Match Column-I with Column-II :
Column-I Column -II
( A) H2(g)+I2(g)→2HI(g) ( p ) Unaffected by inert gas addition
( B ) CaCO3(s)→CaO(s)+CO2(g) ( q) Forward shift by rise in pressure and backward shift by inert gas addition
( C ) N2(g)+3H2(g)→2NH3(g) ( r ) Unaffected by increase in pressure
( D ) PCl5(g)→PCl3(g)+Cl2(g) ( s ) Backward shift by rise in pressure and forward shift by inert gas addition
The correct Answer is:(A→p,r),(B→p,r),(C→q),(D→s)
Similar Questions
Lis−IList−II(A)H2(g)+I2(g)⇔2HI(g)(P)Unaffected by inert gas addition (B)CaCO3(s)⇔CaO(s)+CO2(g)(Q) Forward shift by rise in pressure and backward shift by inert gas addition at constant pressure (C)N2(g)+3H2+(g)⇔2NH3(g)(R) Unaffected by increase in pressure(D)PCl3(g)⇔PCl3(g)+Cl2(g)(S)ackward shift by rise in pressure and forward shift by inert gas addition at constant pressure
View Solution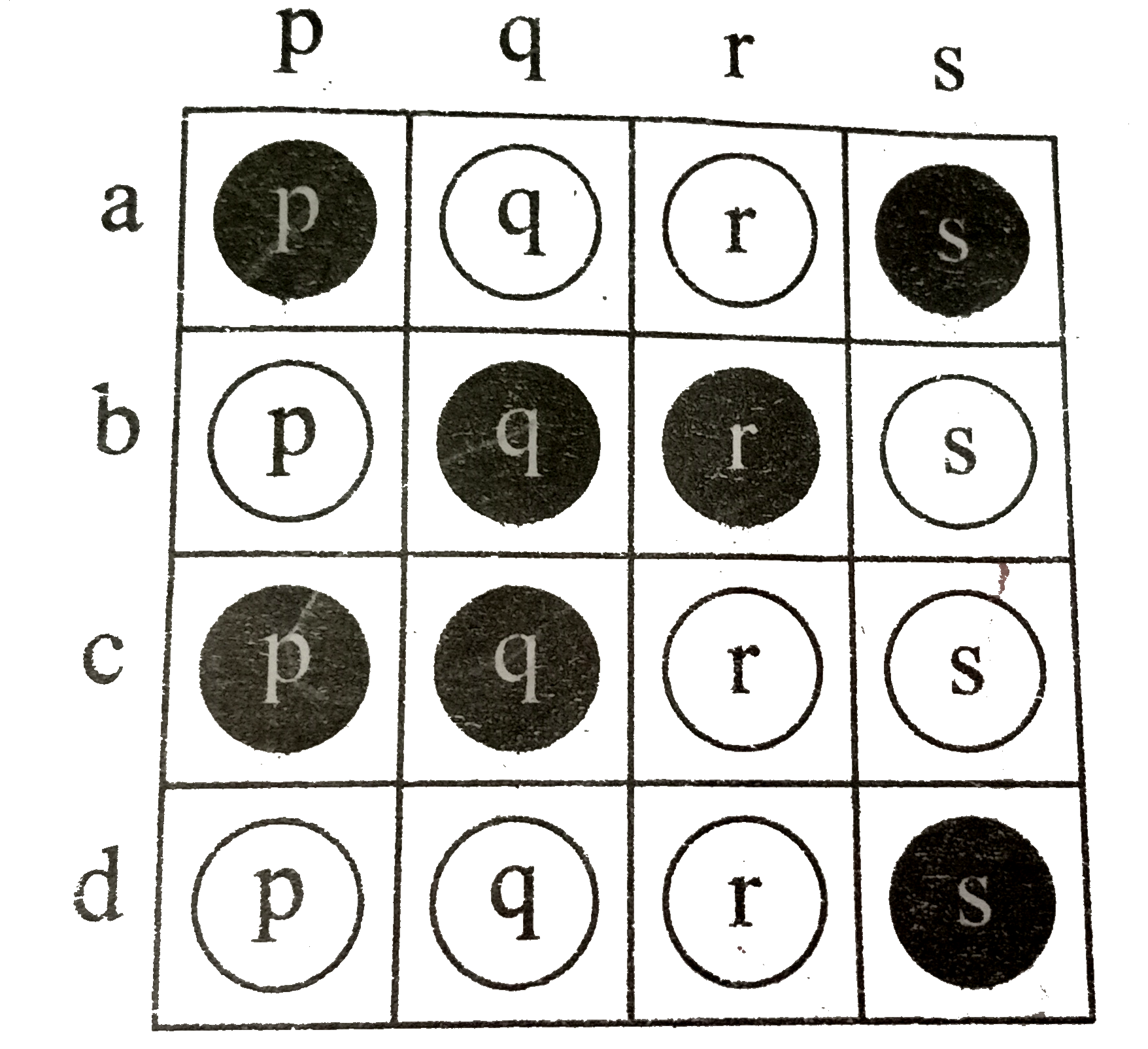
Q. Match the column-I with Column-II
 .
.
View Solution
Knowledge Check
Match the following :
List-I List-II
(P) N2(g)+3H2(g)→2NH3(g) (1) Increase in volume favours forward reaction
( Q ) 2NO(g)→N2(g)+O2(g) ( 2) Increase in pressure accelerate the forward reaction
( R ) CaCO3(s)→CaO(s)+CO2(g) (3) Kp=Ptotal
( S) PCl5(g)→PCl3_(g)+Cl2(g) (4) At constant volume introduction of inert gas, has no effect.
Codes :APQRS2431BPQRS2314CPQRS3142DPQRS4312Consider the reactions
(i)PCl5(g)⇔PCl3(g)+Cl2(g)
(ii)N2O4(g)⇔2NO2(g)
The addition of an inert gas at constant volumeAwill increase the dissociation of PCl5 as well N2O4Bwill reduce the dissociation of PCl5 as well as N2O4Cwill increase the dissociation of PCl5 and step up the formation of NO2Dwill not disturb the equilibrium of the reactions.The equilibrium constant for the given reaction,
CaCO3(g)→CaOs+CO2(g) is given by :AKc=[CaO]⋅[CO2][CaCo3]BKc=[CaO][CaCO3]CKc=[CO2]DKc=[CaO][CO2]
For CaCO3(S)⇔CaO(s)+CO2(g),ΔH = + Q at equilibrium. The addition of more CaCO3(s) causes?
View SolutionMatch the pollution(s) in column I with the effect(s) in column II.

View SolutionMatch the pollution(s) in column I with the effect(s) in column II.

View SolutionFor the reaction H2(g)+I2(g)⇔2HI(g), the equilibrium can be shifted in favour of product by
View SolutionFor the reaction H2(g)+I2(g)⇔2HI(g), the equilibrium can be shifted in favour of product by
View Solution

