Which will undergo fastest SN2 substitution reaction when treated with NaOH ?
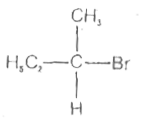
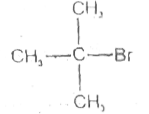
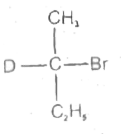
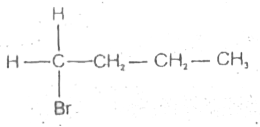
The correct Answer is:D
To determine which alkyl halide will undergo the fastest SN2 substitution reaction when treated with NaOH, we need to consider the structure of the alkyl halides and the concept of steric hindrance. Here’s a step-by-step solution:
Step 1: Understand the SN2 Mechanism
The SN2 (Substitution Nucleophilic Bimolecular) reaction involves a nucleophile attacking the carbon atom that is bonded to the leaving group (the halide). The nucleophile attacks from the opposite side of the leaving group, leading to an inversion of configuration.
Hint: Remember that SN2 reactions are favored by less steric hindrance around the carbon atom being attacked.
Step 2: Identify the Degree of Alkyl Halides
Alkyl halides can be classified based on the degree of the carbon atom attached to the halide:
- 1° (Primary): The carbon is attached to one other carbon.
- 2° (Secondary): The carbon is attached to two other carbons.
- 3° (Tertiary): The carbon is attached to three other carbons.
Hint: The degree of the alkyl halide affects the steric hindrance experienced by the nucleophile.
Step 3: Analyze Steric Hindrance
In SN2 reactions, steric hindrance plays a crucial role. The more bulky groups attached to the carbon, the slower the reaction will be due to increased steric hindrance.
- 1° alkyl halides have the least steric hindrance and will react the fastest.
- 2° alkyl halides have moderate steric hindrance and will react slower than 1°.
- 3° alkyl halides have the most steric hindrance and will not undergo SN2 reactions efficiently.
Hint: Consider how many carbon groups are attached to the carbon bearing the halide.
Step 4: Compare the Given Alkyl Halides
Assuming we have a set of alkyl halides to compare, identify which ones are 1°, 2°, or 3°. The one that is 1° will undergo the fastest SN2 reaction.
Hint: Look for the structure with the least number of alkyl groups attached to the carbon with the halide.
Step 5: Conclusion
Based on the analysis, the alkyl halide that is classified as 1° will undergo the fastest SN2 substitution reaction when treated with NaOH.
Final Answer: The fastest SN2 substitution reaction will occur with the 1° alkyl halide.
The SN2 (Substitution Nucleophilic Bimolecular) reaction involves a nucleophile attacking the carbon atom that is bonded to the leaving group (the halide). The nucleophile attacks from the opposite side of the leaving group, leading to an inversion of configuration.
Alkyl halides can be classified based on the degree of the carbon atom attached to the halide:
- 1° (Primary): The carbon is attached to one other carbon.
- 2° (Secondary): The carbon is attached to two other carbons.
- 3° (Tertiary): The carbon is attached to three other carbons.
In SN2 reactions, steric hindrance plays a crucial role. The more bulky groups attached to the carbon, the slower the reaction will be due to increased steric hindrance.
- 1° alkyl halides have the least steric hindrance and will react the fastest.
- 2° alkyl halides have moderate steric hindrance and will react slower than 1°.
- 3° alkyl halides have the most steric hindrance and will not undergo SN2 reactions efficiently.
Assuming we have a set of alkyl halides to compare, identify which ones are 1°, 2°, or 3°. The one that is 1° will undergo the fastest SN2 reaction.
Based on the analysis, the alkyl halide that is classified as 1° will undergo the fastest SN2 substitution reaction when treated with NaOH.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES Book:AAKASH INSTITUTEChapter:HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES Exercise:ASSIGNMENT SECTION -D
Explore 15 Videos
- HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES Book:AAKASH INSTITUTEChapter:HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES Exercise:ASSIGNMENT SECTION - B
Explore 25 Videos
- GENERAL PRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES OF ISOLATION OF ELEMENTSBook:AAKASH INSTITUTEChapter:GENERAL PRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES OF ISOLATION OF ELEMENTSExercise:Try Yourself
Explore 33 Videos
- HYDROCARBONSBook:AAKASH INSTITUTEChapter:HYDROCARBONSExercise:Assignment(Section - D) (Assertion -Reason Type Question)
Explore 24 Videos
Similar Questions
In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is following by a statement of reason (R )
A : when chloroform is obtained from bleaching powder and ethanol then chlorine acts as oxidising agent only.
R : It oxidises ethanol into acetic acid.
View SolutionWhich of the following is least reactive towards SN2 mechanism ?
View SolutionMatch the following from column I to column II
Column IColumn IIMalachiteFeSphaleriteAgHorn silverZnChromineCu
View SolutionA : CH≡C−CH2−CH=CH2 adds up HBr to give CH≡C−CH2−C∣BrH−CH3 while CH=C∣Br−CH=CH2 adds up HBr to give CH2=C∣Br−CH=CH2
R : Double bond is always more reactive than triple bond towards electrophillic addition reaction.
View SolutionThe compound which undergoes fastest reaction with aq. NaOH solution is :
View SolutionWhich of the following alkyl halides undergoes the fastest S_(N^(1)) reaction ?
View SolutionWhich will undergo SN2 reaction fastest amont the following halogen compounds
View SolutionWhich will undergo S_(N^(2)) reaction faster
View SolutionSN2 reaction will be fastest in:
View SolutionSN2 reaction will be fastest in:
View SolutionS_(N^(2)) reaction will be fastest in :
View SolutionWhich will undergo fastest SN2 substitution reaction when treated with NaOH ?
View SolutionSN1 reaction is fastest in
View SolutionWhich of the following alkyl halides undergoes the fastest S_(N^(1)) reaction ?
View SolutionWhich will undergo fastest SN2 substitution reaction when treated with NaOH ?
View Solution
