A smooth uniform rod of length L and mass M has two identical beads of negligible sixe , each has two identical beads of negligible size , each of mass m , which can slide freely along the rod . Intially the two beads are at athe centre of the rod and the system is rotating with angular velocity ω0 about its axis perpendicular to the rod passing trough its mid point ( see figure ) . There are no through its mid point ( see figure ) . There are no external forces . When the beads reach the ends of the rod , the angular velocity of the system is

Mω0M+3m
Mω0M+6m
(M+6m)ω0M
ω0
The correct Answer is:B
L=Icmω+m(→c×→vcm)
=12Mr2ωˆk+m(4Rˆi+3Rˆj)×(ωRˆi)
=−52MR2ωˆk
Topper's Solved these Questions
- SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION BOOK - NARAYNACHAPTER - SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION EXERCISE - EXERCISE - II (H.W)
60 Videos
- SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION BOOK - NARAYNACHAPTER - SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION EXERCISE - EXERCISE - III
43 Videos
- SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION BOOK - NARAYNACHAPTER - SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION EXERCISE - EXERCISE - I(H.W)
63 Videos
- SYSTEM OF PARTICLESBOOK - NARAYNACHAPTER - SYSTEM OF PARTICLESEXERCISE - Level-VI
78 Videos
- THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTERBOOK - NARAYNACHAPTER - THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTEREXERCISE - LEVEL - II (H.W.)
19 Videos
Similar Questions
Figure shows composite system of two uniform rods of length as indicated . Then the coordinates of the centre of mass of the system of rods are

View SolutionThe moment of inertia of a uniform circular disc of radius R and mass M about an axis passing from the edge of the disc and normal to the disc is.
View SolutionThe distance of centre of mass from 'O ' is

View SolutionThe point P of a string is pulled up with an acceleration g. Then the acceleration of the hanging disc (w.r.t ground) over which the string is wrapped, is
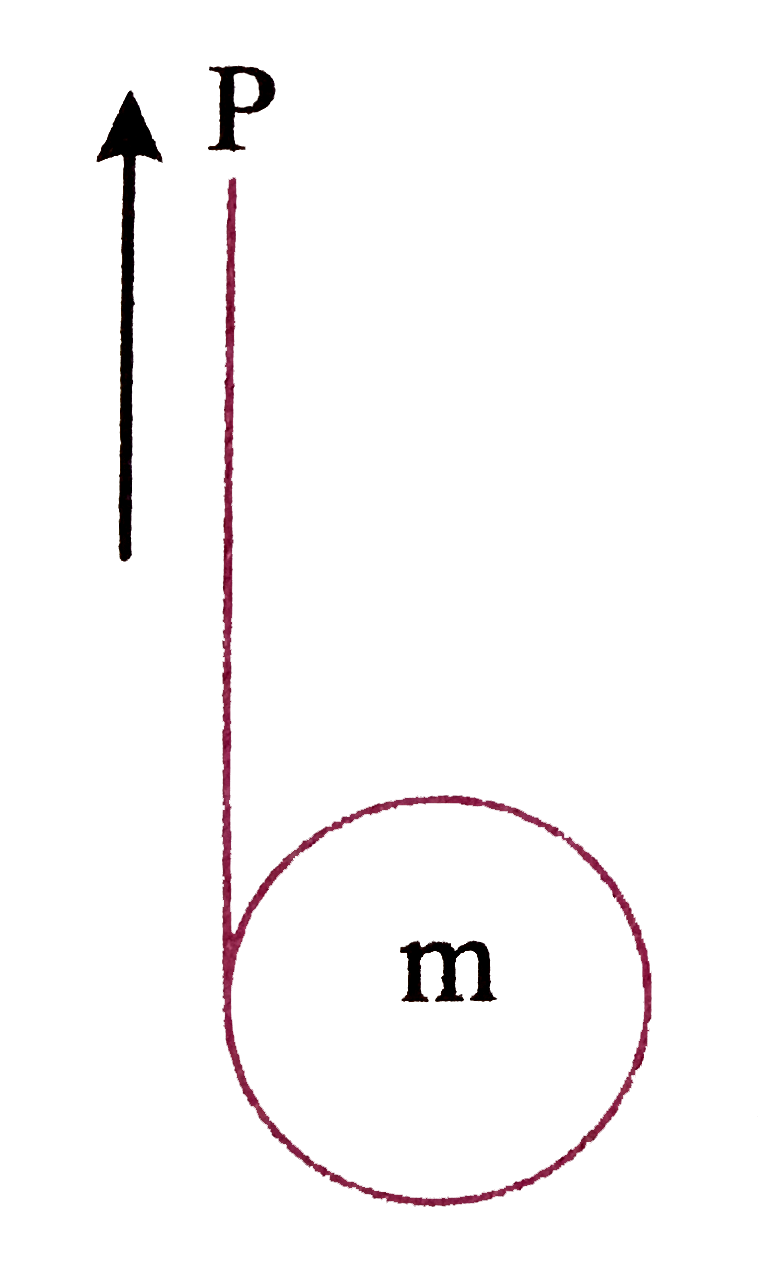
View SolutionThe ratio of coefficients of apparent expansions of the same liquid in two different vessels is 1:2. If α1 and α2 are the coefficient of linear expansions then coefficient of real expansion of the liquid is
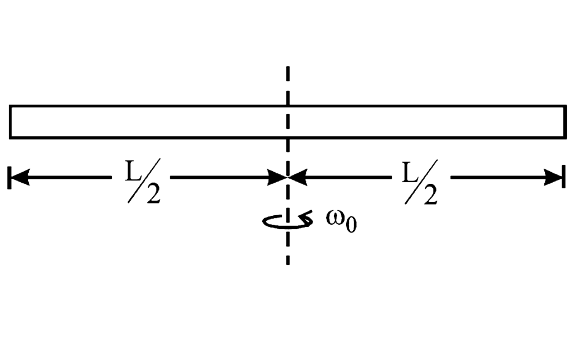
View SolutionA smooth uniform rod of length L and mass M has two identical beads of negligible size each of mass m which can slide freely along the rod. Initially the two beada are at the centre of the rod and the system is rotating with an angular velocity ω0 about an axis perpenducular to the rod and passing through the midpoint of the rod. There are no external forces. When the beads reach the ends of the rod, the angular velocity of the system is ......
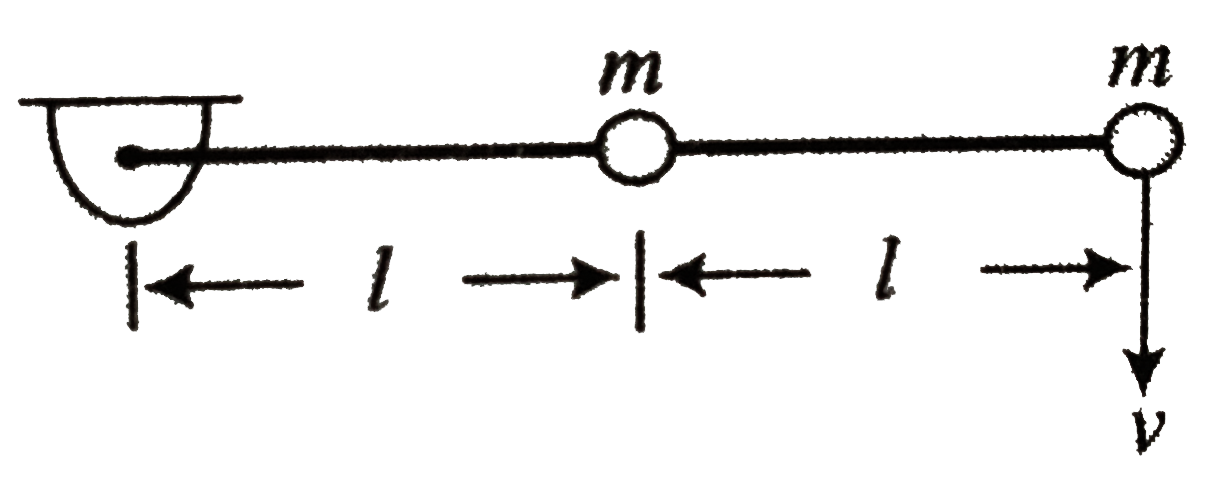
View SolutionTwo beads each of mass m are welded at the ends of two light rigid rods each of length l. if the pivots are smooth, find the ratio of translational and rotational kinetic energy of system.
View SolutionTwo beads of mass 2m and m , connected by a rod of length l and of negligible mass are free to move in a smooth vertical circular wire frame of radius l as shown. Initially the system is held in horizontal position ( Refer figure ) If the rod is replaced by a massless string of length l and the system is released when the string is horizontal then :
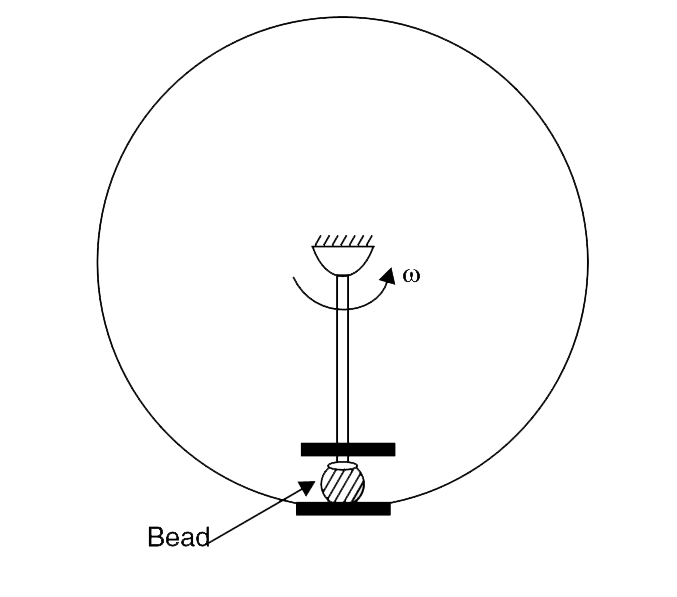
View SolutionA rigid mass less rod of length L is rotating in a vertical plane about a horizontal axis passing through one of its ends. At the other end of the rod there is a mass less metal plate welded to the rod. This plate supports a heavy small bead that can slide on the rod without friction. Just above the bead there is another identical metal plate welded to the rod. The bead remains confined between the plates. The gap between the plates is negligible compared to L. The angular speed of the rod when the bead is at lowest position of the circle is ω=2√gL. How many times a clink of the bead hitting a metal plate is heard during one full rotation of the rod ?
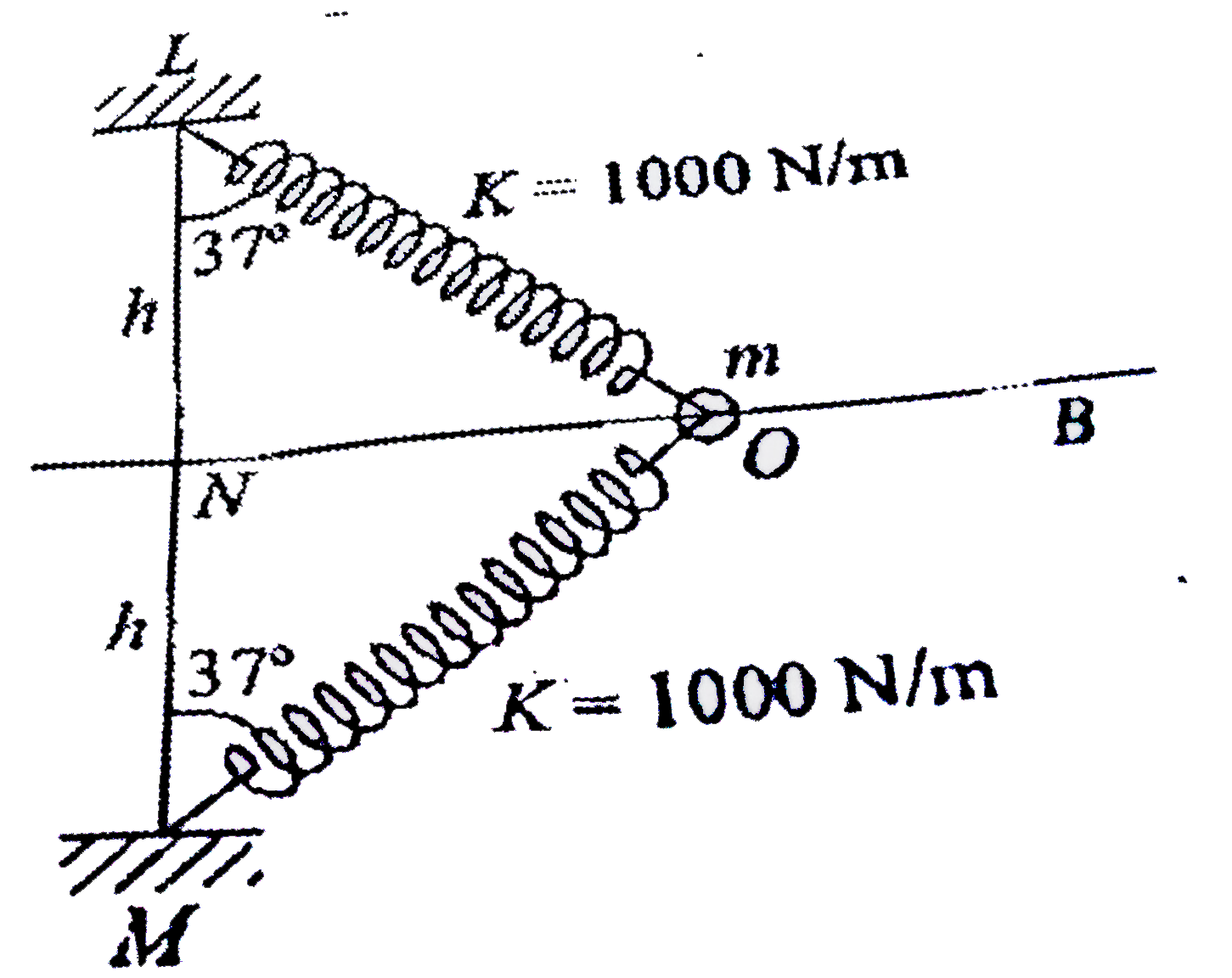
View SolutionA bead of mass 5 kg is free to slide on the horizontal rod AB. They are connected to two identical springs of natural length h ms. As shown. If initially bead was at O & M is vertically below L then, velocity of bead at point N will be :
View SolutionA thin smooth rod of length L and mass M is rotating freely with angular speed omega_(0) about an axis perpendicular to the rod and passing through its center. Two beads of mass m and negligible size are at the center of the rod initially. The beads are free to slide along the rod. The angular speed of the system, when the beads reach the opposite ends of the rod, will be
View Solutionद्रव्यमान M तथा लम्बाई L की एक पतली छड़ कोणीय चाल ω0 से छड़ के लम्बवत तथा उसके केंद्र से जाने वाली अक्ष के परितः स्वतंत्र रूप से घूम रही है। द्रव्यमान m तथा नगण्य आकार की दो मणिकाये आरम्भ में छड़ के केंद्र पर है। यह मणिकाये जब छड़ के विपरीत सिरों पर पहुँचती है, तो इस विन्यास की कोणीय चाल होगी
View SolutionA long horizontal rod has a bead which can slide along its length, and initially placed at a distance L from one end A of the rod. The rod is set in angular motion about A with constant angular acceleration a. If the coefficient of friction between the rod and the bead is u, and gravity is neglected, then the time after which the bead starts slipping is :
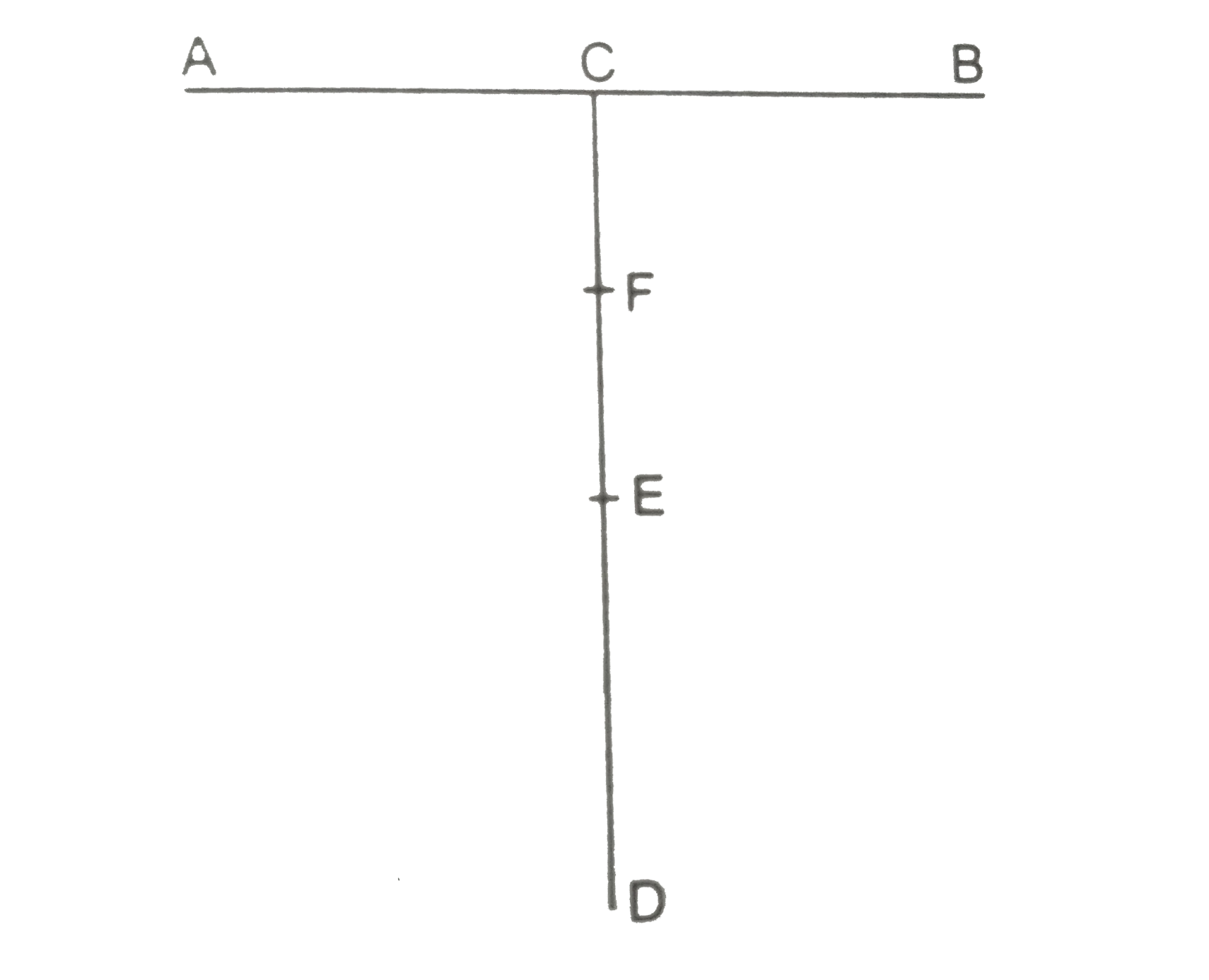
View SolutionTwo identical uniform rods AB and CD, each of length L are jointed to form a T-shaped frame as shown in figure. Locate the centre of mass of the frame. The centre of mass of a uniform rod is at the middle point of the rod.
View SolutionA thin smooth rod of length L and mass M is rotating freely with angular speed ω0 about an axis perpendicular ot the rod and passing through its centre. Two beads of mass m and negligible sizer are at the center of the rod intially. The beads are free to slide along the rod. the angular speed of the system, when the beads reach the oppsite ends of rod, will be :
View SolutionTwo identical uniform rods AB and CD, each of length L are jointed to form an inverted T-shaped frame as shown in figure. Locate the centre of mass of the frame. The centre of mass of a uniform rod is at the middle point of the rod.
View Solution

