There is a hemisphere whose radius of curvature is r and inner side of it is made completely reflecting . A point source of light of power P is kept at the centre of curvature of hemisphere . Calculate the force exerted by the light falling on inner side of hemispherical surface.
If P is power of point source , then intensity of light which means energy crossing per unit area per unit time can be written as P/4πr2 . Let us select a small are ΔA at angle θ with the vertical radius of hemisphere as shown in the following figure:
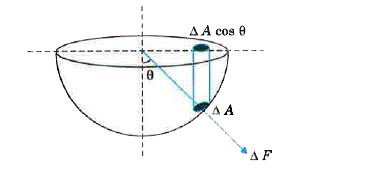
Amount of energy falling on this area will be PΔA4πr2
per unit time . Hence , amount of linear momentum imparted to the surface per unit time can be written as PΔA4πr2c . Since surface is completely reflecting and hence it will reflect back the light and hence rate of change of linear momentum will be double to this value , hence equal to 2PΔA4πr2c . From Newton.s second law , we known that rate of chane of linear momentum is equal to the force exerted , and hence force exerted by the light on the surface area ΔA selected can be written as follows :
ΔF=2PΔA4πr2c
We can see that horizontal component of this force ΔFsinθ will be balanced by the force on corresponding area selected on hemisphere due to symmetry , and hence contribution to the net force by this selected area will be ΔFcosθ and direction will be vertically downward as per figure . Net vertical downward force applied by the light on this hemisphere can be calculated by summig up forces on such small areas selected .
F=∑ΔFcosθ=∑2PΔAcosθ4πr2c
F=2P4πr2c∑ΔAcosθ ...(i)
In the above expression , we can see that ΔAcosθ is projected area of selected are ΔA as shown in figure .
We can understand that total projected area will be πr2 and hence force can be written as follows :
F=2P4πr2cπr2=P2c
Topper's Solved these Questions
- DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER Book:MODERN PUBLICATIONChapter:DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER Exercise:Revision Exercises (Very Short Answer Questions)
Explore 45 Videos
- DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER Book:MODERN PUBLICATIONChapter:DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER Exercise:Revision Exercises (Additional Questions)
Explore 8 Videos
- DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER Book:MODERN PUBLICATIONChapter:DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER Exercise:NCERT FILE (NCERT - Exemplar Problems - Subjective Questions (Short Answer Type Questions))
Explore 6 Videos
- CURRENT ELECTRICITYBook:MODERN PUBLICATIONChapter:CURRENT ELECTRICITYExercise:Chapter Practice Test
Explore 15 Videos
- ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS Book:MODERN PUBLICATIONChapter:ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS Exercise:Chapter Practice Test
Explore 15 Videos
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
A perfectly reflecting solid hemisphere of radius R is placed in the path of a parallel beam of light of large aperture. If the beam carrries an intensity l, find the force exerted by the beam on the hemisphere.
A2πR2lcBπR2lcC4πR2lcDNone of these
A point source of light is placed at the centre of curvature of a hemispherical surface. The radius of curvature is r and the inner surface is completely reflecting. Find the force on the hemisphere due to the light falling on its if the source emits a power W.
View SolutionA point source of light is placed at the centre of curvature of a hemispherical surface. The radius of curvature is r and the inner surface is completely reflecting. Find the force on the hemisphere due to the light falling on its if the source emits a power W.
View SolutionA hemisphere of radius R, made of glass of refractive index (3/2) is placed on 'the table. A point source of light is placed at a distance 2R from the centre, of hemisphere. If source is viewed diametrically opposite side of hemisphere. Find the position of image of source.

View SolutionThere is a parallel beam of light of larger aperture . Let I be the intensity of light . Perfectly reflecting sphere of radius r is kept in the path of this parallel beam . Find the force exerted by the light beam on sphere .
View SolutionA point source of light of constant power P is placed at centre of curvature of a concave mirror. If angle substented by aperature at centre of curvature is 120∘, calculate force an surface of mirror.
View SolutionThe heat of neutralization for a strong acid by a strong base is a constant
View SolutionA spherical concave mirror has aperture diameter d and radius of curvature R. A point source of light is placed at its centre of curvature. Source emits power W and the mirror surface is completely reflecting. Find force on the mirror due to light incident on it.

View Solution