Explain the mechanism of nucleophilic addition reactions of aldehyde and ketone?
Text Solution
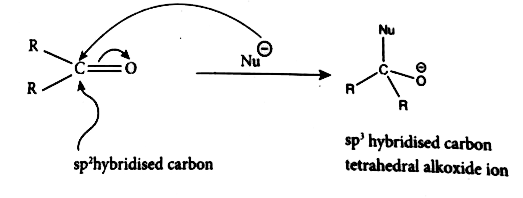
The carbonyl carbon carries a small degree of positive charge.
(ii) Nucleophile such as CN− can attack the carbonyl carbon and uses its bond pair to form a new carbon – nucleophile . σ . bond, at the same time two electrons from the carbon – oxygen double bond move to the most electronegative oxygen atom.
(iii) This results in the formation of an alkoxide ion. In this process, the hybridisation of carbon changes from spa to sp3
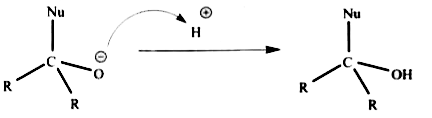
The tetrahedral intermediate can be protonated by water or an acid to form an alcohol..
|
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
The shape of the intermediate formed In nucleophilic addilion reaction of aldehydes and ketones is
ATrigonal planarBTetrahedralCTrigonal bipyramidalDBent
Reactions of aldehyde and ketones
View SolutionReactions of aldehyde and ketones-1
View SolutionNucleophilic addition reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones- Part 2
View SolutionNucleophilic addition reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones- Part 1
View SolutionDiscuss the mechanism of nucleophilic addition reactions to aldehydes/ketones taking addition of HCN an an example.
View SolutionQuestion based on Nucleophilic addition reactions of aldehydes and ketones
View SolutionThe shape of the intermediate formed In nucleophilic addilion reaction of aldehydes and ketones is
View Solution

