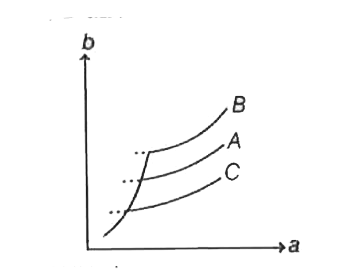
The vapour pressure of a solution (b) as a function of temperature (a) is plotted as a graph for two solutions of same molar concentration along with water as shown below. A, B and C are respectively.
 Solution in Telugu
Solution in Telugu
H2NCONH2,H2O,NaCl
H2O,H2NCONH2,NaCl
NaCl,H2O,H2NCONH2
NaCl,H2NCONH2,H2O
The correct Answer is:A
The vapour pressure of a solution (b) as a function of temperature (a) is plotted as a graph for two solutions of same molar concentration along with water.
Here, A is 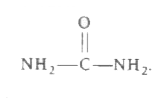
B is H2O.
C is NaCl.
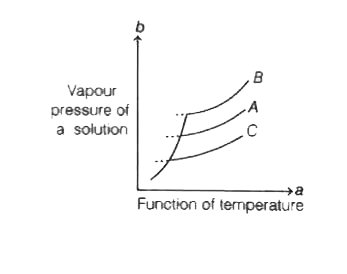 When number of moles of solute decreases, then vapour pressure of solution increses.
When number of moles of solute decreases, then vapour pressure of solution increses.
So, H2NCONH2 does not associate or dissociate.
H2O forms hydrogen bonding and associates vapour pressure increases. It dissociates to very small extent.
NaCl dissociates, (as it is a strong electrolyte there number of moles increases therefore vapour pressure decreases).
Similar Questions
Two liquids A and B form an ideal solution. At 300 K, the vapour pressure of a solution containing 1 mole of A and 3 moles of B is 550 mm of Hg. At the same temperature, if one mole of B is added to this solution, the vapour pressure of the solution increases by 10 mm of Hg. Determine the vapour pressure of A and B in their pure states
View SolutionThe vapour pressure of a solution of 5g of a non-electrolyte in 100g water at a particular temperature is 2950Pa and that of pure water at the same temperature is 3000Pa. The molar mass of the solute is
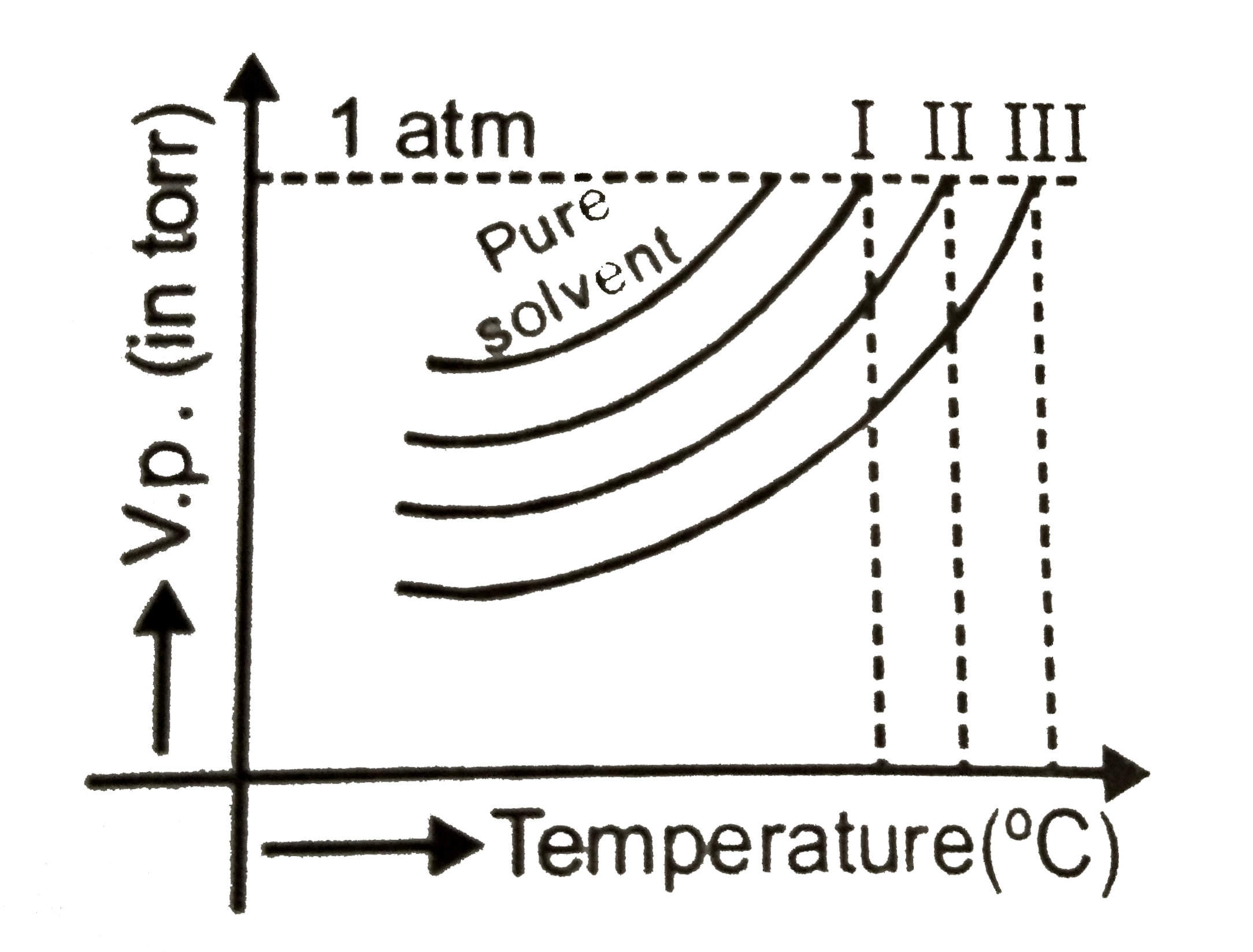
View SolutionThe vapour pressure curves of the same solute in the same solvent are shown below. The curves are parallel to each other andnot intersectt. The concentrations of solutions are in order of :
View SolutionTwo liquids A and B form ideal solution. At 300K, the vapour pressure of a solution containing 1 mole of A and 3 moles of B is 550mm of Hg. At the same temperature, if one more mole of B is added to this solution, the vapour pressure of the solution increases by 10mm of Hg. Determine the vapour pressure of a and B in their pure states.
View SolutionAt 27∘C.the vapour pressure of an ideal solution containing 1 mole of A and 1 mole and B is 500mm of Hg. At the same temperature, if 2 mol of B is added to this solution the vapour pressure of solution increases by 50mm of Hg. The vapour pressure of A and B in their pure states is respectively.
View SolutionTwo liquids A and B form an ideal solution. At 300 k, the vapour pressure of a solution containing 1 mole of A and 3 moles of B is 550 mm of Hg. At the same temperature, if one mole of B is added to this solution, the vapour pressure of the solution increases by 10 mm of Hg. Determine the vapour pressure of A and B in their pure states.
View SolutionIf same volume solution of different solute is used then what is order of (a) vapour pressure (b) moles solute (c) molar mass of solute.
View Solution
