An aromatic compound (A), C9H12O was subjeted to a series of tests in the laboratory. It was found that this compound ,
(i) does not form silver mirror with Tollens' reagent.
(ii) rotates the plane of polarised light.
(iii) reacts with sodium metal to evolve hydrogen gas. ltbr> (iv) does not decolourise pink colour of bromine water.
(v) reacts with hot KMnO4 to form monocarboxylic acid 'B' which on decarboxylation gives benzene.
(vi) reacts with Lucas reagent in about 5 min.
(vii) reacts with I2 and NaOH to produce yellow coloured precipitation of the compound (C ) .
(viii) loses its optical activity due to formation of compound (D ) on reaction with Red P and HI.
The functional groups present in the compound (A) is :
aldehydic (-CHO)
ketonic ⎛⎜ ⎜⎝−O∣∣C−⎞⎟ ⎟⎠
alcoholic (−OH)
alkoxy group (−OR)
The correct Answer is:C
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERSBook:OP TANDONChapter:ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERSExercise:ETHERS Passage 6
Explore 5 Videos
- ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERSBook:OP TANDONChapter:ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERSExercise:Passage 7
Explore 6 Videos
- ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERSBook:OP TANDONChapter:ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERSExercise:Passage 4
Explore 5 Videos
- ALDEHYDES AND KETONES Book:OP TANDONChapter:ALDEHYDES AND KETONES Exercise:SINGLE INTEGER ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Explore 10 Videos
Similar Questions
Alexander Williamson prepared diethyl by a simple method, now called as Williamson's ether synthesis . In this method, an alkyl halide is treated with sodium alkoxide prepared from sodium and alcohol.
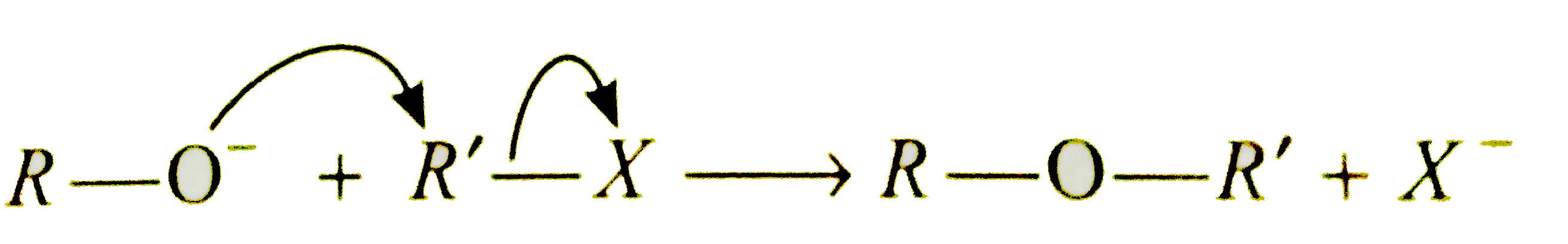
This reaction is used in the synthesis of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers.
It may be noted taht for preparing unsymmetrical ethers, the halide used should preferably be primary because secondary and tertiary alkyl halides may form alkenes as major product due to elimination process.
CH3−CH3∣C∣CH3−Br+Na+O−−C2H5Sodium ethoxide→CH3−CH3∣C=CH22-methylpropene+C2H5OH+NaBr
Aryl ethers or phenolic ethers can be prepared by using sodium phenoxide and alkyl halides. However, aryl halides and sodium alkoxide cannot be used for preparing phenolic ethers because aryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction
Arrange the following halides in decreasing order of reactivity towards Williamson's ether synthesis :
CH3CH2CH2Cl(u), CH3CH2CH2Br(v),
(CH3)3C−CH2Br(w), H2C=CH−CH2Cl(x)
View SolutionCarbon-oxygent bond in ethers can be cleaved b halogen acids, sulphuric acid, phosphorus pentachlodie, etc. The cleavage of C-O bond take place under drastic conditions with excess of hydrogen halides.
R−O−R+2HX→2RX+H2O
If hydrogen halide is not taken in excess then a molecule of alcohol and alkyl halide are formed.
R−O−R+HI373K−−→R−OH+R−I
The order of reactivity of hydrogen halides towards the given reaction depends on the bond strength of halogenated acids, weaker is the H-X bond, greter is its reactivity. In case of unsymmetrical ethers, the site of cleavage is such that the halide is formed from the alkyl group which is smaller in size. However, when one of the alkyl group is tertiary, the halide formed is the tertiary halide.
Indiate wheterh the following statements / reactions are true or false.
Hydrogen fluoride (HF) is not effective in ether cleavage.
(a) True (b) False
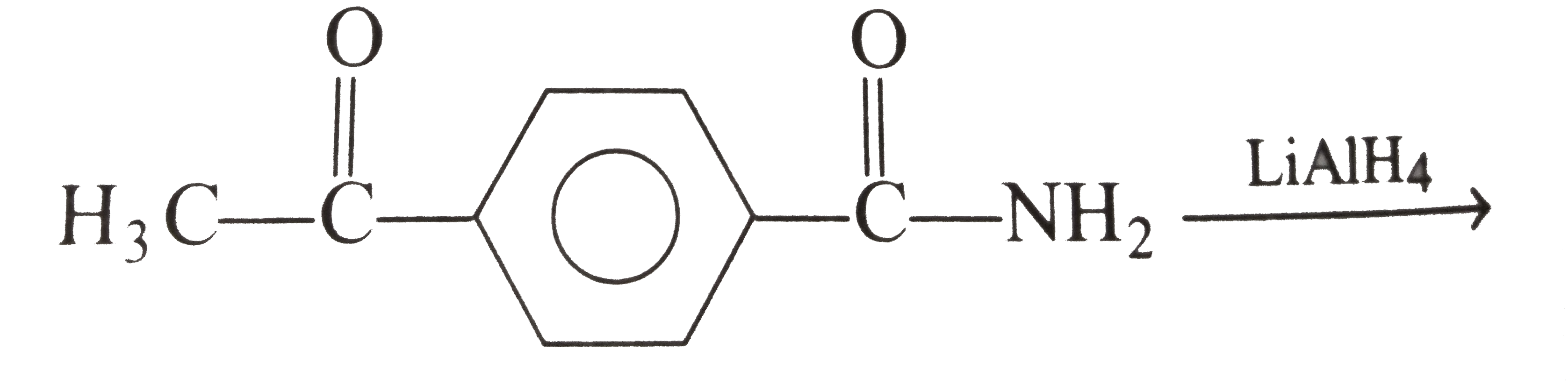
View SolutionCarbon-oxygen double bond are easily reduced by NaBH4 or LiAlH4. The actual reducing agent in these reduction is hydride ion (H−).
The metal-hydrogen bond in LiAlH4 is more polar than metal-hydrogen bond in NaBH4. As a result LiAlH4 is strong reducing agent than NaBH4. Esters, carboxylic acids, amides cannot be reducted by NaBH4.
The carbonyl group of amide to methylene group by LiAlH4.
Find the correct product of the following reaction :
View SolutionIsomeric aldehydes and ketones having the formula C5H10O are :
View Solution(A) (C_(9)H_(12)O)underset(Hot KMnO_(4))overset([O])(rarr) PhCOOH i. (A) does not decolourise Br_(2) in C Cl_(4) , reacts with Na to give a colourless and odourless gas (B). ii. (A) does not give iodoform test. iii. (A) is a chiral compound and oxidation of (A) with CrO_(3)//Py gives a chiral compound (C ). iv. The colour of Cr_(2)O_(7)^(2-) change to blue-green when added to compound (A). The structure of compound (A) is:
View Solution(A) (C_(9)H_(12)O)underset(Hot KMnO_(4))overset([O])(rarr) PhCOOH i. (A) does not decolourise Br_(2) in C Cl_(4) , reacts with Na to give a colourless and odourless gas (B). ii. (A) does not give iodoform test. iii. (A) is a chiral compound and oxidation of (A) with CrO_(3)//Py gives a chiral compound (C ). iv. The colour of Cr_(2)O_(7)^(2-) change to blue-green when added to compound (A). The colourless and odourless gas (B) is:
View Solution(A)(C9H12O)[O]−−−−−−−−→HotKMnO4PhCOOH
i. (A) does not decolourise Br2 in CCl4, reacts with Na to give a colourless and odourless gas (B).
ii. (A) does not give iodoform test.
iii. (A) is a chiral compound and oxidation of (A) with CrO3/Py gives a chiral compound (C ).
iv. The colour of Cr2O2−7 change to blue-green when added to compound (A).
The compound (C ) is:
View SolutionA organic compound with the molecular formula C3H6O does not respond positively to the silver mirror test with Tollens reagent but produces on oxmime. The compound is
View SolutionCompound C4H8CI2(A) on hydrolysis gives a compound C4H8O(B) which reacts with hydroxylamine and does not give any test with Tollens reagent . What are (A) and (B) ?
View SolutionA compound (A) with molecular formula C_(4)H_(10)O reacts rapidly with metallic sodium but reacts very slowly with Lucas reagent. (A) when treated with hot concentrated H(2)SO_(4) gives a compound (B) , C_(4)H_(8) on hydration with aqueous H_(2)SO_(4) forms a compound (C ) with moolcular formula C_(4)H_(10)O . (C ) is almost inert to metallic sodium but reacts readily with Lucas reagent. What are (A),(B) and (C ) ? Explain the reactions involved.
View SolutionAn aromatic compound (A), C_(9)H_(12)O was subjeted to a series of tests in the laboratory. It was found that this compound , (i) does not form silver mirror with Tollens' reagent. (ii) rotates the plane of polarised light. (iii) reacts with sodium metal to evolve hydrogen gas. ltbr> (iv) does not decolourise pink colour of bromine water. (v) reacts with hot KMnO_(4) to form monocarboxylic acid 'B' which on decarboxylation gives benzene. (vi) reacts with Lucas reagent in about 5 min. (vii) reacts with I_(2) and NaOH to produce yellow coloured precipitation of the compound (C ) . (viii) loses its optical activity due to formation of compound (D ) on reaction with Red P and HI. Structure of the compound (A ) will be :
View SolutionAn aromatic compound (A), C9H12O was subjeted to a series of tests in the laboratory. It was found that this compound ,
(i) does not form silver mirror with Tollens' reagent.
(ii) rotates the plane of polarised light.
(iii) reacts with sodium metal to evolve hydrogen gas. ltbr> (iv) does not decolourise pink colour of bromine water.
(v) reacts with hot KMnO4 to form monocarboxylic acid 'B' which on decarboxylation gives benzene.
(vi) reacts with Lucas reagent in about 5 min.
(vii) reacts with I2 and NaOH to produce yellow coloured precipitation of the compound (C ) .
(viii) loses its optical activity due to formation of compound (D ) on reaction with Red P and HI.
Molecular formula of the compound (C ) will be :
View SolutionAn aromatic compound (A), C9H12O was subjeted to a series of tests in the laboratory. It was found that this compound ,
(i) does not form silver mirror with Tollens' reagent.
(ii) rotates the plane of polarised light.
(iii) reacts with sodium metal to evolve hydrogen gas. ltbr> (iv) does not decolourise pink colour of bromine water.
(v) reacts with hot KMnO4 to form monocarboxylic acid 'B' which on decarboxylation gives benzene.
(vi) reacts with Lucas reagent in about 5 min.
(vii) reacts with I2 and NaOH to produce yellow coloured precipitation of the compound (C ) .
(viii) loses its optical activity due to formation of compound (D ) on reaction with Red P and HI.
Monocarboxylic acid (B) will be :
View SolutionAn aromatic compound (A), C9H12O was subjeted to a series of tests in the laboratory. It was found that this compound ,
(i) does not form silver mirror with Tollens' reagent.
(ii) rotates the plane of polarised light.
(iii) reacts with sodium metal to evolve hydrogen gas. ltbr> (iv) does not decolourise pink colour of bromine water.
(v) reacts with hot KMnO4 to form monocarboxylic acid 'B' which on decarboxylation gives benzene.
(vi) reacts with Lucas reagent in about 5 min.
(vii) reacts with I2 and NaOH to produce yellow coloured precipitation of the compound (C ) .
(viii) loses its optical activity due to formation of compound (D ) on reaction with Red P and HI.
The compound (D ) will be :
View SolutionThe compound of molecular formula C_(5)H_(10)O (A) reacts with Tollen's reagent to give silver mirror but does not undergo aldol condensation. The compound (A) is :
View Solution

