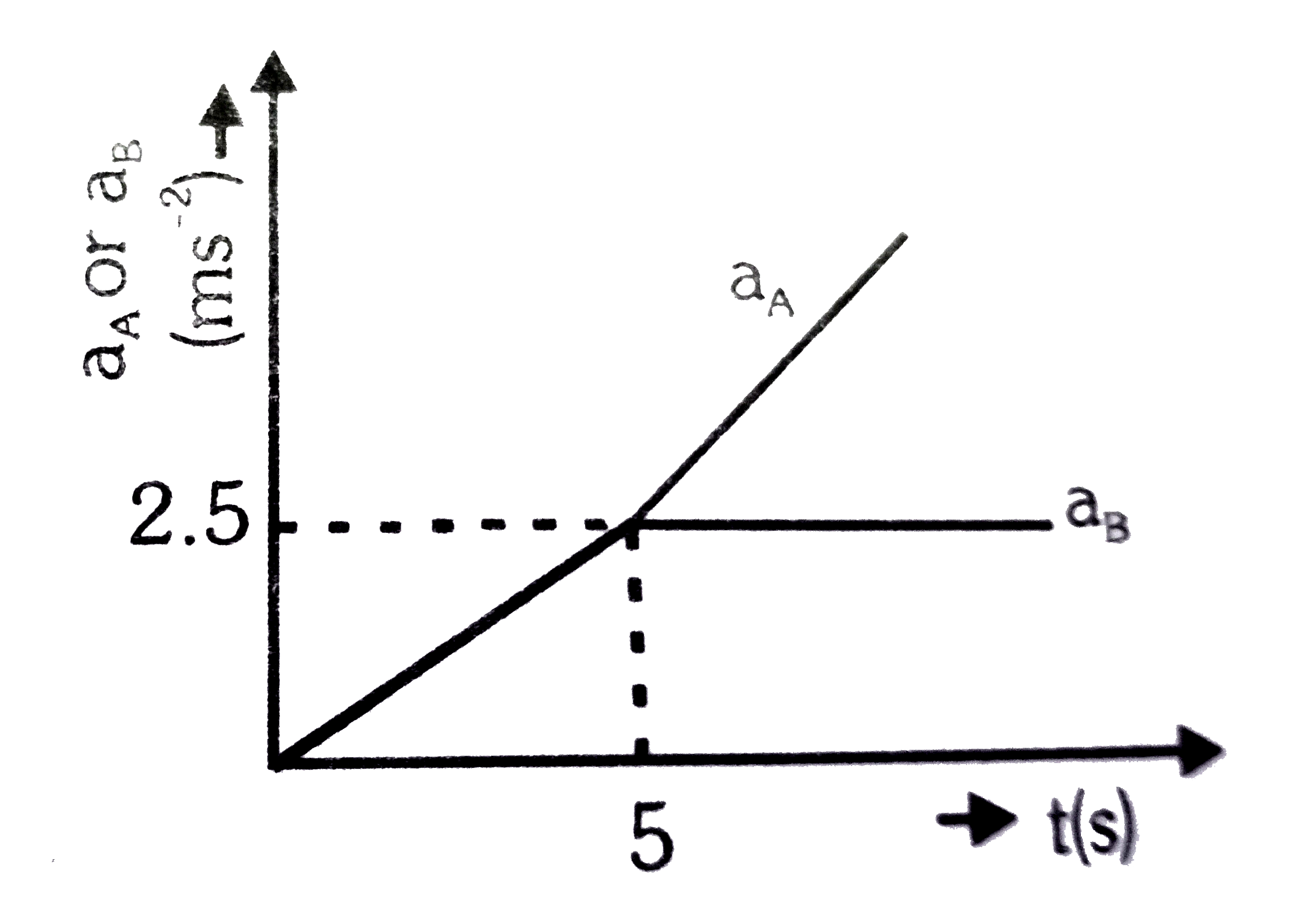
B,amax=f1mB=104−2.5ms−2. So both the blokcs move together till the common acceleration becomes 2.5ms−2, after that acceleration of B will become constant while that of A will go on increasing. Slipping will starts between A&B at 2.5ms−2⇒2.5=FmA+mB=3t6⇒t=5s
Hence for ≤5s,aA=aB=FmA+mB=3t6=12
and for t>5saB=2.5ms−2aA=F−f1mA=3t−102=32t−5
Similar Questions
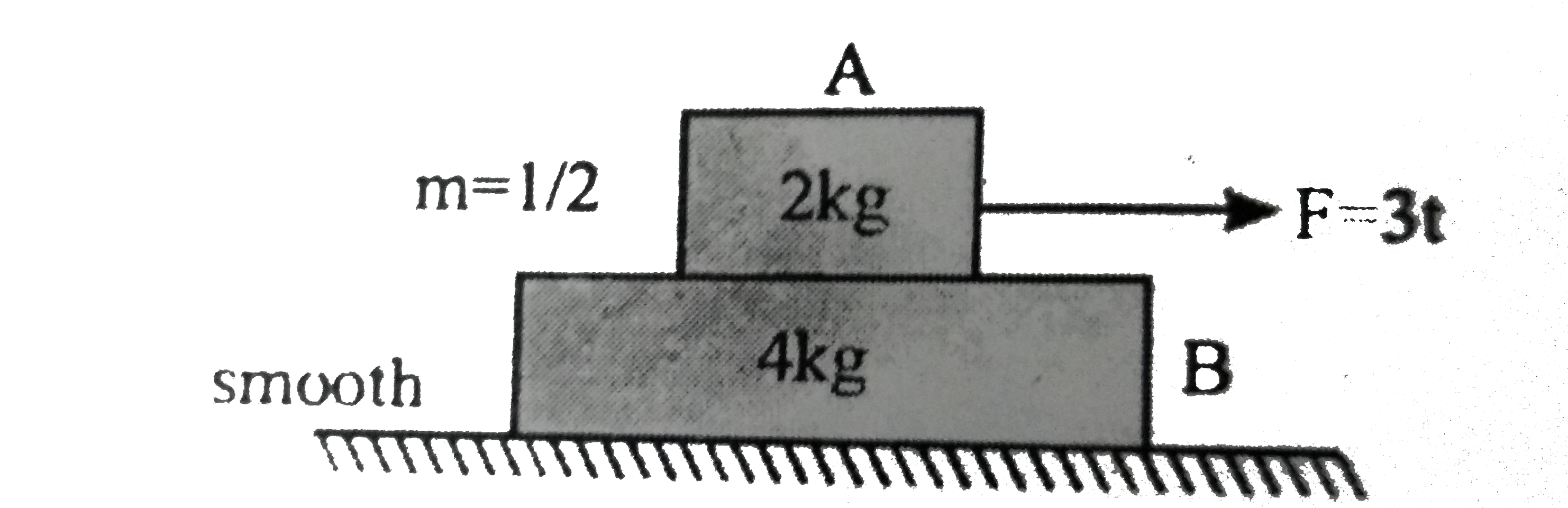
For shown situation draw a graph showing accelerations of A and B on y-axis and time of x-axis. (g=10ms−2)
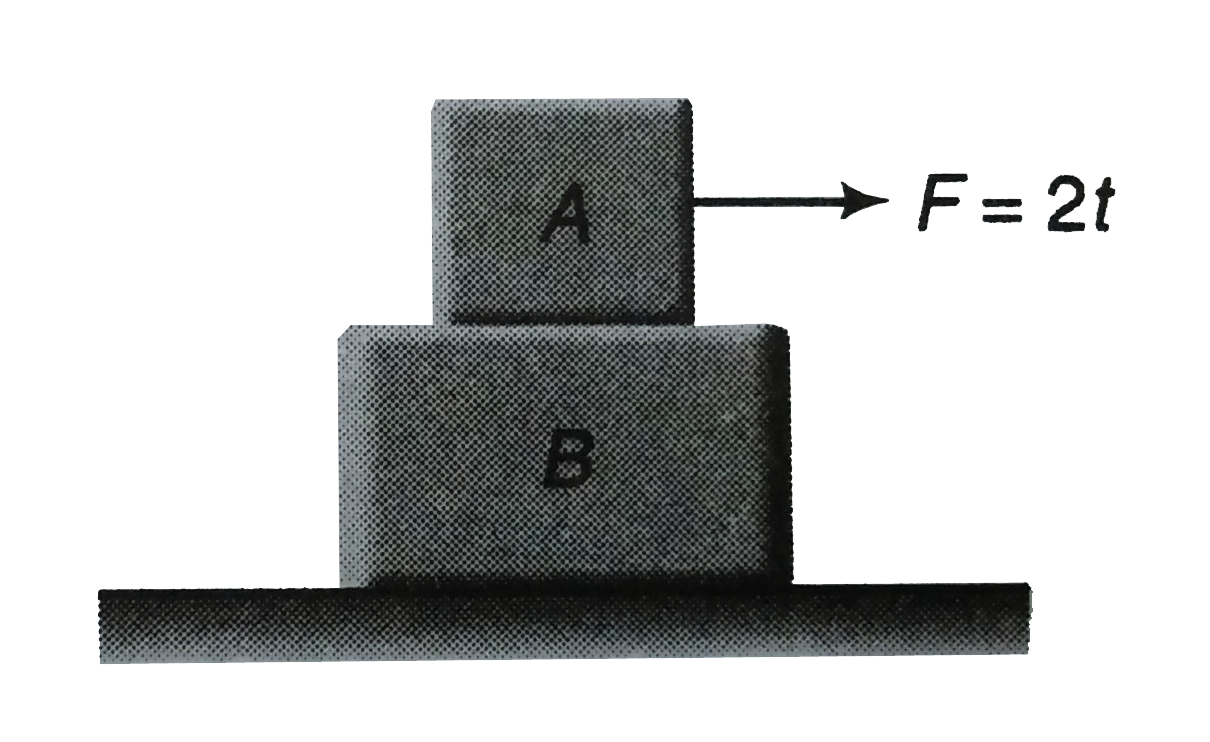
View SolutionTwo blocks A and B of masses 2kg and 4kg are placed one over the other as shown in figure. Atime varying horizontal force F=2t is applied on the upper block as shown in figure. Here t is in second and F is in newton. Drow a graph showing acceleration of A and B on y-axis and time on x-axis.Coefficient of friction between A and B is μ=12 and the horizontal surface over which B is placed smooth. (g=10m/s2)
View Solution
Knowledge Check
If the particle in linear S.H.M. starts from the extreme left position, then its equation of motion is given by
A B
B C
C D
D
The slope of the graph showing the variation of potential difference V on X-axis and current Y-axis gives conductor
AresistanceBresistivityCreciprocal of resistanceDconductivityFor a zero order reaction a graph of conc. (along Y axis) and time (along X-axis) is linear with
Aa +ve slope and a non - zero Y- interceptBa −ve slope with a non - zero Y-interceptCa +ve slope with a zero Y - interptDa −ve slopw with a zero Y-intercept
A particle starts with uniform acceleration. Draw a graph taking the displacement(s) of the particle along y-axis and time(t) along x-axis. What is the curve known as?
View SolutionA body starts from the origin with an acceleration of 6ms−1 along the x - axis and 8ms−1 along the y - axis. Find its distance from the origin after 4s.
View SolutionTwo graphs of the same projectile motion (in the xy-plane) projected from origin are shown. X-axis is along horizontal direction and y-axis is vertically upwards. Take g=10ms−2.
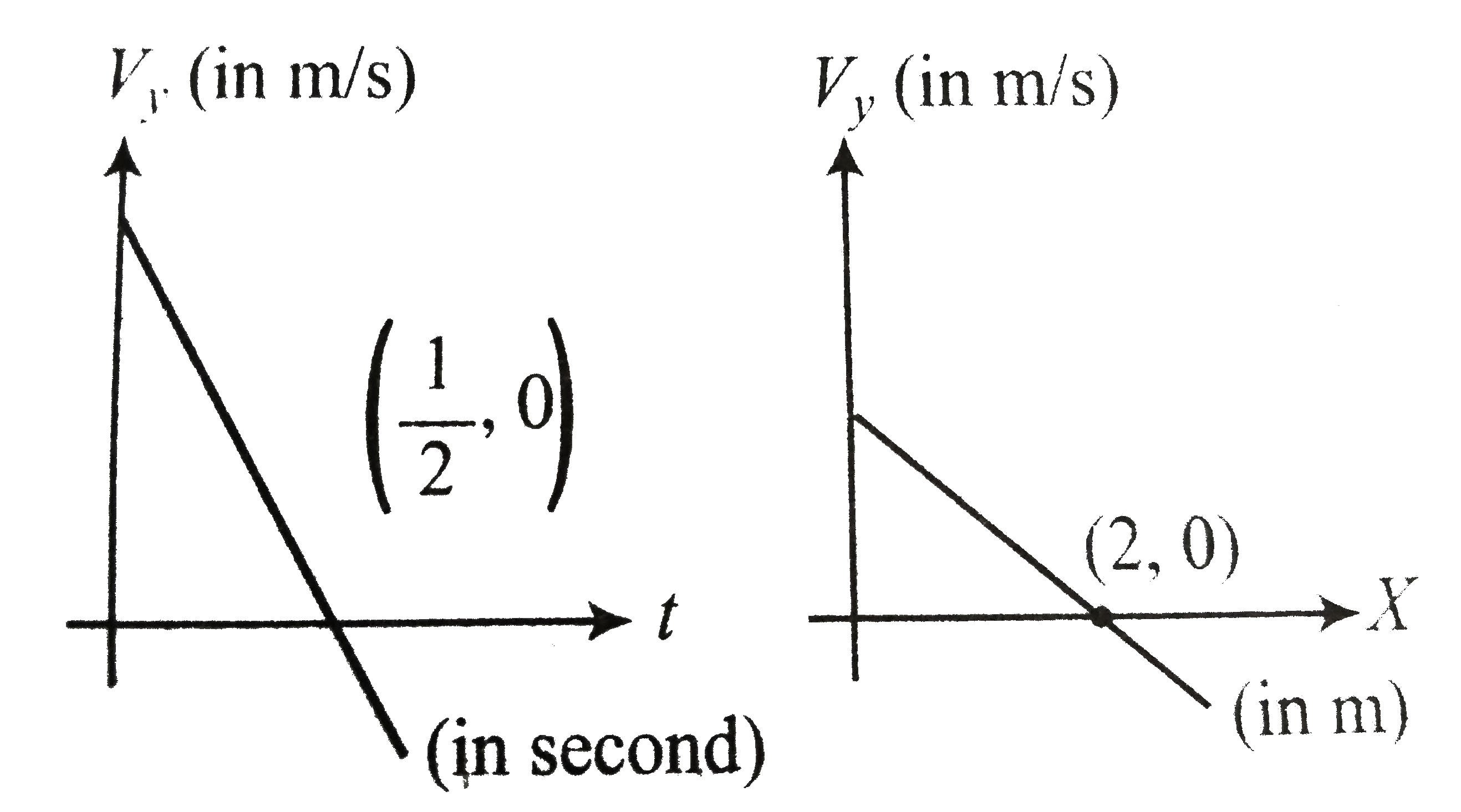
Projection angle with the horizontal is :
View SolutionTwo graphs of the same projectile motion (in the xy-plane) projected from origin are shown. X-axis is along horizontal direction and y-axis is vertically upwards. Take g=10ms−2.
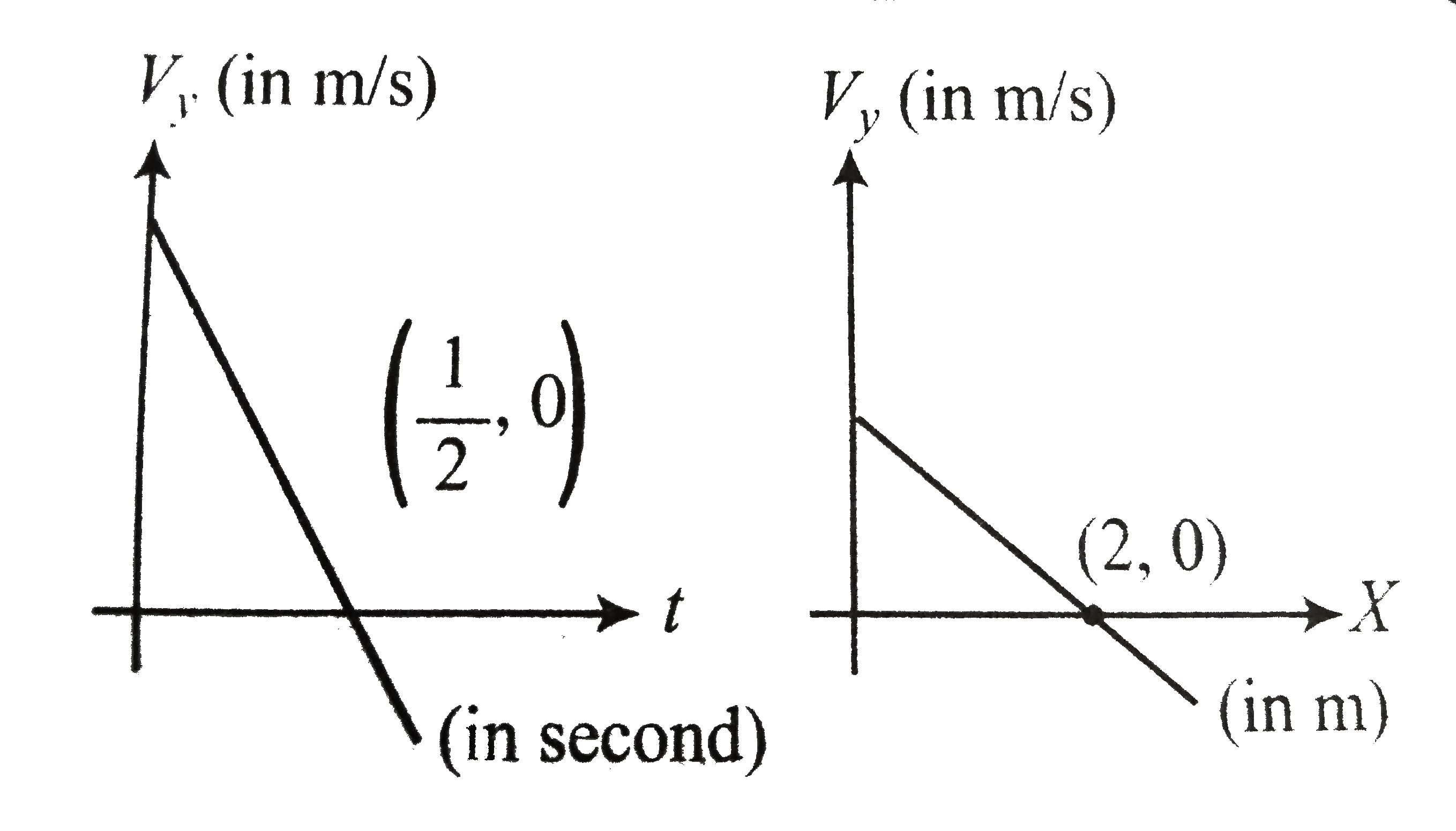 ,
,
The projection speed is :
View SolutionTwo graphs of the same projectile motion (in the xy-plane) projected from origin are shown. X-axis is along horizontal direction and y-axis is vertically upwards. Take g=10ms−2.
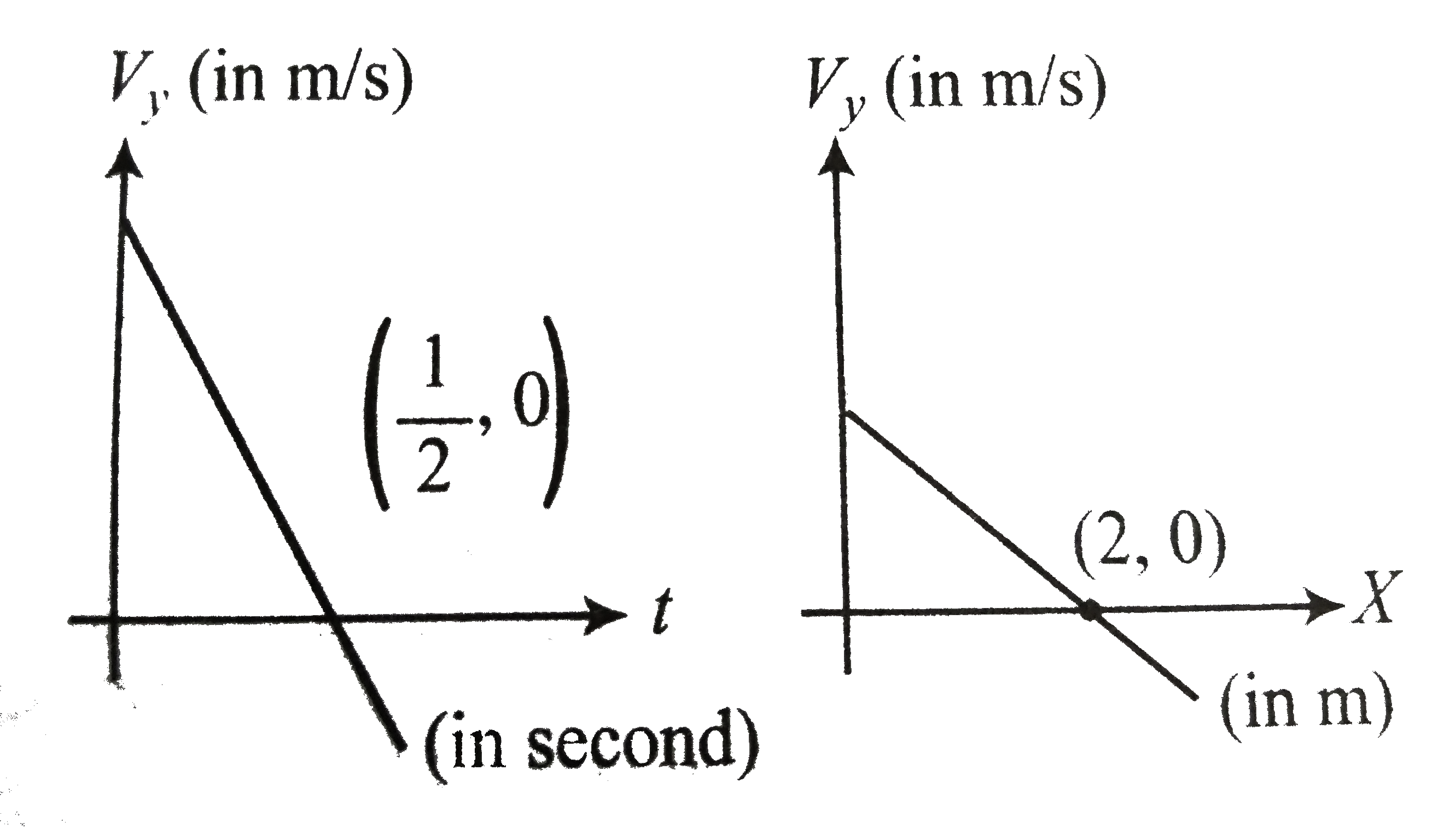 ,
,
Maximum height attained from the point of projection is
View Solution
