Reagent used in ELISA test is
Step-by-Step Solution:
1. Understanding ELISA:
- ELISA stands for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. It is a laboratory technique used to detect and quantify proteins, such as antibodies, in a sample, typically blood.
2. Role of Antibodies:
- Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system in response to foreign substances (antigens). In the context of ELISA, the test is designed to detect these antibodies.
3. Key Reagent in ELISA:
- One of the primary reagents used in the ELISA test is Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP).
4. Function of HRP:
- HRP is an enzyme that acts as a hydrogen donor. It catalyzes reactions that convert colorless substrates into colored products, allowing for the visual detection of the antibodies.
5. Application of ELISA:
- The ELISA test is widely used in clinical laboratories to detect disease infections by measuring the presence of specific antibodies in the blood.
Summary of Reagents Used in ELISA:
- Main Reagent: Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP)
- Function: Converts colorless substrates to colored products for detection.
---
- ELISA stands for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. It is a laboratory technique used to detect and quantify proteins, such as antibodies, in a sample, typically blood.
- Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system in response to foreign substances (antigens). In the context of ELISA, the test is designed to detect these antibodies.
- One of the primary reagents used in the ELISA test is Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP).
- HRP is an enzyme that acts as a hydrogen donor. It catalyzes reactions that convert colorless substrates into colored products, allowing for the visual detection of the antibodies.
- The ELISA test is widely used in clinical laboratories to detect disease infections by measuring the presence of specific antibodies in the blood.
- Main Reagent: Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP)
- Function: Converts colorless substrates to colored products for detection.
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
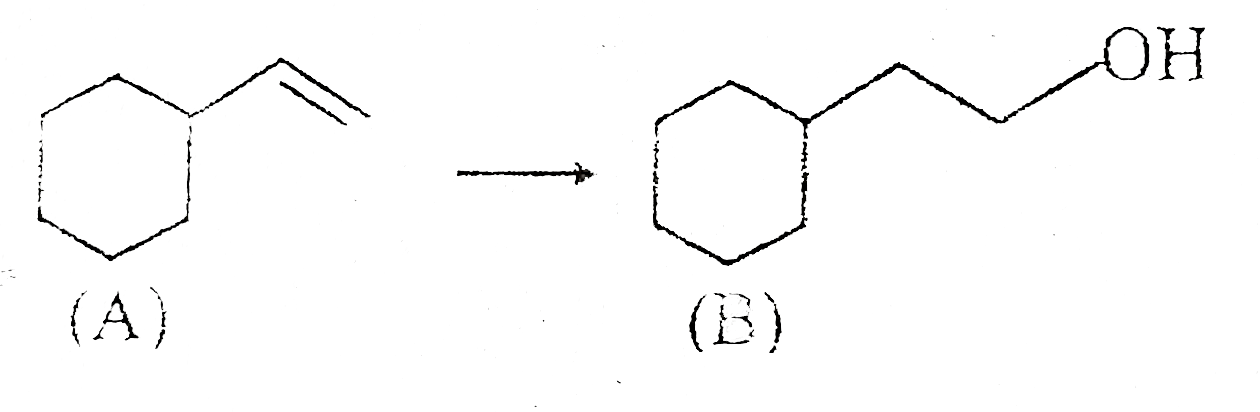
Reagent used is :AHg(OAC)2/NaBH4.NaOHBBH3.THF/H2O2.NaOHCLiAIH4/H2ODAll of theseELISA is
AEnzyme linked immunosorbent assayBEnzyme linked ionsorbent assayCEnzyme linked inductive assayDNone of the aboveWhich is incorrect match with respect to the reagent used for lab test ?
ACarbohydrates " " → " " α-Napthol (Molish reagent)BNitro ethane " " → " " Zn,NH4Cl and AgNO3 (Muliken Barker test)CPhenol " " → " " Anhydrous ZnCl2+Conc.HCl (Lucas Reagent)DBenzoic acid " " → " " NaHCO3
A person's immune system is suppressed, and ELISA test, gives positive indication of a pathogen.
Name the disease the patient is suffering from.
View SolutionA person's immune system is suppressed, and ELISA test, gives positive indication of a pathogen.
What is the causative organism?
View SolutionNessler's reagent is used in testing for ammonia, with whith it forms a brown coloration or precipitate. The count of iodine atoms in one unit is
View SolutionWhat is the basis of detection using ELISA test?
View SolutionWhich is incorrect match with respect to the reagent used for lab test ?
View Solution
