Which out of o-chloronitrobenzene and 2, 4, 6-trinitrochlorobenzene is more reactive towards nucleophilic substitution?
To determine which compound, o-chloronitrobenzene or 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene, is more reactive towards nucleophilic substitution, we need to analyze the effects of the substituents on the aromatic ring.
1. Identify the Compounds:
- The first compound is o-chloronitrobenzene (C6H4ClNO2).
- The second compound is 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene (C6HClN3O6).
2. Understand Nucleophilic Substitution:
- Nucleophilic substitution involves a nucleophile (a negatively charged species) attacking a positively charged carbon in the aromatic ring, leading to the substitution of a leaving group (in this case, chlorine).
3. Analyze the Substituents:
- In o-chloronitrobenzene, there is one nitro group (-NO2) at the ortho position relative to the chlorine atom. The nitro group is a strong electron-withdrawing group, exerting both a -M (mesomeric) and -I (inductive) effect.
- In 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene, there are three nitro groups located at the 2, 4, and 6 positions. The presence of multiple nitro groups significantly enhances the electron-withdrawing effect.
4. Effect of Nitro Groups:
- The nitro group at the ortho position in o-chloronitrobenzene increases the positive character of the carbon attached to the chlorine, making it more susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
- In 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene, the three nitro groups create a much stronger electron-withdrawing effect, which increases the positive charge on the carbon atom bonded to chlorine even more than in o-chloronitrobenzene.
5. Compare Reactivity:
- The presence of three nitro groups in 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene means that the carbon atom attached to chlorine is significantly more positively charged compared to that in o-chloronitrobenzene.
- Therefore, the nucleophile will find it easier to attack and substitute the chlorine in 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene than in o-chloronitrobenzene.
6. Conclusion:
- Based on the analysis, 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene is more reactive towards nucleophilic substitution than o-chloronitrobenzene due to the stronger electron-withdrawing effect of the three nitro groups.
- The first compound is o-chloronitrobenzene (C6H4ClNO2).
- The second compound is 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene (C6HClN3O6).
- Nucleophilic substitution involves a nucleophile (a negatively charged species) attacking a positively charged carbon in the aromatic ring, leading to the substitution of a leaving group (in this case, chlorine).
- In o-chloronitrobenzene, there is one nitro group (-NO2) at the ortho position relative to the chlorine atom. The nitro group is a strong electron-withdrawing group, exerting both a -M (mesomeric) and -I (inductive) effect.
- In 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene, there are three nitro groups located at the 2, 4, and 6 positions. The presence of multiple nitro groups significantly enhances the electron-withdrawing effect.
- The nitro group at the ortho position in o-chloronitrobenzene increases the positive character of the carbon attached to the chlorine, making it more susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
- In 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene, the three nitro groups create a much stronger electron-withdrawing effect, which increases the positive charge on the carbon atom bonded to chlorine even more than in o-chloronitrobenzene.
- The presence of three nitro groups in 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene means that the carbon atom attached to chlorine is significantly more positively charged compared to that in o-chloronitrobenzene.
- Therefore, the nucleophile will find it easier to attack and substitute the chlorine in 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene than in o-chloronitrobenzene.
- Based on the analysis, 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene is more reactive towards nucleophilic substitution than o-chloronitrobenzene due to the stronger electron-withdrawing effect of the three nitro groups.
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
Least reactive towards nucleophilic additon is
ACH2=OBCCl3−C∣∣O−C2H5CCH3−C∣∣O−C2H5DCH3−C∣∣O−HWhich of most reactive towards nucleophilic aromatic substitution.
A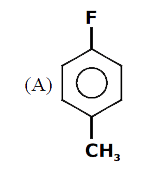 B
B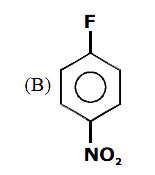 C
C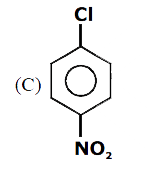 D
D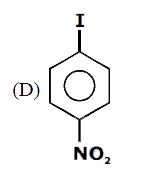
Which is least reactive towards nucleophilic substitution (SN2)
ACH2=CH−CH2ClB(CH3)3CClC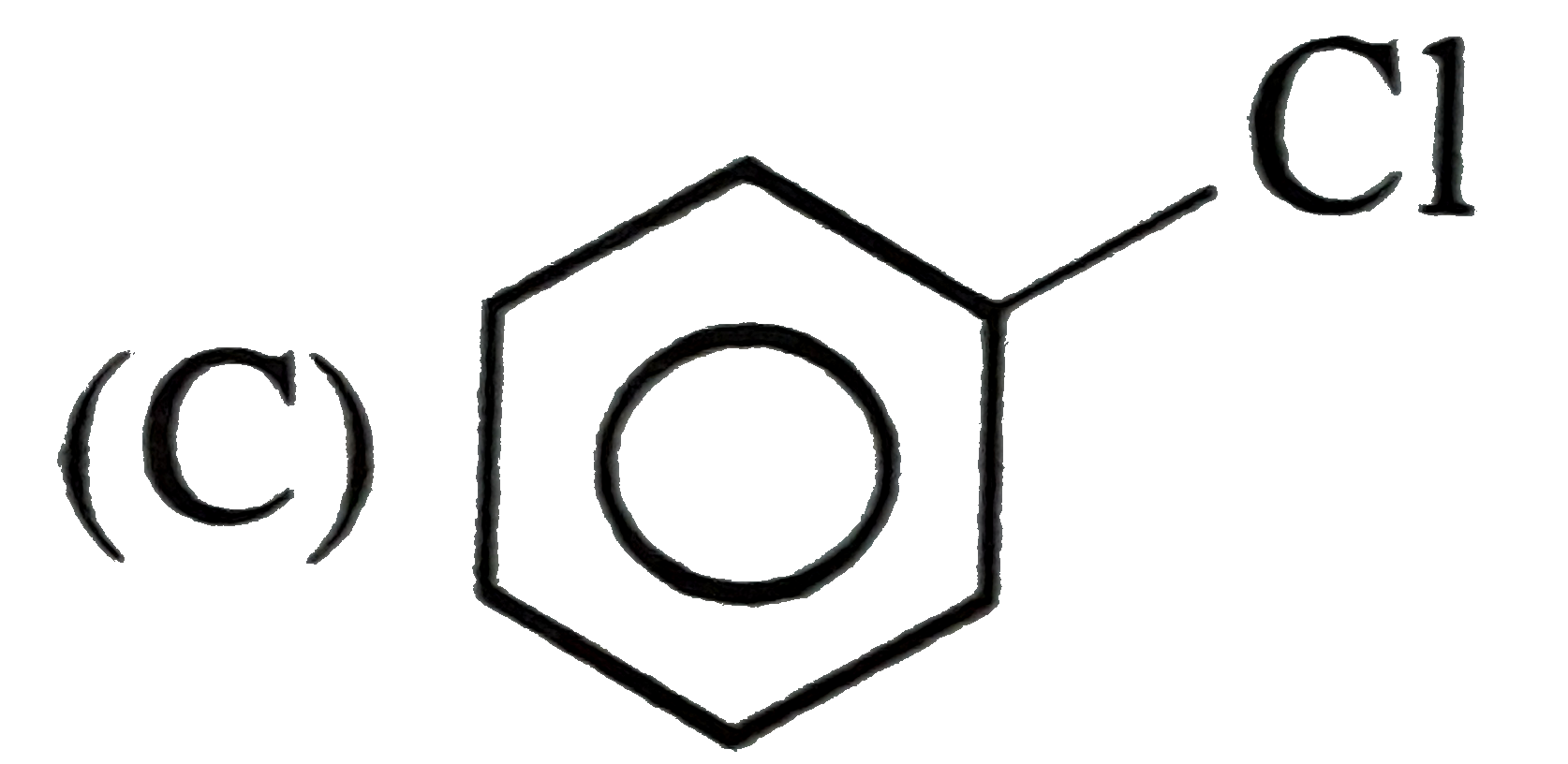 DCH3CHClCH3
DCH3CHClCH3
Which of the following is least reactive towards nucleophilic substitution?
View SolutionWhich compound is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition ?
View SolutionAryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution because
View SolutionWhich is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions?
View SolutionWhich one is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution reaction?
View Solution
