(a) An ambident nucleophile is:
(i) Ammonia (ii) Ammonium ion
(iii) Chloride ion (iv) Nitrite ion
(b) Haloalkanes and haloarenes are organohalogen compounds.
(i) Suggest a method for the preparation of alkyl chloride.
(ii) Aryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions. Give reasons.
Step by step video & image solution for (a) An ambident nucleophile is: (i) Ammonia (ii) Ammonium ion (iii) Chloride ion (iv) Nitrite ion (b) Haloalkanes and haloarenes are organohalogen compounds. (i) Suggest a method for the preparation of alkyl chloride. (ii) Aryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions. Give reasons. by Chemistry experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Updated on:21/07/2023Topper's Solved these Questions
- HALOALKANES AND HALOARENESBOOK - MODERN PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - HALOALKANES AND HALOARENESEXERCISE - HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS
13 Videos
- HALOALKANES AND HALOARENESBOOK - MODERN PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - HALOALKANES AND HALOARENESEXERCISE - A. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (with only one correct answer)
35 Videos
- HALOALKANES AND HALOARENESBOOK - MODERN PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - HALOALKANES AND HALOARENESEXERCISE - REVISION EXERCISE (Short Answer Questions) (CBSE Qs....)
3 Videos
- GENERAL PRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES OF ISOLATION OF ELEMENTSBOOK - MODERN PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - GENERAL PRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES OF ISOLATION OF ELEMENTSEXERCISE - COMPETION FILE (Integer Type Numerical Value Type Questions)
5 Videos
- ORGANIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING NITROGEN BOOK - MODERN PUBLICATIONCHAPTER - ORGANIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING NITROGEN EXERCISE - UNIT PRACTICE TEST
5 Videos
Similar Questions
Why alkyl halides are generally not prepared in the laboratory by free radical halogenation of alkanes?
View SolutionThe IUPAC nane of the compound
CH3−CH=CH−CH2Br is
View SolutionHow would you differentiate between SN1 and SN2 mechanisms of substitution reactions? Give one example of each.
View SolutionAmongst following, total number of metals which occur in native state in the earth's crust are : Pt, Ni, C, Hg, S, Zn, Au, Pb
View SolutionConvert
(i) 3-Methylaniline into 3-nitrotoluene.
(ii) Aniline into 1,3,5 - tribromobenzene.
View SolutionAryl halides are extermely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution. Predictand explain the order of reactivity of the compounds towards nucleophilic substitution.
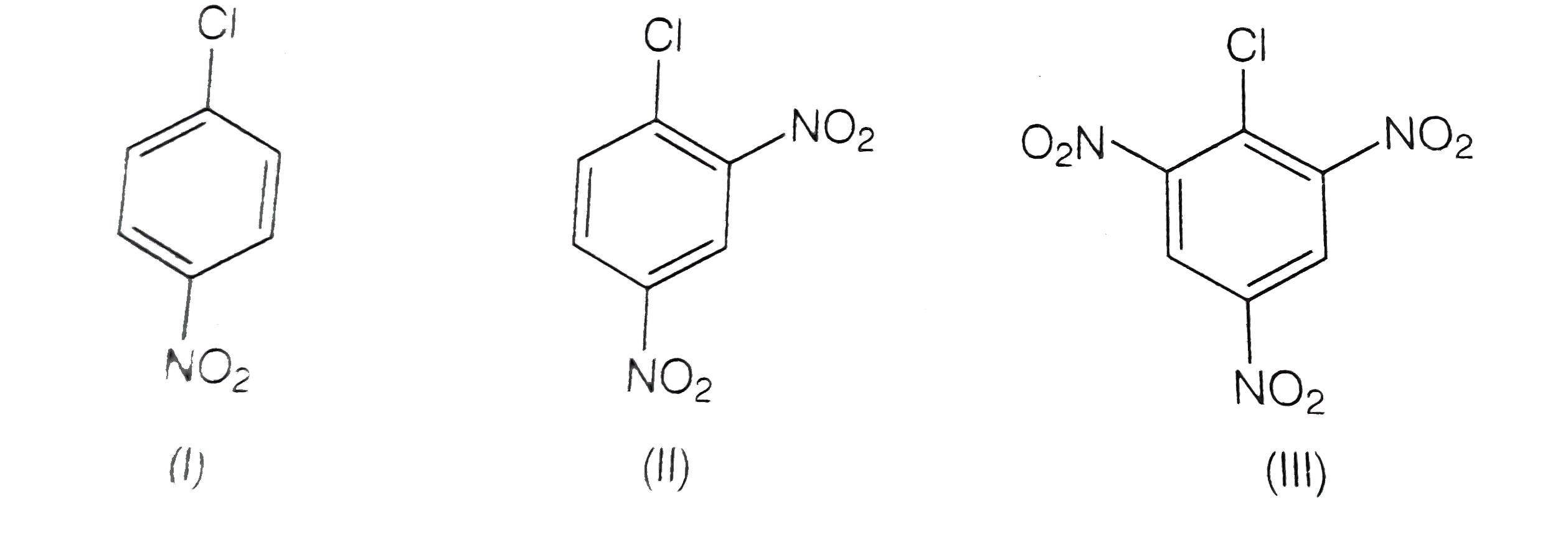
View SolutionAryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction as compared to alkyl halides due to
View SolutionWhy are aryl halides less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions than alkyl halides? How can we enhance the reactivity of aryl halides?
View SolutionAryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction as compared to alkyl halides due to
View Solution(a) Aryl halides are less reactive in nucleophilic substitution reactions. (i) Write any two reasons for less reactivity. (ii) Give one example for nucleophilic substitution reactions of aryl halides (b) Write a method for the preparation of alkyl halides. (c) Which of the following is not a polyhalogen compound. (i) Chloroform (ii) Freon (iii) Carbon tetrachloride (iv) Chlorobenzene
View SolutionAryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction as compared to alkyl halides due to
View SolutionAryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction as compared to alkyl halides due to
View SolutionAryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction than alkyl halides due to _________.
View SolutionChlorobenzene is less reactive that alkyl chlorides towards nucleophilic substitution reactions . Explain the reason for the less reactivity of chlorobenzene.
View SolutionAryl halides are less reactive than alkyl halides towards nucleophilic reagents
View Solution

