A particle of mass 0.01 kg moving horizontally with velocity 20 m/s strikes a stationary wedge ABC of mass 0.05 kg with a velocity of 20 m/s near the apex of the wedge is free to move. Second collision of the particle with the wedge occurs at B. Find.
(a) the length AB of the wedge
(b) the normal reaction between the ground and the wedge during the first collision. [Given that angle θ=cot−1 (2)]
![A particle of mass 0.01 kg moving horizontally with velocity 20 m/s strikes a stationary wedge ABC of mass 0.05 kg with a velocity of 20 m/s near the apex of the wedge is free to move. Second collision of the particle with the wedge occurs at B. Find. (a) the length AB of the wedge (b) the normal reaction between the ground and the wedge during the first collision. [Given that angle theta = cot^(-1) (2)]](https://d10lpgp6xz60nq.cloudfront.net/physics_images/FIITJEE_PHY_MB_01_C01_E02_021_Q01.png)
The correct Answer is:(a) 1.8 m (b) 0.5 N
Similar Questions
A particle of mass m moving horizontal with v_(0) strikes a smooth wedge of mass M, as shown in figure. After collision, the ball starts moving up the inclined face of the wedge and rises to a height h. When the particle has risen to a height h on the wedge, then choose the correct alternative(s)
View SolutionA smooth wedge of mass M is kept at rest on a smooth horizontal surface . Inclined face of the wedge make an angle theta with the horizontal . A particle of mass m collides normal to inclined face of wedge . If speed of the particle just before collision is u and coefficient of restitution is e then find velocity of wedge after collision .
View SolutionA particle of mass m strikes normally to a stationary wedge of mass 5m kept on the smooth horizontal surface as shown.If the particle sticks to the wedge then loss in kinetic energy of the system during collision is?
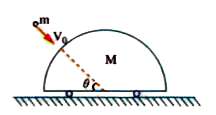
View SolutionA particle, (a mud pellet, say) of mass m strikes a smooth stationary wedge of mass M with a velocity Vo, at an angle θ with horizontal. If the collision is perfectly inelastic, find the :
a) velocity of the wedge just after the collision.
b) change in KE of the system (M + m) in the collision.
View SolutionA ball of mass m= 1 kg falling vertically with a velocity v_(0) = 2 m/s strikes a wedge of mass M = 2 kg kept on a smooth, horizontal surface as shown in figure The coefficient of restitution between the ball and the wedge is e = (1)/(2). Find the velocity of the wedge and the ball immediately after collision.
View SolutionA particle (a mud pallet, say) of mass m strikes a smooth stationary wedge of mass M with as velocity v_(0) at an angle theta with horizontal. If the collision is perfectly inelastic, find the a. velocity of the wedge just after the collision. b. Change in KE of the system (M+m) in collision.
View SolutionA wedge of mass M is kept at rest on smooth surface a particle of mass m hits the wedge normally. Find the velocity of wedge and particle just after collision. Take coefficient of restitution as e.
View Solution

