
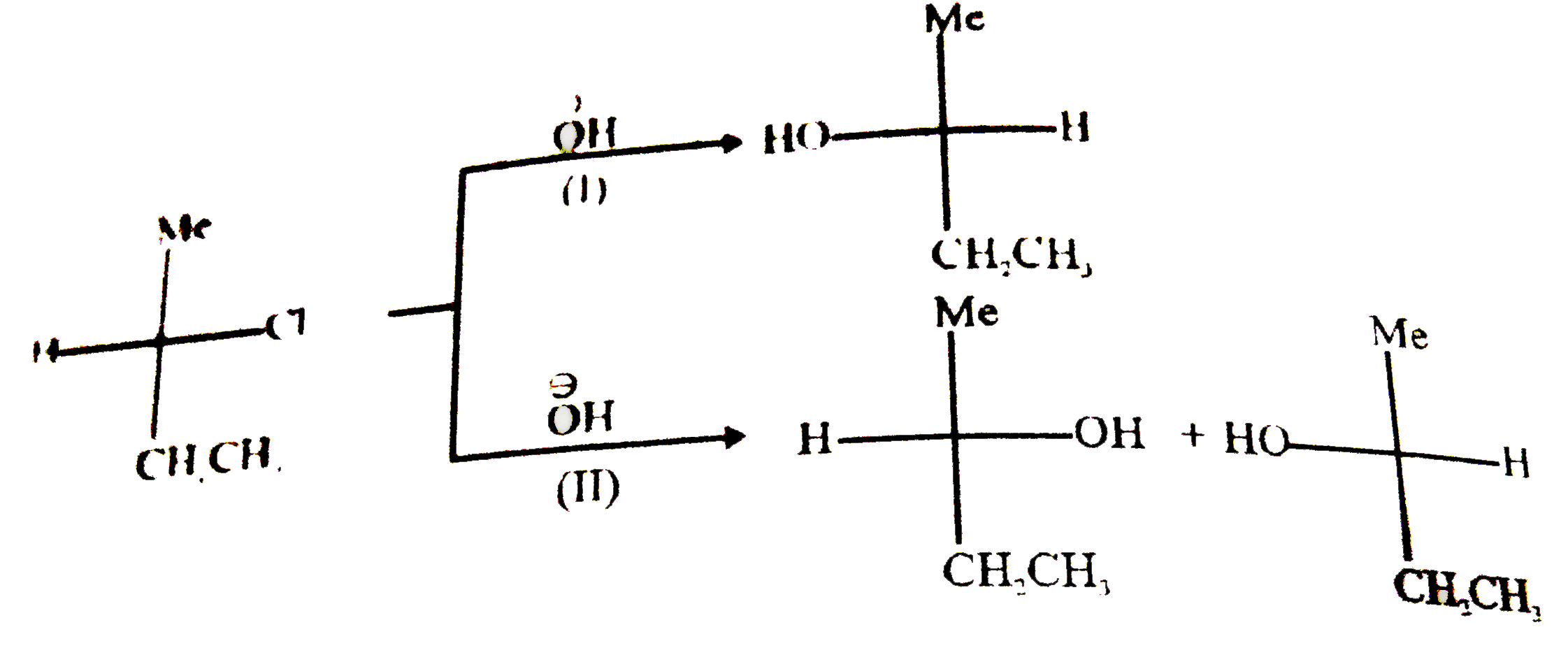
(I)(Reactant)
In this reaction I and II are ,
Enantiomers
Structure isomers
Geometrical isomers
Identical compounds
The correct Answer is:C
Similar Questions
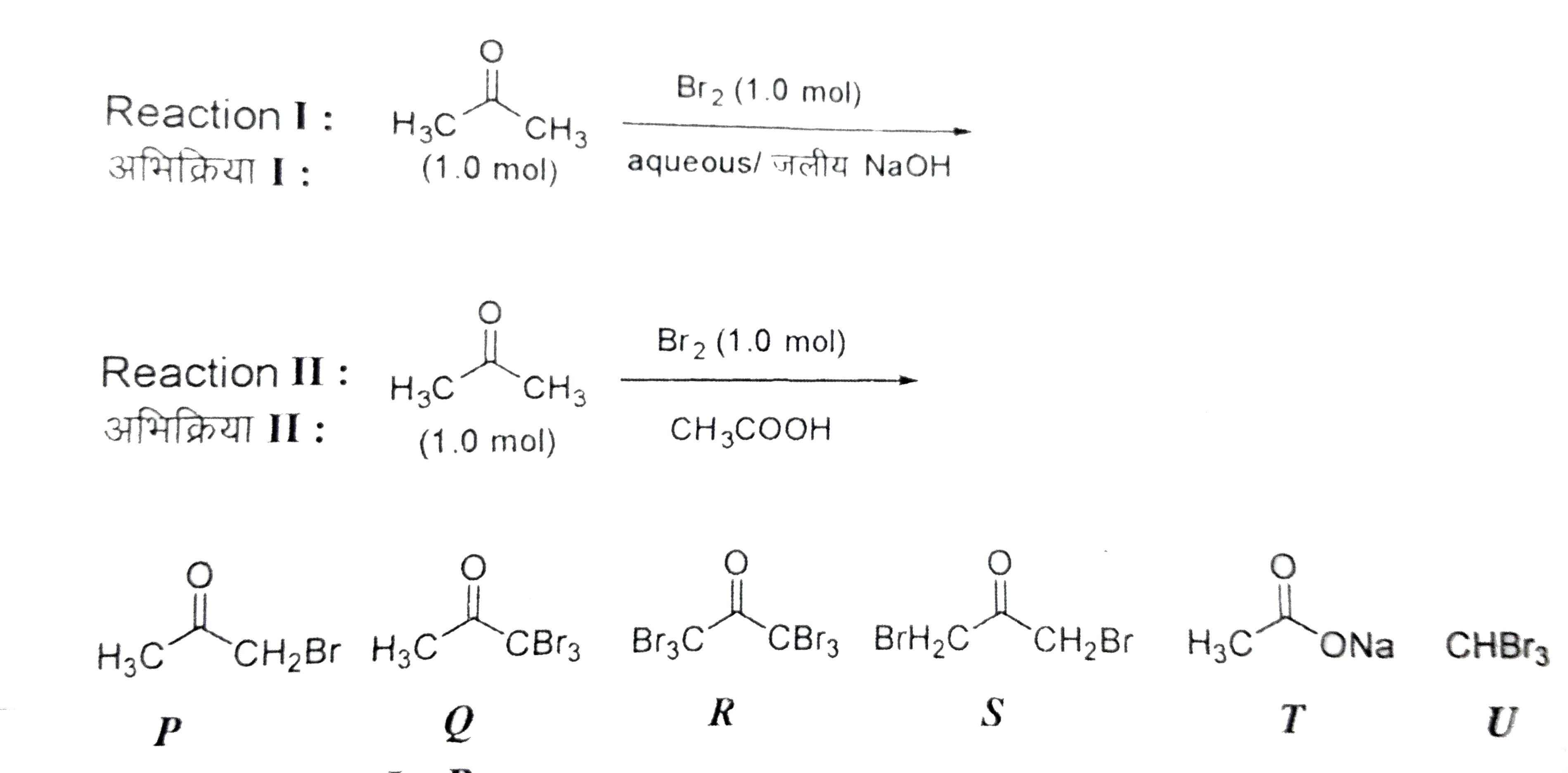
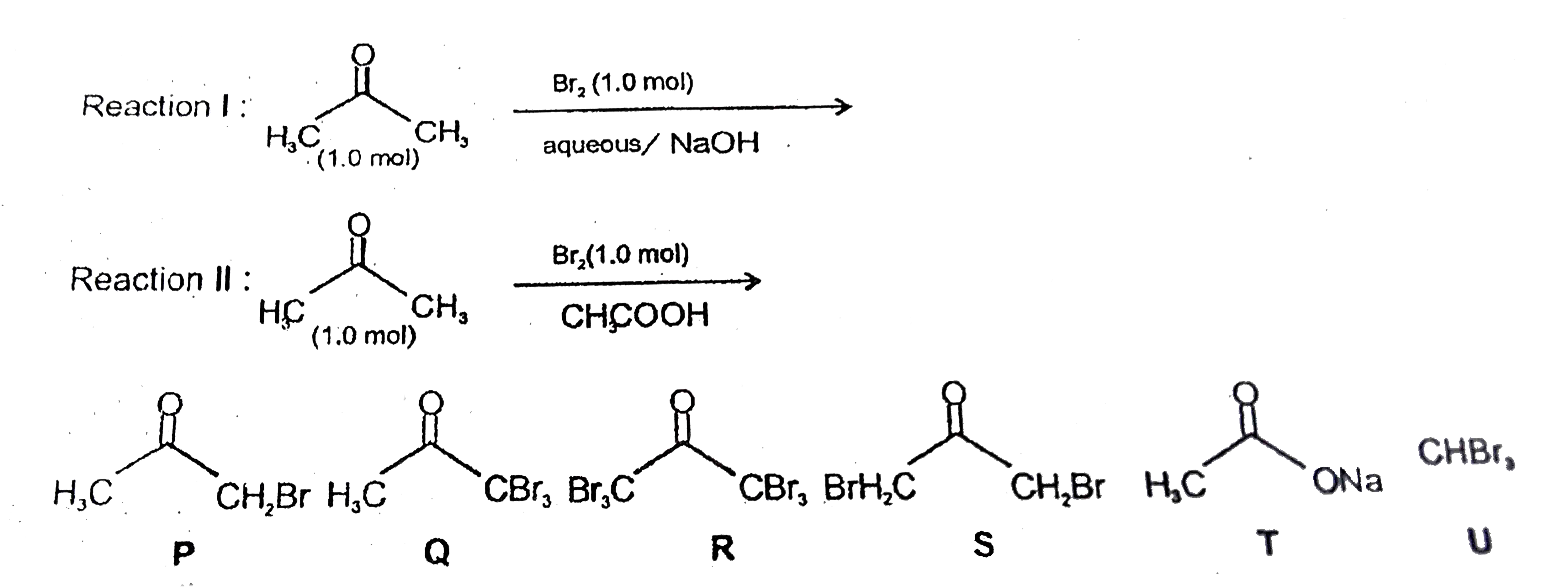
After completion of the reactions (I and II) , the organic compound(s) in the reaction mixtures is(are)
View SolutionA reaction is of second order with respect to its reactant. How will its reaction rate be affected if the concentration of the reactant is (i) doubled (ii) reduced to half ?
View Solution
Knowledge Check
Reaction Ist and IInd areABoth SN 1BBoth SN 1C(I)SN1,(II)SN2D(I)SN2,(II)SN1_E01_302_Q01.png) Gases released in reaction (I) and (II) are:ACO2CO2BSO2,NO2CSO2,CO2DSO2,NO
Gases released in reaction (I) and (II) are:ACO2CO2BSO2,NO2CSO2,CO2DSO2,NO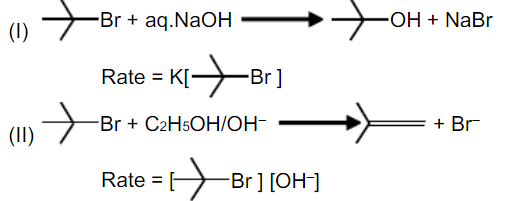
Correct statement regarding these two reaction I and IIARate of I reaction remain unchanged if concentration of OH− increases.BRate of II reaction remain unchanged if concentration of OH− increases.CRate of both reactions become double if concentration of OH− become doubleDRate of both reactions donot depend upon concentration of OH−
After completion of the reaction (I and II), the orgnanic compound(s) in the reaction mixtures is(are)
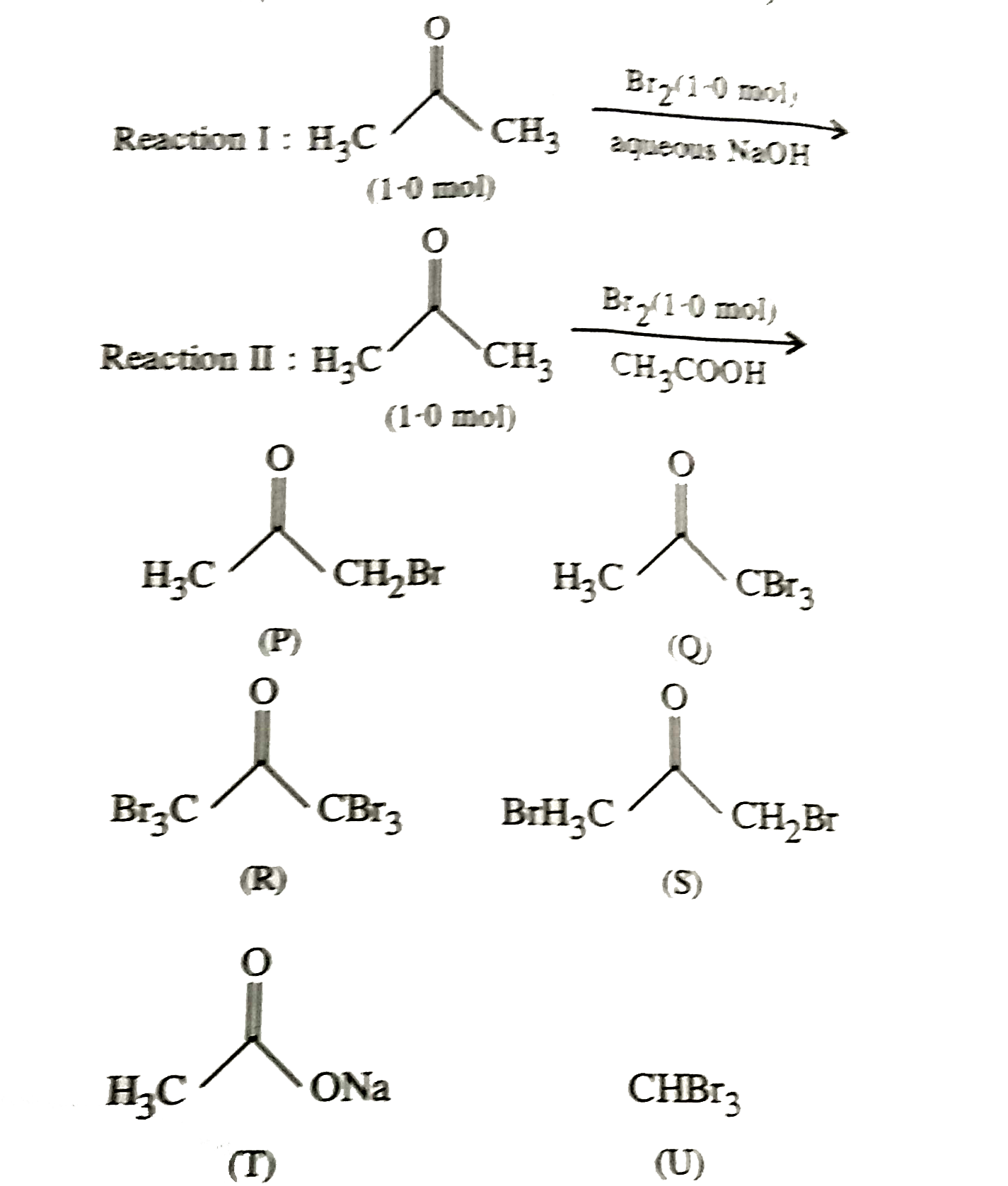
View SolutionAfter completion of the reactions (I and II ), the organic compound (s) in the reactions mixtures is (are )
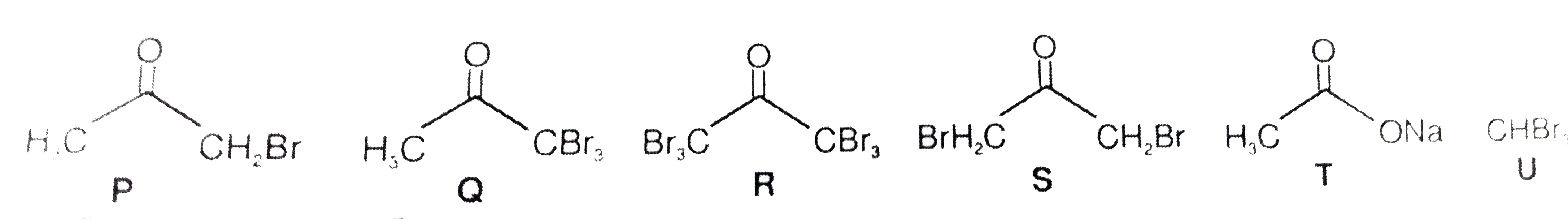
View SolutionAfter completion of the reactions (I and II) , the organic compounds (s) in the reaction mixtures is :
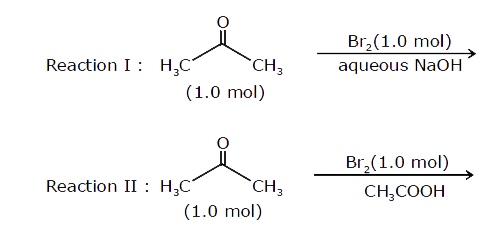
View SolutionAfter completion of the reaction (I and II), the organic compound(s) in the reaction mxitures is (are)
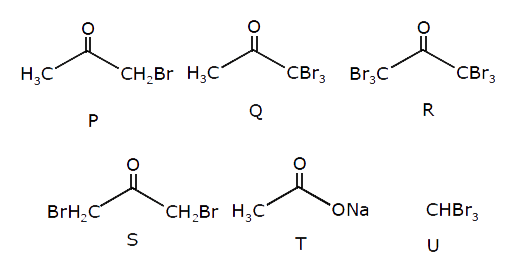
View SolutionIf initial concentration of reactants in certain reaction is doubled, the half-life period of the reaction doubles, the order of a reaction i
View Solution

