Two identical very small metal spheres, A and B, that are electrically neutral are fixed at a distance R On insulating handles. A third identical sphere C carrying charge Q is also connected to an insulating handle. C ia first brought into contact with A and B and then moved away from these two spheres. It is found that A and B apply F1 force on each other.
Now C with the remaining charge is again brought into contact with A and then moved away from A and B. It is found that A and B apply F2 force on each other. Now C is further brought into contact with B and then moved away from A and B. It is found that A and B apply F3 force on each other Finally B is moved closer to A at a distance r, such that the force between them again becomes F1.
The magnitude of r/R is
√1516
√1615
√2012
√1220
The correct Answer is:A
Now the distance between A andB is changed to r so that new force between A and B becomes equal to F1. Hence we can write the following equation for the new distance between the charges.
1512814πε0Q2r2=18×14πε0Q2R2⇒15128r2=18R2⇒r=R√1516
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS BOOK - MODERN PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS EXERCISE - COMPETITION FILE ( Objective Question (Assertion Reason ) )
15 Videos
- ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS BOOK - MODERN PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS EXERCISE - COMPETITION FILE ( Objective Question (Matching ) )
1 Video
- ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS BOOK - MODERN PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS EXERCISE - COMPETITION FILE ( Objective Question (C.MCQ))
19 Videos
- DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER BOOK - MODERN PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER EXERCISE - CHAPTER PRACTICE TEST
15 Videos
- ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTIONBOOK - MODERN PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTIONEXERCISE - CHAPTER PRACTICE TEST FOR BOARD EXAMINATION
14 Videos
Similar Questions
Assertion:A pair of closely spaced electron and proton behaves like an electrically neutral particle system and do not apply electric force on isolated proton or electron.
Reason: Two types of charges exist in nature, which are opposite to'each other in polarity. These two types of charges have a tendency to cancel the electrical effect of each other. Benjamin Franklin suggested the use of positive and negative signs to represent these two types of charges. We can calculate the net charge of any system by evaluating the algebraic sum of individual charges.
View SolutionMatch the following

View SolutionA dipole of Dipole moment →p=p0√2(ˆi+ˆj). Is placed at origin. Now a uniform external electrical filed at magnitude E0 is applied along direction of dipole. Two points A and B are lying on a equipotential surface of radius R centered at origin. A is along axial position of dipole and B is along equatorial position. There correct option are :
_PHY_E01_006_Q01.png)
View SolutionDefine the term 'stopping potential' in relation to photoelectric effect.
View SolutionWill any emf be induced between the ends of a vertical magnetic pole falling through the plane of magnetic meridian?
View SolutionTwo equally charged, indentical metal spheres A and B repel each other with a force F" . The spheres are kept fixed with a distance r between them. A third identical, but uncharged sphere C is brought in contact with A and The magnitude of the net electric force on C is
View SolutionThree metallic spheres A, B and C having radii are in ratio1:2:3. Charge on sphere A is 6 μC and sphere B and C are electrically neutral. If sphere A first contact with sphere B and then from C and ultimately contact from sphere B, then now charge on spheres A, B and C respectively will be-
View SolutionThere are two charged identical metal spheres A and B repel each other with a force 3×10−5N. Another identical uncharged sphere C is touched with A and then placed at the mid-point between A and B. Net force on C is
View SolutionTwo insulated charged copper spheres A and B have their centres separated by a distance of 0.5 m. The charge on each spheres is 6.5×10−7C. A third sphere c of identifical shape and size is brought in contanct with A and them brought in contact with B and finally removed. What is the new force between A and B?
View SolutionTwo identical very small metal spheres, A and B, that are electrically neutral are fixed at a distance R On insulating handles. A third identical sphere C carrying charge Q is also connected to an insulating handle. C ia first brought into contact with A and B and then moved away from these two spheres. It is found that A and B apply F1 force on each other.
Now C with the remaining charge is again brought into contact with A and then moved away from A and B. It is found that A and B apply F2 force on each other. Now C is further brought into contact with B and then moved away from A and B. It is found that A and B apply F3 force on each other Finally B is moved closer to A at a distance r, such that the force between them again becomes F1.
The magnitude of F1/F2 is
View SolutionTwo identical very small metal spheres, A and B, that are electrically neutral are fixed at a distance R On insulating handles. A third identical sphere C carrying charge Q is also connected to an insulating handle. C ia first brought into contact with A and B and then moved away from these two spheres. It is found that A and B apply F1 force on each other.
Now C with the remaining charge is again brought into contact with A and then moved away from A and B. It is found that A and B apply F2 force on each other. Now C is further brought into contact with B and then moved away from A and B. It is found that A and B apply F3 force on each other Finally B is moved closer to A at a distance r, such that the force between them again becomes F1.
The magnitude of F2/F3 is
View SolutionThere are two small identical metallic spheres A and B each carrying same charge. These two spheres are found to repel each other with a force P. A third identical neutral metal sphere C is first brought in contact with A and then B. The sphere C is taken away from A and B. The magnitude of electric force now is found to be 3F/x. What is x?

View SolutionIn Frame 1, two identical conducting spheres, A and B, carry equal amounts of excess charge that have the same sign. The spheres are separated by a distance d, and sphere A exerts an electrostatic force on sphere B that has a magnitude F. A third sphere, C, Which is handled only by an insulating rod, is introduced in Frame 2. Sphere C is identical to A and B except that it initially uncharged. Sphere C is touched first to sphere A, in Frame 2, and then to sphere B, in Frame 3, and is finally removed in Frame 4.
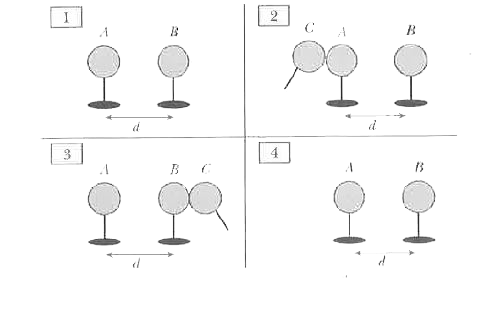
Determine the magnitude of the electrostatic force that sphere A exerts on sphere B in Frame 4.
View SolutionTwo identical metallic sphere's A and B having charges +4Qand−10Q are kept a certain distance apart. A third identical uncharged sphere C is first placed in contact with sphere A and then with sphere B. Spheres A and B are then brought in contact and then separated. Find the charges on the spheres A and B.
View SolutionThere are two identical spheres A and B. Now charge Q is established on each sphere. There is a third identical neutral sphere C. Now sphere C is first brought in contact with A and separated then brought in contact with B and separated. After this what will be charge on C ?
View Solution

