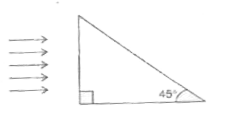
Preferential filtering of light consisting of different wavelengths can be done using total internal reflection. The concept of filtering lies in the fact that different wavelengths have different refractive indices in a medium The beam of light with different wavelengths are made incident on an isosceles right angled prism as shown in the figure. The wavelength or wavelengths which satisfy the condition of totai internal reflection, θsin≥(1μ), get reflected
Others get refracted, hence gets separated. G is the angle of incidence and u. is the refractive index .of the particular wavelength in that particular medium. Thus, by changing the medium and by changing the angles of the prism we can satisfy the condition df total internal reflection for a particular wavelength, which gets separated out.
Q Now instead of changing the material of prism, we change one of the angle of prism to 300 Then, which of the colour gets separated?

red
green
blue
none of these
The correct Answer is:D
Topper's Solved these Questions
- OPTICSBOOK - FIITJEECHAPTER - OPTICSEXERCISE - Comprehension - III
3 Videos
- OPTICSBOOK - FIITJEECHAPTER - OPTICSEXERCISE - Comprehension - IV
2 Videos
- OPTICSBOOK - FIITJEECHAPTER - OPTICSEXERCISE - COMPREHENSION- I
5 Videos
- MODERN PHYSICSBOOK - FIITJEECHAPTER - MODERN PHYSICSEXERCISE - Numerical based questions
5 Videos
- PHYSICS PART-IIIBOOK - FIITJEECHAPTER - PHYSICS PART-IIIEXERCISE - NUMERICAL BASED QUESTIONS DECIMAL TYPE
11 Videos
Similar Questions
A telescope is an optical instrument used to increase the visual angle of distant objects such as stars, planets etc.
An astronomical telescope consists of two converging lenses. The one facing the object is called objective and the lens close to the eye is called an eyepiece. It can be adjusted by displacing relative to the objective. The angular magnification is defined as the ratio of focal length of objective and eyepiece. One can see the image with unstrained eye if it forms at infinity. An astronomical telescope has an objective of focal length 50 cm and a magnification of 20.
Q Focal length, of the eyepiece is
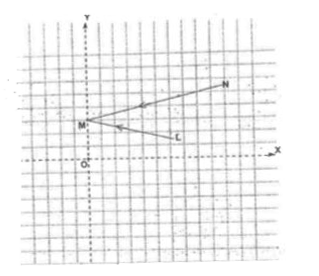
View SolutionIn the adjacent figure 'OX' is the principal axis of a stationary spherical mirror (either concave mirror or convex mirror). NM is an incident ray, after reflection it passes through the origin O, such that ZOMN=106∘
LM is another incident ray, which after reflection, passes through the point K having coordinates^,, 0), such.that ZOML=76∘. The point P (x2 , 0) is the pole of the spherical mirror and point C(x3 , 0) is the centre of the curvature of spherical mirror. In the figure side of each square is equal to 1cm.
QFind the value of Xi (in cm)
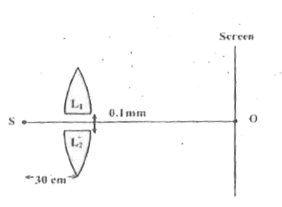
View SolutionTwo independent light sources are always incoherent. This is because phase of light emitted is random and phase difference, at any point, changes very rapidly with time. So as to obtain observable interference, we require coherent sources which emit light of same wavelength such that phase difference at any point does not change with time. In different interference experiments, the method to obtain two coherent sources could be different. In Fresnel's biprism experiment, two virtual images of a real source, which are formed due to refraction at the biprism, act as coherent source. In Lloyd’s mirror experiment, a real source and its virtual image formed due to reflection at a plane mirror act as coherent source. Two images of a source or a source and its image are coherent because of their phase correlation. It is also possible to obtain coherent sources by forming two images of a point source in the following manner.As shown in the figure, S is a monochromatic point source. A thin circular lens is cut into two identical halves L, and L2 by a plane passing through a diameter. L1 is kept above the axis and L2 below it is in a symmetrical manner such that the gap between the two is 0.1 mm. Each forms an image Qf the source and the two images, say, Si and S2 , act as coherent sources. Superposition of waves from these coherent sources will result in observable interference and a pattern can be obtained on a screen.The lens which has been cut to from L, and L2 is made of a material of refractive index 1.5 for the wavelength emitted by the source S. Radius of curvature of each surface of the lens is 18 cm. Source S is 30 cm along the axis fro Li and L2 . It is found that smallest distance from O along the screen at which intensity is half of the maximum intensity is 0.1 mm. It is also observed that the highest order of maximum intensity in the interference patter is 416.
QDistance between the images Si and S2 will be
View SolutionPhotons with energy 5eV are incident on a cathode C in a photoelectric cell . The maximum energy of emitted photoelectrons is 2eV. When photons of energy 6eV are incident on C , no photoelectrons will reach the anode A , if the stopping potential of A relative to C is
View SolutionThe range for a projectile that lands at the same elevation from which it is fired is given by R=(u2/g)sin2θ . Assume that the angle of projection = 30∘. If the initial speed of projection is increased by 1% , while the angle of projection is decreased by 2% . Then by what percentage does the range change ?
View SolutionLight of wavelength 5000Å falls on a plane reflecting surface. What are the wavelength and frequency of reflected light ? For what angle of incidence is the reflected ray normal to the incident ray ?
View SolutionSTATEMENT-1 Different cololures travel with difference speed in vaccum
STATEMENT2 Wavelength of light depends on refractive index of medium.
View SolutionWhen a beam of light wavelength lambda is incident on the surface of a liquid at an angle phi , the reflected ray in completely polarized. The wavelength og light in the liquid medium is
View Solutionकिसी परावर्तक तल पर 5000Å तरंगदैधर्य का प्रकाश आपतिति होता है|परावर्तित प्रकाश की आवृत्ति एव तरंगदैधर्य ज्ञात कीजिये|
View Solution6000Å तरंग-दैधर्य की प्रकाश-किरण निवृत 2.0 अपवर्तनांक के माधयम में प्रवेश करती है|माध्यम में प्रकाश-किरण की तरंग-दैधर्य होगी-
View SolutionA ray of light of wavelength λ is incident on mirror at an angle of incidence 60∘. The wavelength of light after reflection will be
View SolutionA prism of a refracting angle60∘ is made with a material of refractive index μ. For a certain wavelength of light, the angle of minimum deviation is 30∘ . For this wavelength, the value of μ of material is
View Solutionतरंगदैर्ध्य 6000Å की एकवर्णी प्रकाश किरण वायु से अपवर्तनांक 1⋅62 वाले माध्यम के सीमापृष्ठ पर टकराती है | यदि सीमापृष्ठ के आंशिक परावर्तित व अपवर्तित प्रकाश किरणे परस्पर लम्बवत हो तो गणना कीजिए : परावर्तित प्रकाश की तरंगदैर्ध्य
View SolutionLight of wavelength 5000Å falls on a plane reflecting surface. What are the wavelength and frequency of the reflected light? For what angle of incidence is the reflected ray normal to the incident ray?
View SolutionA prism of a refracting angle 60^(@) is made with a material of refractive index mu . For a certain wavelength of light, the angle of minimum deviation is 30^(@) . For this wavelength, the value of mu of material is
View Solution

