Which of the following reaction will get affected by increase of pressure? Also mention, whether change will cause the reaction to go into the right or left direction?
(i) CH4(g)+2S2(g)⇔CS2(g)+2H2S(g)
(ii) CO2(g)+C(s)⇔2CO(g)
(iii) 4NH3(g)+5O2(g)⇔4NO(g)+6H2O(g)
(iv) C2H4(g)+H2(g)⇔C2H6(g)
The correct Answer is:(i) unaffected;no shift (ii) affected; left direction.
(iii) affected; left (iv) affected; right
(i) In this case np is equal to nr
This reaction will not be affected by increase of pressure.
(ii) CO2(g)+C(s)⇔2CO(g)
In this reaction, moles of gases on product side (np=2) is more than on reactant side (nr=1). This reaction will be affected by increase in pressure. Increase in pressure shifts the equilibrium in that direction where there is less no. of moles gases. In this reaction increase in pressure will cause the reaction to go into the left direction.
(iii) 4NH3(g)+5O2(g)⇔4NO(g)+6H2O(g)
The reaction would be affected by increase in pressure because Np is different form nr
Increase in pressure shifts the equilibrium in left direction because nt is less than np
Topper's Solved these Questions
- CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUMBook:RESONANCEChapter:CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUMExercise:Exercise-1 (Part-2)
Explore 88 Videos
- CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUMBook:RESONANCEChapter:CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUMExercise:Exercise-2 (Part-1)
Explore 28 Videos
- CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUMBook:RESONANCEChapter:CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUMExercise:Board Level Exercise
Explore 33 Videos
- CHEMICAL BONDINGBook:RESONANCEChapter:CHEMICAL BONDINGExercise:Inorganic chemistry (Chemistry Bonding)
Explore 49 Videos
- D & F-BLOCK ELEMENTS & THEIR IMPORTANT COMPOUNDS Book:RESONANCEChapter:D & F-BLOCK ELEMENTS & THEIR IMPORTANT COMPOUNDS Exercise:Match the column
Explore 1 Video
Similar Questions
A reversible reaction is one which
View SolutionThe equilibrium constant (Kp) for the reaction, PCl5(g)⇔PCl3(g)+Cl2(g) is 16. If the volume of the container is reduced to half of its original volume, the value of Kp for the reaction at the same temperature will be:
View SolutionThe equilibrium constant expression for a gas reaction is :
Kc=[NH3]4[O2]5[NO]4[H2O]6
Write the balanced chemical equation corresponding to this expression.
View SolutionWhich is correct order ofr net dipole moment :
View SolutionMatch the reactions in Column I with the types of products/the use of products in Column II.
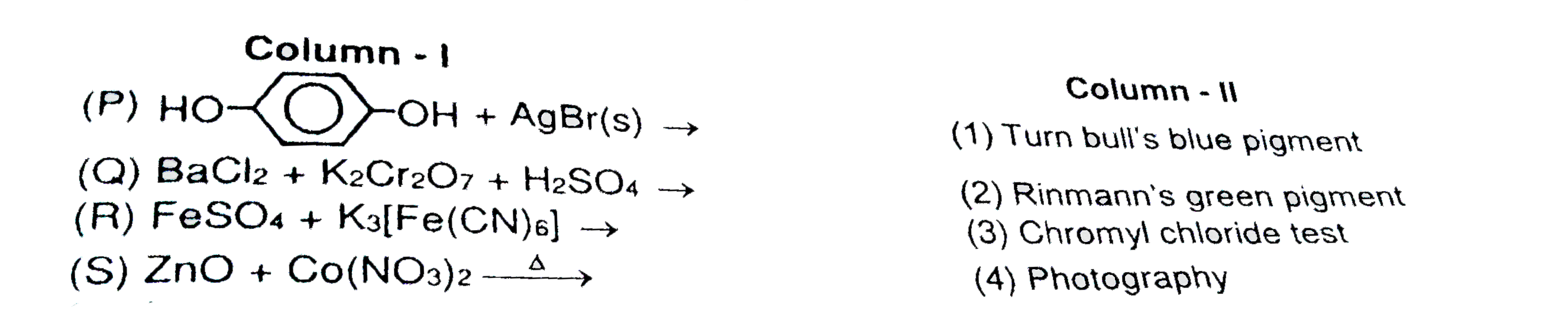
View SolutionWhich of the following reaction will get affected by increase of pressure? Also mention, whether change will cause the reaction to go into the right or left direction? ( i ) CH_(4(g))+2S_(2(g))hArrCS_(2(g))+2H_(2)S_((g)) ( ii ) CO_(2(g))+C_((s))hArr2CO_((g)) ( iii ) 4NH_(3(g))+5O_(2(g))hArr4NO_((g))+6H_(2)O_((g)) ( iv ) C_(2)H_(4(g))+H_(2(g))hArrC_(2)H_(6(g))
View Solutionwhich of the following reactions will get affected by increase in pressure ? Also mention whether the change will cause the reaction to go the right or left direction. (i) CH_(4)(g)+2S)_(2) (g) hArr CS_(2) (g) + 2H_(2)S(g) (ii) CO_(2) (g) +C(s) hArr 2CO (g) (iii) 4NH_(3)(g) +5O_(2)(g) hArr 4NO (g) + 6H_(2)O(g) (iv) C_(2)H_(4)(g) +H_(2)(g) hArr C_(2)H_(6) (g) (v) COCI_(2)(g) hArr CO(g) +CI_(2)(g) (vi) CaCO_(3)(g) hArr CaO(s)+CO_(2)(g)
View SolutionFor the following three reaction 1, 2 and 3, equilibrium constants are given:
(1) CO(g)+H2O(g)⇔CO2(g)+H2(g),K1
(2) CH4(g)+H2O(g)⇔CO(g)+3H2(g),K2
(3) CH4(g)+2H2O(g)⇔CO2(g)+4H2(g),K3
Which of the following relations is correct ?
View SolutionWhich of the following reactions will get affected by increasing the pressure ? Also mention whether change will cause the reaction to go into forward or backward direction ? (i) COCL_(2) (g) hArr CO(g) + Cl_(2) (g) (ii) CH_(4) (g) + 2 S_(2) (g) hArr CS_(2) (g) + 2 H_(2) S (g) (iii) CO_(2) (g) + C (s) hArr 2 CO (g) (iv) 2 H_(2) (g) + CO (g) hArr CH_(3) OH (v) CaCO_(3) (s) hArr CaO (s) + CO_(2) (g) (vi) 4 NH_(3) (g) + 5 O_(2) (g) hArr 4 NO (g) + 6 H_(2) O (g)
View Solutionनिम्नलिखित में कौन-सी अभिक्रियाएँ दाब में वृद्धि द्वारा प्रभावित होगी ? यह भी बताइये की यह परिवर्तन अभिक्रिया को अग्र दिशा की ओर प्रेरित अथवा पश्च दिशा की ओर ।
(i) CH4(g)+2S2⇔CS2(g)+2H2S(g)
(ii)CO2(g)+C(s)⇔2COg
4NH3(g)+5O2(g)⇔4NO(g)+6H2Og
(iv)C2H4(g)+H2g⇔C2H6(g)
View Solutionनिम्नलिखित में से दाब बढ़ने पर कौन-कौन से अभिक्रियाएँ प्रभावित होंगी? यह भी बताएँ की दाब परिवर्तन करने पर क्या अभिक्रिया अग्र या प्रतीप दिशा में गतिमान होगी ?
(i)COCI2(g)⇔CO(g)+CI2(g)
(ii) CH4(g)+2S2⇔CS2+2H2S(g)
(iii) CO2(g)+C(s)⇔2CO(g)
(iv)2H2(g)+CO(g)⇔CH3OH(g)
(v)CaCO3(s)⇔CaO(s)+CO2(g)
(vi) 4NH3(g)+5O2(g)⇔4NO(g)+6H2O(g)
View Solutionनिम्नलिखित में दाब बढ़ाने पर कौन- कौन सी अभिक्रियाएँ प्रभावित होगी ? यह भी बताएँ की दाब परिवर्तन करने पर अभिक्रिया अग्र या प्रतीप दिशा में गतिमान होगी ?
(i)COCl2(g)⇔CO(g)+Cl2(g)
(ii)CH4(g)+2S2(g)⇔CS2(g)+2H2S(g)
(iii)CO2(g)+C(s)⇔2CO(g)
(iv)2H2(g)+CO(g)⇔CH3OH(g)
(v)CaCO3(s)⇔CaO(s)+CO2(g)
(vi)NH3(g)+5O2(g)⇔4NO(g)+6H2O(g)
View SolutionWhich of the following reactions will get affected by increasing the pressure? Also mention whether chasnge will cause the reaction to go into forward or backward direction. (i) COCl_(2)(g)hArrCO(g)+Cl_(2)(g) (ii) CH_(4)(g)+2S_(2)(g)hArrCS_(2)(g)+2H_(2)S(g) (iii) CO_(2)(g)+C(s)hArr2CO(g) (iv) 4NH_(3)+(g)+5O_(2)(g)hArr4NO(g)+6H_(2)O(g)
View SolutionFrom the following data, C(s , graphite) + O_(2) (g) to CO_(2) (g) H_(2) (g) + (1)/(2) O_(2) (g) to H_(2) O (l) Delta H_("reaction")^(@) = -286 kJ/mole 2 C_(2) H_(6) (g) + 7O_(2) (g) to 4 CO_(2) (g) + 6H_(2) O (l) Delta H_("reaction")^(@) = -3120 kJ/mole Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of C_(2) H_(6) (g) ( in kJ/mole)
View SolutionFor the following three reactions I, II and III, equilibrium constants are given : I. H_(2)(g) + 1/2O_(2)(g) rarr H_(2)O ....K_(1) II. C_(2)H_(4)(g) + 3O_(2)(g) rarr 2CO_(2)(g) + 2H_(2)O(g) ....K_(2) III. C_(2)H_(6)(g) + 7/2O_(2)(g) rarr 2CO_(2)(g) + 3H_(2)O(g) ...K_(3) IV. C_(2)H_(4) + H_(2) rarr C_(2)H_(6) ...K_(4) Which of the following relations is correct?
View SolutionWhich of the following reactions will get affected by increasing the pressure? Also, mention whether change will cause the reaction to go into forward or backward direction. (i) COCl_(2)(g)hArrCO(g)+Cl_(2)(g) (ii) CH_(4)(g)+2S_(2)(g)hArrCS_(2)(g)+2H_(2)S(g) (iii) CO_(2)(g)+C(s)hArr2CO(g) (iv) 2H_(2)(g)+CO(g)hArrCH_(3)OH(g) (v)CaCO_(3)(s)hArrCaO(s)+CO_(2)(g) (vi) 4NH_(3)(g)+5O_(2)(g)hArr4NO(g)+6H_(2)O(g)
View Solution
