Match the complexes in Column-I with their information in Column-II
(A)[Cu(NH3)2]SO4(p)dsp2(B)[Pt[NH3)2Cl2](q)Octahedral(C)K4[Fe(CN)6](r)sp3d2(D)[Fe(H2O)6Cl3](s)square planar
(A→p,s)(B→p,s)(C→q),(D→q,r)
Topper's Solved these Questions
- CHEMICAL ENERGETICS Book:FIITJEEChapter:CHEMICAL ENERGETICS Exercise:MATCHING LIST TYPE QUESTIONS
Explore 5 Videos
- CHEMICAL ENERGETICS Book:FIITJEEChapter:CHEMICAL ENERGETICS Exercise:NUMERICAL BASED PROBLEMS
Explore 12 Videos
- CHEMICAL ENERGETICS Book:FIITJEEChapter:CHEMICAL ENERGETICS Exercise:COMPREHENSIONS (COMPREHENSION-XI)
Explore 3 Videos
- CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND ITS DERIVATIVESBook:FIITJEEChapter:CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND ITS DERIVATIVESExercise:SINGLE INTEGER ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Explore 1 Video
- CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUMBook:FIITJEEChapter:CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUMExercise:MATCHING TYPE QUESTIONS
Explore 3 Videos
Similar Questions
Match list -I with list -II and select the correct answer using the codes given below:
List-IList-II(P)Haber process(1)Na2CO3(Q)Birkeyland -Eyde process(2)NH3(R)Solvay's process(3)HNO3
View SolutionWhen 1-pentyne (A) is formed with 4N alcoholic KOH at 175∘ C, it is converted into an equilibrium mixture of 1.3% 1-pentyne (A), 95.2 % 2-pentyne (B) and 3.5% of 1.2 pentadierie (C ). The equilibrium is maintained at 175∘ C. Calculate ΔG∘2 for the following equilibria.
B<⇒C......ΔG∘2.
View SolutionFor an ideal gas, an illustration of three different paths, A,(B+C) and (D+E) from an initial state P1,V1,T1 to final state P2,V2,T1 is shown in the given figure.

Path (A) represents a reversible isothermal expansion from P1,V1 to P2,V2. Path (B+C) represents reversible adiabatic expansion (B) from P1,V1,T1 P3,V2,T2 followed by reversible heating the gas constant volume ( C) from P3,V2,T2 to P2,V2,T1. Path (D+E) represents a reversible expansion constant pressure P1(D) from P1,V1,T1 to P1,T2,T3 followed by reversible cooling at constant volume V2(E) from P1,V2,T3 to P2,V2,T1.
What is qrev for path (A)?
View SolutionFind the number of geometrical isomers of the given compound .
C6H5−CH=CH−CH−CH=CH−CH=CH−COOH
View Solution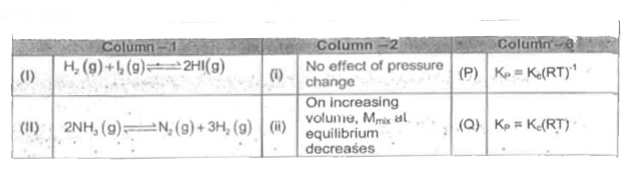

Which of the following combination is correct ?
View SolutionMatch the complexed listed column −I with type of hybridisation listed in column −II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists :
Column−IColumn−II(a)[AuF4]−(p) dsp2hybridisation(b)[Cu(CN)4]3−(q) sp3hybridisation(c)[Co(NH3)6]3+(r) sp3d2hybridisation(d)[Fe(H2O)5NO]2+(s) d2sp3hybridisation
View SolutionMatch the complexes in Column I with their properties liested in Column II
A[Co(NH3)4(H2O)2]Cl2pGeometrical isomersB[Pt(NH3)2Cl2]qParamagneticC[Co(H2O)5Cl]ClrDiamagnetic D[Ni(H2O)6]Cl2sMetal ion with +2oxidation state
View Solutionनिम्न के IUPAC नाम लिखिए -
(i)[Ag(NH3)2]Cl(ii)[Pt(NH3)2Cl2](iii)K3[Cr(CN)6](iv)K3[Al(C2O4)3](v)[Cr(H2O)6]Cl3(vi)[Pt(NH3)6]Cl4(vii)Na2[Fe(CN)5No](viii)[Co(NO3)5Cl]SO4(ix)[Cr(CO)6](x)[Pt(NH3)4Br2]Cl2(xi)[Fe(H2O)6]Cl3
View SolutionName the type of isomerism exibited by the following isomers :
(1) [Cr(NH3)6][Cr(CN)6]and[Cr(NH3)4(CN)2][Cr(NH3)2(CN)4]
(2) [Co(py)2(H2O)2Cl2]Cland[Co(py)2(H2O)Cl3]H2O
(3) [Pt(NH3)4Br2]Cl2and[Pt(NH3)4Cl2]Br2
(4) [Co(NH3)5NO2]Cl2and[Co(NH3)5ONO]Cl2
View Solutionनिम्नलिखित में से धनायनिक, ऋणायनिक तथा उदासीन जटिलों को पृथक कीजिए-
K2[Hgl4],[Co(NH3)6]Cl3,K3[Fe(CN)6],[Ni(CO)4],[Pt(NH3)2Cl2],[Fe(H2O)6]Cl3.
View Solutionनिम्नलिखित का IUPAC नाम लिखिए -
(i) [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3
(ii) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2]
(iii) [Pt(NH3)6]Cl4
(iv) Na2[Fe(CN)5NO].
View Solutionनिम्न के I U P A C पद्धति में नाम लिखिए-
{:((a) [Pt(NH_(3))_(2)Cl_(2)], (b) K_(3) [Fe (CN)_(6)]),
View Solution[Fe(H_(2)O)_(6)]Cl_(3) and [Pt(NH_(3))_(2)Cl_(2)] are
View SolutionName the complexes (i) K4[Fe(CN)6] (ii) [Pt(NH3)3(NO)Cl2]Br
View SolutionWrite the IUPAC name of (i)Zn2[Fe(CN)6]
(ii) Pt[Cl2(NH3)2]
View Solution

