If ax+bsec(tan−1x)=canday+bsec(tan−ly)=c, then x+y1−xy is equal to
2aba2−b2
c2−b2a2−b2
c2−b2a2+b2
none of these
The correct Answer is:B
Given ax+b(sec(tan−1x))=canday+b(sec(tan−1y))=c
Let tan−1x=αandtan−1y=β, then the given relations are atanα+bsecα=candatanβ+bsecβ=c
From these two releations, we can conclude that equation
atanθ+bsecθ=c has roots αandβ
atanθandbsecθ=c
or bsecθ=c−atanθ
or b2sec2θ=c2−2actanθ+a2tan2θ
or b2+b2tan2θ=c2−2actanθ+a2tan2θ
or (a2−b2)tan2θ−2actanθ+c2−b2=0
Therefore, sum of the roots, tanα+β=xy=c2−b2a2−b2andx+y1−xy=2aca2−b21−c2−b2a2−b2=2aca2−c2
Topper's Solved these Questions
- INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONSBOOK - CENGAGECHAPTER - INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONSEXERCISE - Exercise (Matrix)
5 Videos
- INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONSBOOK - CENGAGECHAPTER - INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONSEXERCISE - Exercise (Numerical)
18 Videos
- INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONSBOOK - CENGAGECHAPTER - INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONSEXERCISE - Exercise (Multiple)
24 Videos
- INTRODUCTION TO VECTORS BOOK - CENGAGECHAPTER - INTRODUCTION TO VECTORS EXERCISE - JEE Previous Year
20 Videos
- JEE 2019BOOK - CENGAGECHAPTER - JEE 2019EXERCISE - Chapter 10
9 Videos
Similar Questions
Match the following List I to List II
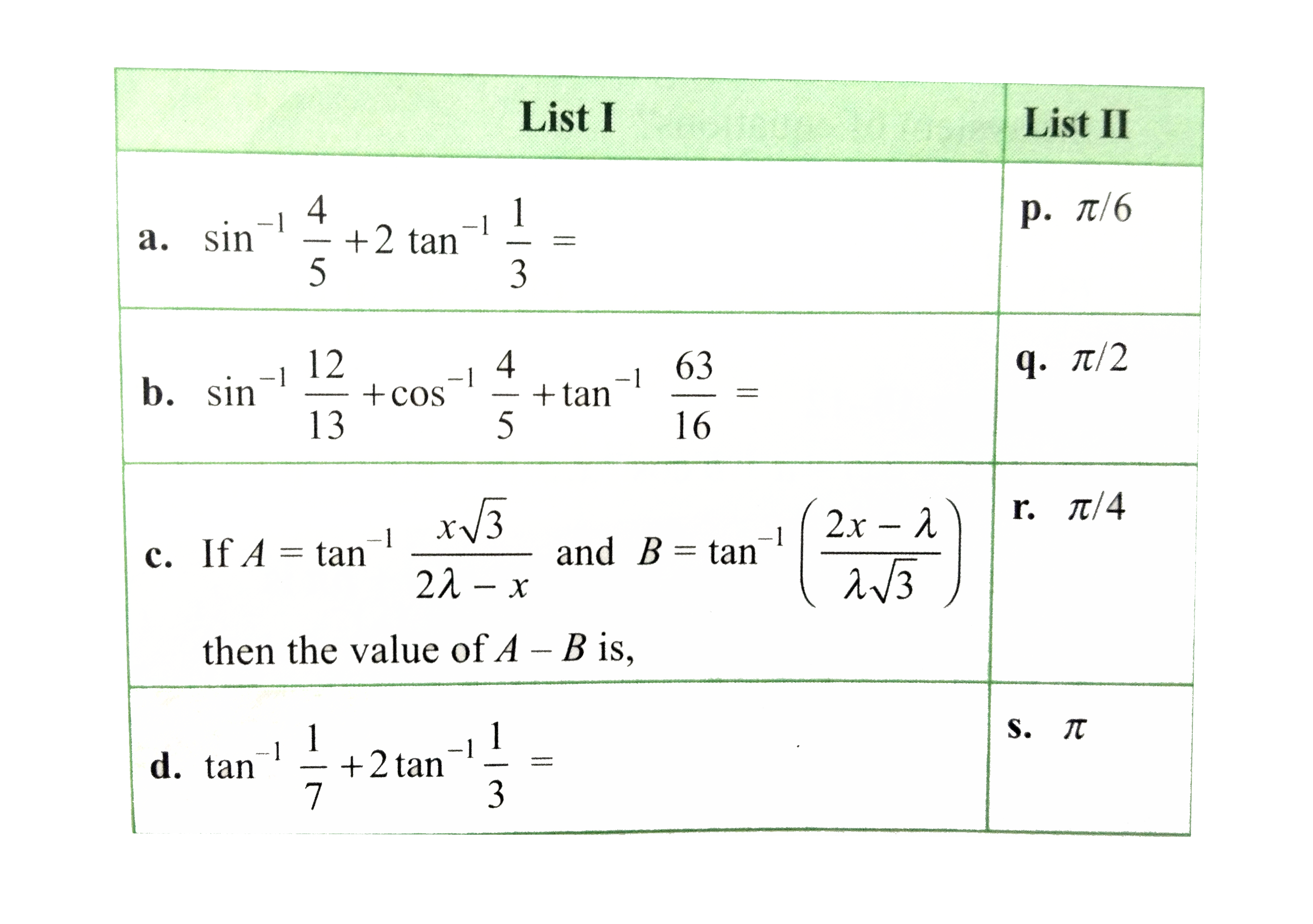
View SolutionThe solution set of inequality (cot−1x)(tan−1x)+(2−π2),cot−1x−3tan−1x−3(2−π2)>0 is (a,b), then the value of cot−1a+cot−1b is____
View SolutionIf α,β(α<β) are the roots of the equation 6x2+11x+3=0, then which of the following are real ?
View SolutionFind the all the values of lamda such that (x,y,z)!=(0,0,0)andx(hati+hatj+3hatk)+y(3hati-3hatj+hatk)+z(-4hati+5hatj)=lamda(xhati+yhatj+zhatk)
View SolutionIf y = y(x) is the solution of the differential equation, xdydx+2y=x2 satisfying y(1) = 1, then y(12) is equal to
View SolutionIf ax+b sec(tan^(-1)x)=c and ay+b sec(tan^(-l)y)=c then (x+y)/(1-xy) is equal to
View Solutionयदि ax+b{sec(tan−1x)}=c तथा ay+b{sec(tan−1y)}=c, तब
xy का मान होगा
View Solutionयदि ax+b{sec(tan−1x)}=c तथा ay+b{sec(tan−1y)}=c, तब
x + y का मान होगा
View Solutionयदि ax+b{sec(tan−1x)}=c तथा ay+b{sec(tan−1y)}=c, तब
x+y1−xy का मान होगा
View Solutionयदि ax+b{sec(tan−1x)}=c तथा ay+b{sec(tan−1y)}=c, तब
1+xyx+y का मान होगा
View Solutionax+b(sec(tan−1x))=canday+b(sec(tan−1y))=c
The value of x+y1−xy is
View SolutionIf ax+bsec(tan−1x)=canday+bsec(tan−ly)=c, then x+y1−xy is equal to
View SolutionIf ax+bsec(tan−1x)=canday+bsec(tan−ly)=c, then x+y1−xy is equal to
View SolutionIf ax+bsec(tan−1x)=canday+bsec(tan−ly)=c, then x+y1−xy is equal to
View Solutionax+b(sec(tan−1x))=canday+b(sec(tan−1y))=c
The value of xy is
View Solutionax+b(sec(tan−1x))=canday+b(sec(tan−1y))=c
The value of x + y is
View Solution

