Dehydration of alcohol into alkene by concentration H2SO4 involves which among the following reaction intermediate ?
Free radical
Carbocation
Carbanion
Carbene
The correct Answer is:B
To determine the reaction intermediate formed during the dehydration of alcohol into alkene using concentrated sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), we can follow these steps:
1. Understanding the Reactants:
- We start with an alcohol (RCH₂OH) and concentrated sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄). H₂SO₄ acts as a strong acid in this reaction.
2. Protonation of Alcohol:
- The first step involves the protonation of the alcohol. The hydroxyl group (-OH) of the alcohol can accept a proton (H⁺) from H₂SO₄, forming an oxonium ion (RCH₂OH₂⁺).
- This step can be represented as:
RCH2OH+H2SO4→RCH2OH+2+HSO−4
3. Formation of Carbocation:
- The oxonium ion (RCH₂OH₂⁺) is unstable and can lose a water molecule (H₂O) to form a carbocation (RCH₂⁺). This step is crucial as it leads to the formation of the carbocation intermediate.
- This can be represented as:
RCH2OH+2→RCH+2+H2O
4. Deprotonation to Form Alkene:
- The carbocation (RCH₂⁺) can then lose a proton (H⁺) to form an alkene (RCH=CH₂). This step completes the dehydration process.
- This can be represented as:
RCH+2→RCH=CH2+H+
5. Conclusion:
- The intermediate formed during the dehydration of alcohol using concentrated H₂SO₄ is a carbocation.
Final Answer:
The reaction intermediate involved in the dehydration of alcohol into alkene by concentrated H₂SO₄ is carbocation.
- We start with an alcohol (RCH₂OH) and concentrated sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄). H₂SO₄ acts as a strong acid in this reaction.
- The first step involves the protonation of the alcohol. The hydroxyl group (-OH) of the alcohol can accept a proton (H⁺) from H₂SO₄, forming an oxonium ion (RCH₂OH₂⁺).
- This step can be represented as:
RCH2OH+H2SO4→RCH2OH+2+HSO−4
- The oxonium ion (RCH₂OH₂⁺) is unstable and can lose a water molecule (H₂O) to form a carbocation (RCH₂⁺). This step is crucial as it leads to the formation of the carbocation intermediate.
- This can be represented as:
RCH2OH+2→RCH+2+H2O
- The carbocation (RCH₂⁺) can then lose a proton (H⁺) to form an alkene (RCH=CH₂). This step completes the dehydration process.
- This can be represented as:
RCH+2→RCH=CH2+H+
- The intermediate formed during the dehydration of alcohol using concentrated H₂SO₄ is a carbocation.
The reaction intermediate involved in the dehydration of alcohol into alkene by concentrated H₂SO₄ is carbocation.
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Dehydration of ethylene glycol in presence of concentration H2SO4 will give
A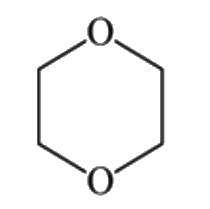 B
B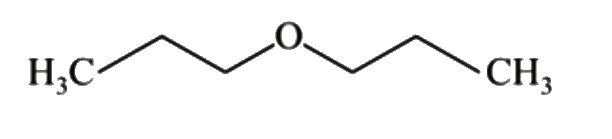 C
C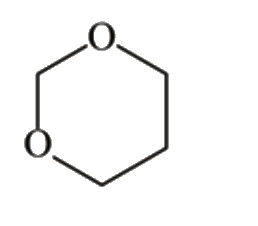 D
D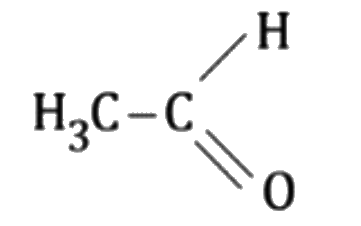
Which of the following reactions involve benzyne intermediate?
A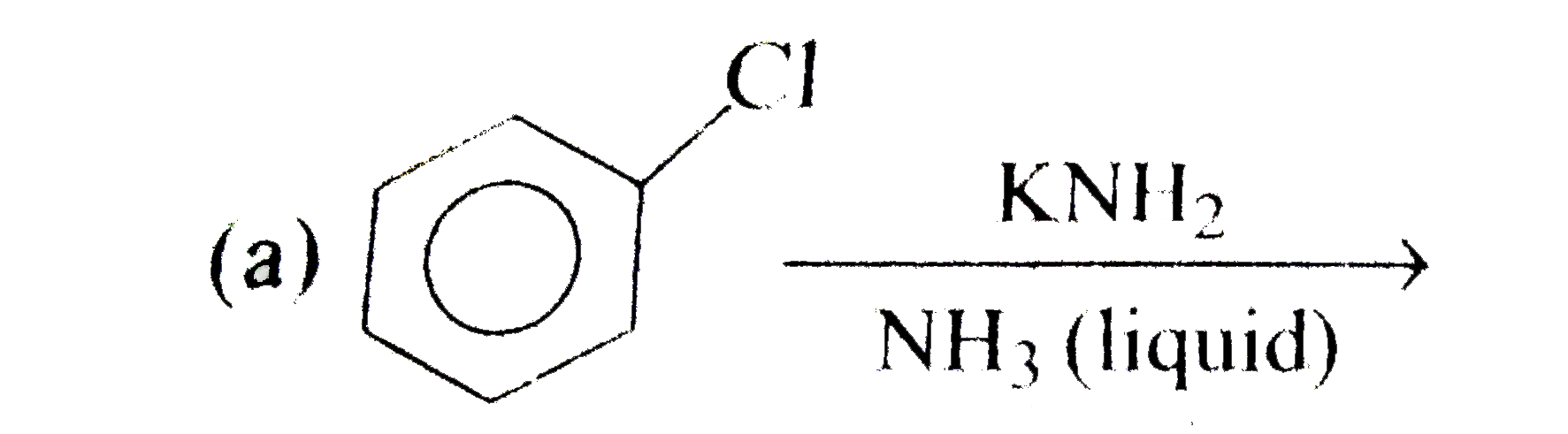 B
B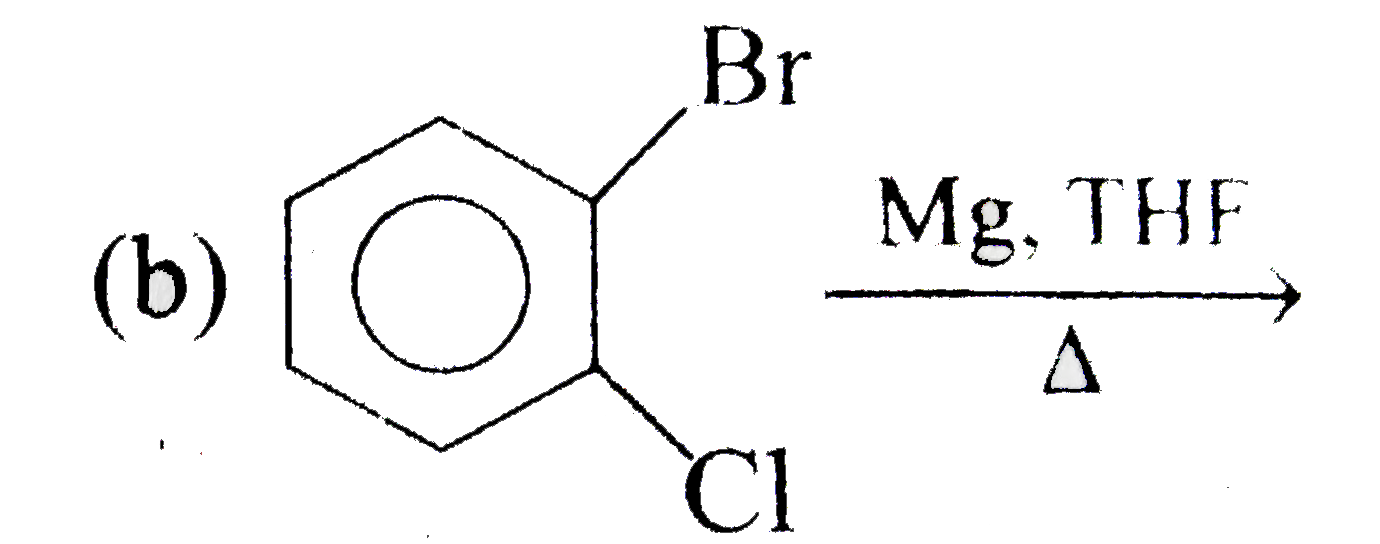 C
C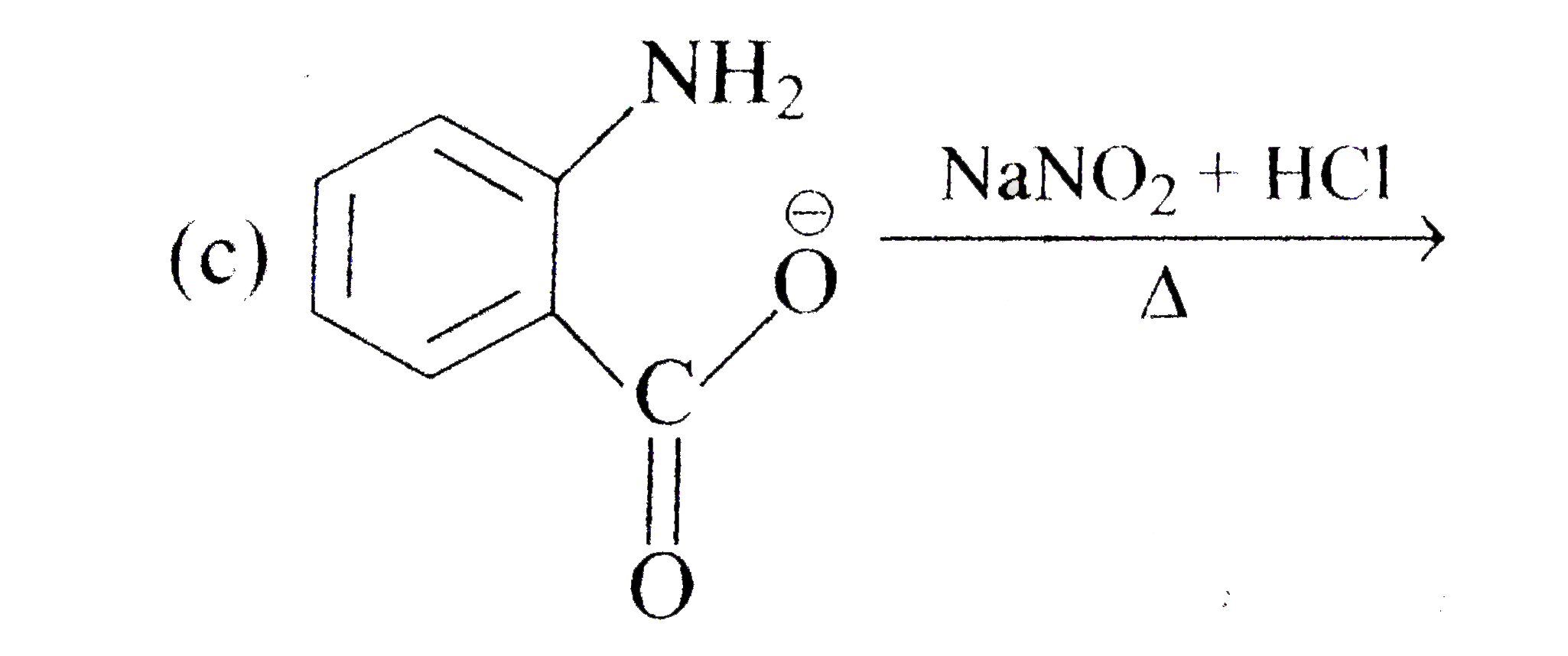 D
D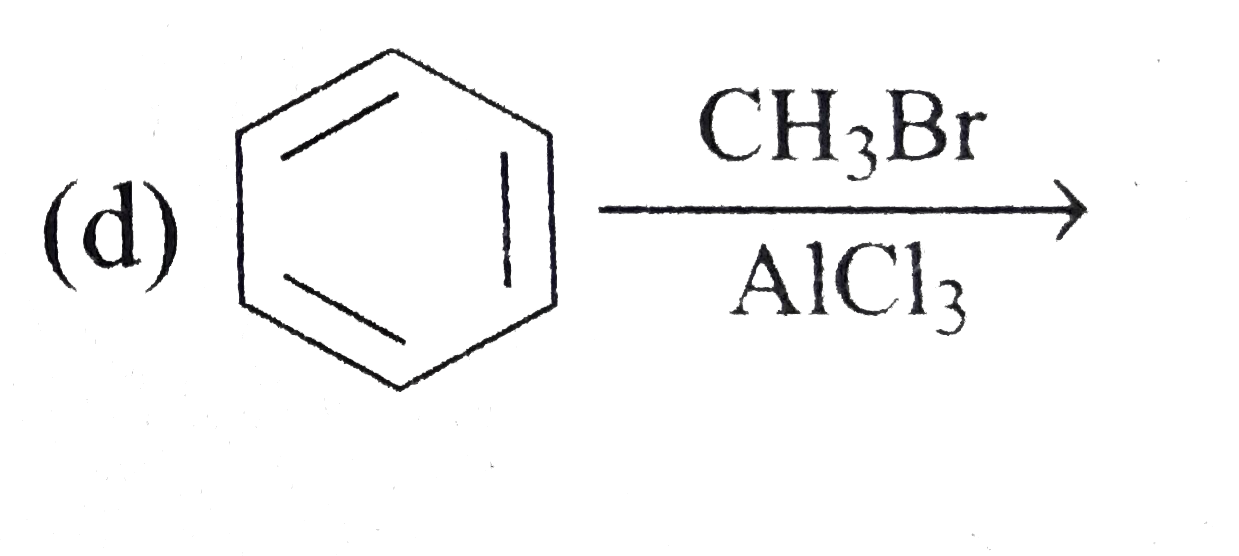
The ease of dehydration of an alcohol with concentrated H2SO4 is
A3∘>2∘>1∘B3∘<2∘<1∘C3∘>2∘<1∘D3∘<2∘<1∘
During the dehydration of alcohols to alkenes by heating with conc. H2SO4, the initiating step is :
View SolutionDehydration of alcohol produces alkene, the reaction intermediate is
View SolutionDuring dehydration of alcohols to alkenes by heating with concentrated H2SO4 the initiation step is
View SolutionDuring the dehydration of alcohols to alkenes by heating with conc. H2SO4, the initiating step is :
View SolutionConcentrated H2SO4will not dehydrate the following complex :
View Solution
