Why alkyl halides are generally not prepared in the laboratory by free radical halogenation of alkanes?
Free radical halogenation is not suitable method for laboratory preparation of alkyl halides because of the following reasons : (i) Because of the presence of different types of hydrogen atoms present in alkanes they give a mixture of isomeric monohalogenated products whose boiling points are so close that they cannot be easily separated in the laboratory.
(ii) Substitution of more than one hydrogen atom yields polyhalogen compounds making the mixture more complex and hence difficult to separate.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- HALOALKANES AND HALOARENESBOOK - MODERN PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - HALOALKANES AND HALOARENESEXERCISE - A. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (with only one correct answer)
35 Videos
- HALOALKANES AND HALOARENESBOOK - MODERN PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - HALOALKANES AND HALOARENESEXERCISE - B. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (from competitive Examinations)
63 Videos
- HALOALKANES AND HALOARENESBOOK - MODERN PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - HALOALKANES AND HALOARENESEXERCISE - REVISION EXERCISE (Long Answer Questions)
2 Videos
- EQUILIBRIUMBOOK - MODERN PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - EQUILIBRIUMEXERCISE - Unit Practice Test
13 Videos
- HYDROCARBONSBOOK - MODERN PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - HYDROCARBONSEXERCISE - UNIT PRACTICE TEST
15 Videos
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Phosphine is generally prepared in the laboratory
ABy heating phosphorus in a current of hydrogenBBy decomposition of P2H4 at 110CBy heating red phosphorus with an aquesous solution of caustic sodaDBy heating white phosphors with caustic potashphosphine is generally prepared in the laboratory
ABy heating phosphorus in a current of hydrogenBBy heating white phosphorus with aqueous solution of caustic potashCBy decomposition of P2H4 at 110∘CDBy heating red phosphorus with an aqueous solution of caustic sodaWhich statement is incorrect about free radical halogenation of alkanes ?
AThe number of product molecules formed by one photon is very high.BIf O2 is added , initially the rate of reaction decreases, then increases.CInhibitors combine with free radical and terminate the chain reaction.DPresence of C6H5−C∣∣OO−OC∣∣O−C6H5 inhibits the free radical reaction.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Alkyl/Aryl halides may be classified as mono, di or polyhalogen compounds depending on one, two or more halogen atoms in their structures. Alkyl halides are prepared by free radical halogenation of alkanes, addition of halogen acids to alkenes and replacement of -OH group of alcohols with halogens using phosphorus halides, thionyl chloride or halogen acids. Aryl halides are prepared by electrophilic substitution to arenes.
The following questions are multiple choice questions.
Choose the most appropriate answer:
Which of the following is halogen exchange reaction ?
View SolutionRead the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Alkyl/Aryl halides may be classified as mono, di or polyhalogen compounds depending on one, two or more halogen atoms in their structures. Alkyl halides are prepared by free radical halogenation of alkanes, addition of halogen acids to alkenes and replacement of -OH group of alcohols with halogens using phosphorus halides, thionyl chloride or halogen acids. Aryl halides are prepared by electrophilic substitution to arenes.
The following questions are multiple choice questions.
Choose the most appropriate answer:
Complete the reaction:
H3C−Br+AgF→
View SolutionRead the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Alkyl/Aryl halides may be classified as mono, di or polyhalogen compounds depending on one, two or more halogen atoms in their structures. Alkyl halides are prepared by free radical halogenation of alkanes, addition of halogen acids to alkenes and replacement of -OH group of alcohols with halogens using phosphorus halides, thionyl chloride or halogen acids. Aryl halides are prepared by electrophilic substitution to arenes.
The following questions are multiple choice questions.
Choose the most appropriate answer:
Name the major monohalo product following reaction:
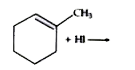
View SolutionRead the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Alkyl/Aryl halides may be classified as mono, di or polyhalogen compounds depending on one, two or more halogen atoms in their structures. Alkyl halides are prepared by free radical halogenation of alkanes, addition of halogen acids to alkenes and replacement of -OH group of alcohols with halogens using phosphorus halides, thionyl chloride or halogen acids. Aryl halides are prepared by electrophilic substitution to arenes.
The following questions are multiple choice questions.
Choose the most appropriate answer:
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points.
(i)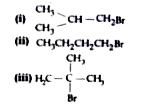
View SolutionRead the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Alkyl/Aryl halides may be classified as mono, di or polyhalogen compounds depending on one, two or more halogen atoms in their structures. Alkyl halides are prepared by free radical halogenation of alkanes, addition of halogen acids to alkenes and replacement of -OH group of alcohols with halogens using phosphorus halides, thionyl chloride or halogen acids. Aryl halides are prepared by electrophilic substitution to arenes.
The following questions are multiple choice questions.
Choose the most appropriate answer:
2-Bromopentane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane.
Write the compound which is most reactive towards P-elimination reaction.
View Solution

