One of the important approach to the study of real gases involves the analysis of parameter Z called the compressibility factor Z=PVmRT where P is pressure, Vm is molar volume, T is absolute temperature and R is the universal gas constant. such a relation can also be expressed as Z=(VmrealVmal) (where Vmal and Vmreal are the molar volume for ideal and real gas respectively). Gas corresponding Z<1 have attractive forces amoung constituent particles. As the pressure is lowered or temperature is increased the value of Z approaches 1. (reaching the ideal behaviour)
ObservationConclusionI.Z=1I.The gas need not be showing the ideal behaviourII.Z>1II.On applying pressure the gas will respond byincreasing its volumeIII.Z<1III.The gas may be liquefiedIV.Z→1for lowPIV.The gas is approaching the ideal behaviour
All conclusions are true
Conclusions I, II & IV ar true
Conclusions I, III & IV are true
Conclusion III & IV are true
The correct Answer is:D
Similar Questions
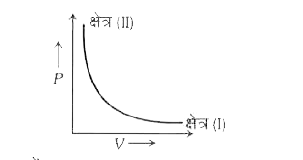
One of the important approach to the study of real gases involves the analysis of parameter Z called the compressibility factor Z = (PV_(m))/(RT) where P is pressure, V_(m) is molar volume, T is absolute temperature and R is the universal gas constant. such a relation can also be expressed as Z = ((V_(m)real)/(V_(m)ideal)) (where V_(m ideal) and V_(m real) are the molar volume for ideal and real gas respectively). Gas corresponding Z lt 1 have attractive forces amoung constituent particles. As the pressure is lowered or temperature is increased the value of Z approaches 1. (reaching the ideal behaviour) Following graph represents a pressure (P) volume (V) relationship at a fixed temperature (T) for n moles of a real gas. The graph has two regions marked (I) and (II) . Which of the following options is true.
View SolutionOne of the approach to the study of real gases involves the analysis of a parameter Z called the compressibility factor Z=(PV_(m))/(RT) where P is pressure, V_(m) is molar volume, T is absolute temperature and R is the universal gas constant . Such a relation can also be expressed as Z =((V_("m real"))/(V_("m ideal"))) (where V_("m ideal ") and V_("m real") are the molar volume for ideal and real gas respectively) . Gas corresponding Z gt 1 have repluive tendenciesamong constituent particles due to their size factor, among constitutent particles . As the pressure is lowered or temperature is increased the value of Z approaches 1. ( reaching the ideal behaviour) For a real gas 'G'Z gt 1 at STP then for 'G' which of the following is true
View SolutionAt constant temperature and pressure, the compressbility factor (Z) for one mole of a van der waals gas is 0.5. if the volumes of the gas molecules are considered to negligible, then show that a=12VmRT, where Vm and T are the molar volume and temperature of the gas respectively.
View SolutionFor a real gas with very large value of molar volume, which of the following equation can most suitably be applied: (A) Z = 1 - (a)/(V_(m)RT) (B) PV =RT (C) Z = 1+ (Pb)/(RT) (D) PV_(m) -RT = (a)/(V_(m)
View Solutionवास्तविक गैसों के अध्ययन की एक महत्वपूर्ण पहुँच जिसमें पैरामीटर Z का विश्लेषण शामिल है सम्पीड़यता गुणांक Z=(PVm)RT) कहलाता है जहाँ P दाब है,Vm मोलर आयतन है, T परम ताप है तथा R सार्वत्रिक गैस स्थिरांक है। अतः इस संबंध को इस प्रकार भी प्रदर्शित कर सकते है Z = ((V_(“mवास्तविक”)/(V_(“m”आदर्श)) (जही V“mआदर्श” तथा V“mवास्तविक” क्रमशः आदर्श तथा वास्तविक गैस के लिए मोलर आयतन है)। Z>1 अनुरूप गैस के घटक कणों के मध्य उनके आकार गुणांक के कारण प्रतिकर्षण की प्रवृति होती है जबकि जो गैस Z<1 के अनुरूप होती है उनके घटक कणों के मध्य आकर्षण बल होता है जैसे-जैसे दाब कम होता है या ताप अधिक होता है तब 2 का मान 1 तक पहुँच जाता है (आदर्श व्यवहार तक पहुंच जाता है)।
निष्कर्ष को चुनिए जो कि नियमित निरीक्षण के लिए योग्य हो

View Solutionवास्तविक गैसों के अध्ययन की एक महत्वपूर्ण पहुँच जिसमें पैरामीटर Z का विश्लेषण शामिल है सम्पीड़यता गुणांक Z=(PVm)RT) कहलाता है जहाँ P दाब है,Vm मोलर आयतन है, T परम ताप है तथा R सार्वत्रिक गैस स्थिरांक है। अतः इस संबंध को इस प्रकार भी प्रदर्शित कर सकते है Z=((V“mreal”V“mal” (जही V“mal” तथा V“mreal” क्रमशः आदर्श तथा वास्तविक गैस के लिए मोलर आयतन है)। Z>1 अनुरूप गैस के घटक कणों के मध्य उनके आकार गुणांक के कारण प्रतिकर्षण की प्रवृति होती है जबकि जो गैस Z<1 के अनुरूप होती है उनके घटक कणों के मध्य आकर्षण बल होता है जैसे-जैसे दाब कम होता है या ताप अधिक होता है तब 2 का मान 1 तक पहुँच जाता है (आदर्श व्यवहार तक पहुंच जाता है)।
STP पर यास्तविक गैस 'G' के लिए Z>1 है तब 'G' के लिए निम्न में से कौनसा कथन सत्य है
View Solutionवास्तविक गैसों के अध्ययन की एक महत्वपूर्ण पहुँच जिसमें पैरामीटर Z का विश्लेषण शामिल है सम्पीड़यता गुणांक Z=(PVm)RT) कहलाता है जहाँ P दाब है,Vm मोलर आयतन है, T परम ताप है तथा R सार्वत्रिक गैस स्थिरांक है। अतः इस संबंध को इस प्रकार भी प्रदर्शित कर सकते है Z=((V“mवास्तविक”V“m”आदर्श (जही V“mआदर्श” तथा V“mवास्तविक” क्रमशः आदर्श तथा वास्तविक गैस के लिए मोलर आयतन है)। Z>1 अनुरूप गैस के घटक कणों के मध्य उनके आकार गुणांक के कारण प्रतिकर्षण की प्रवृति होती है जबकि जो गैस Z<1 के अनुरूप होती है उनके घटक कणों के मध्य आकर्षण बल होता है जैसे-जैसे दाब कम होता है या ताप अधिक होता है तब 2 का मान 1 तक पहुँच जाता है (आदर्श व्यवहार तक पहुंच जाता है)।
वास्तविक गैस के मोलों के लिए स्थिर ताप (T) पर दाब (P) व आयतन (V) के संबंध को निम्न ग्राफ द्वारा दर्शाया गया है। ग्राफ में दो क्षेत्र चिन्ह (I) तथा (I) है। निम्न में से कौनसा विकल्प सही है
View SolutionIf V is the observed molar volume of real gas and Vid is the molar volume of an ideal gas then Z is
View Solution

