A ball of mass 1 kg and charge 1μC is directly projected from infinity toward another stationary ball of mass 2 kg and same charge as the first. The initial velocity of projection is 10 mis. Find the distance of closest separation and their velocities at the closest separation (Fig. 24-76).

3.70×103m, (10)/(3) m//s
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ELECTRIC POTENTIALBOOK - RESNICK AND HALLIDAYCHAPTER - ELECTRIC POTENTIALEXERCISE - (PRACTICE QUESTIONS) Single Correct Choice Type
21 Videos
- ELECTRIC POTENTIALBOOK - RESNICK AND HALLIDAYCHAPTER - ELECTRIC POTENTIALEXERCISE - (PRACTICE QUESTIONS) More than One Correct Choice Type
8 Videos
- ELECTRIC POTENTIALBOOK - RESNICK AND HALLIDAYCHAPTER - ELECTRIC POTENTIALEXERCISE - CHECKPOINT
6 Videos
- ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDSBOOK - RESNICK AND HALLIDAYCHAPTER - ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDSEXERCISE - Practice Questions (Integer Type )
3 Videos
- ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTIONBOOK - RESNICK AND HALLIDAYCHAPTER - ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTIONEXERCISE - PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Integer Type)
14 Videos
Similar Questions
Which one of the following statements best explains why it is possible to define an electrostatic potential in a region of space that contains an electrostatic field?
View SolutionWhen a negative charge moves in a direction opposite to the direction of an electric field,
View SolutionIn the figure, we move a proton from point i to point f in a uniform electric field. Is positive or negative work done by (a) the electric field and (b) our force? (c) Does the electric potential energy increase or decrease? (d) Does the proton move to a point of higher or lower electric potential?
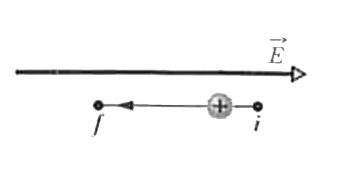
View SolutionA point charge q=1C and mass 1kg is projected with speed 10m/s in the perpendicular direction of unifrom electric field E=100V/m. The value of latus rectum of the path followed by charged particle (in meter) is :
View SolutionA straight conductor 1 m long moves at right angle to both its length and a uniform magnetic field. If the speed of conductor is 2.0 m/s and strength of magnetic field is 104 G, find the value of induced emf in volts.
View SolutionA particle of mass 1kg and charge 1/3μC is projected toward a nonconducing fixed spherical shell of radius r=1mm having the same charge uniformly distributed on its surface. Find th minimum initial velocity of projection requires if the particle just grazes the shell.
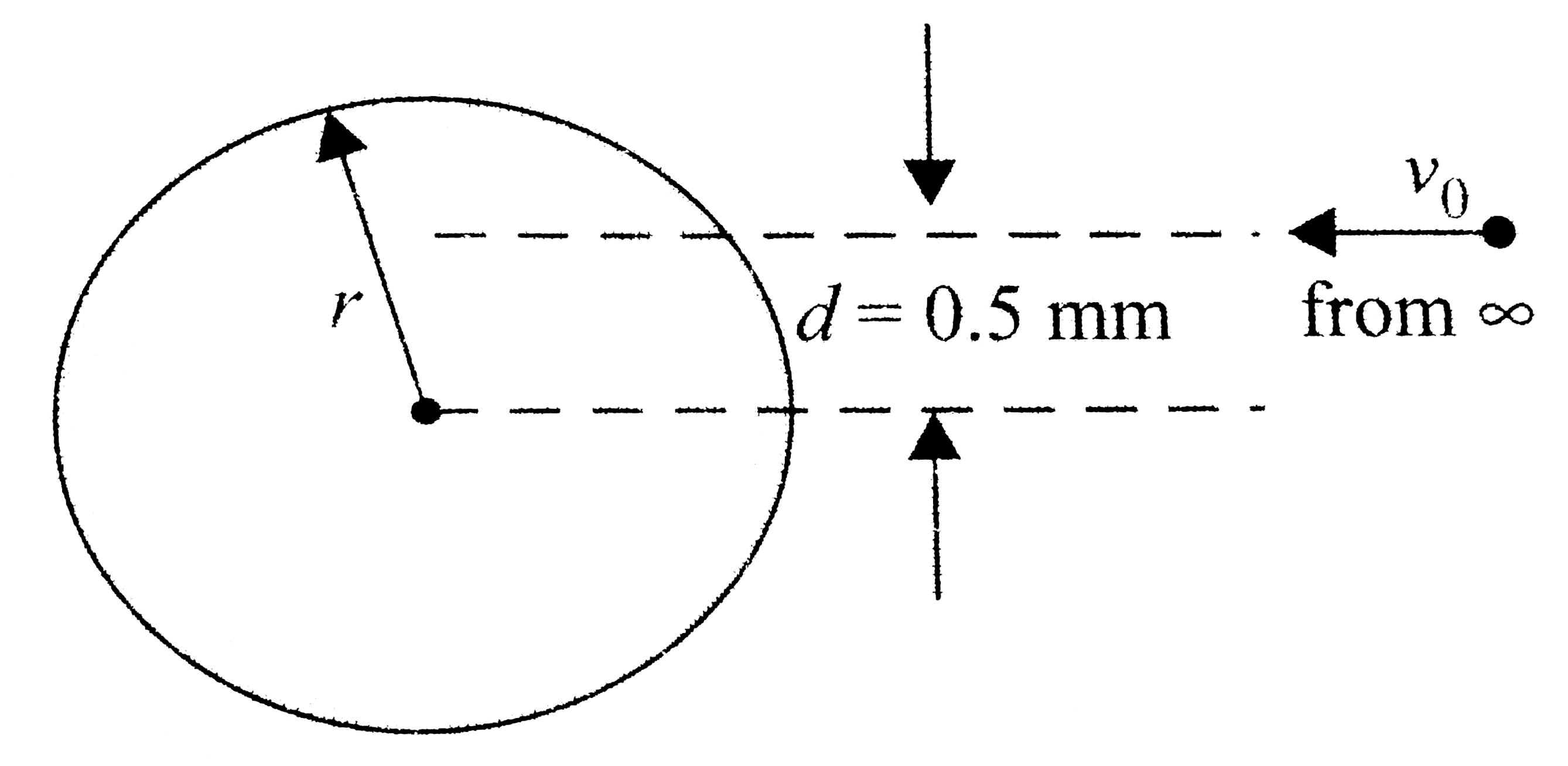 .
.
View SolutionA small ball of mass 2×10−3kg, having a charge 1μC, is suspended by a string of length 0.8m. Another identical ball having the same charge is kept at the point of suspension. Determine the minimum horizontal velocity that should be imparted to the lower ball so that it can make a complete revolution.
View SolutionThe mass of a ball is four times the mass of another ball. When these balls are separated by a distance of 10 cm , the gravitational force between them is 6.67xx10^(-7) N . The masses of the two balls are in kg .
View SolutionA ball of mass 10kg strikes another ball of mass 25kg at rest. If they separated in mutually perpendicular directions then the coefficient of restitution is:
View SolutionA ball of mass 1 kg moving with a velocity of "0.4 ms"^(-1) collides with another stationary ball. After the collision, the first ball moves with a velocity of 0.3ms^(1) in a direction making an angle of 90^(@) with its initial direction. The momentum of the second ball after the collision will be (in kg ms^(-1) )
View Solution10 किग्रा द्रव्यमान की एक गेंद A प्रारम्भिक वेग 8 मी/से से एक दूसरी 20 किग्रा द्रव्यमान की स्थिर गेंद B से टकराती यदि टक्कर के उपरान्त गेंद A तथा B प्रारम्भिक गति की दिशा में क्रमशः 30∘ तथा 45∘ का कोण बनाते हुए जाती है, टक्कर के बाद के उनके वेग ज्ञात कीजिए |
View SolutionThe closed distance of approach of an α− particle travelling with velocity V towards a stationary nucleus is d.For the closest distance to become d3 towards a stationary nucleus of double of the charge,the velocity of projection of the α− particle has to be
View SolutionThe closed distance of approach of an α− particle travelling with velocity V towards a stationary nucleus is d.For the closest distance to become d3 towards a stationary nucleus of double of the charge,the velocity of projection of the α− particle has to be
View SolutionA ball of mass of 1 kg and charge 50μC is directly projected from infinity toward another fixed ball of charge 1/6μC ( as shown in Fig. 24-5). The initial velocity of projection is 10 m/s. Find the distance and its velocity at the closest separation. Assume that the initial line of motion is at a distance of 1 m from the second fixed charge.
View SolutionA pith ball of mass 9×10−5 kg carries a charge of 5μC. What must be charge in another pith ball placed directly 2 cm above the given pith ball such that they held in equilibrium?
View SolutionThe mass of a ball if four times the mass of another ball. When these balls are separated by a distance of 10 cm, the gravitational force between them is 6.67×10−7N. Find the masses of the two balls.
View Solution

