In the reaction A(g)+2B(g)⇔C(g)+QkJ, greater product will be obtained or the forward reaction is foroured by
At high temperature and high pressure
At high temperatue and low pressure
At low temperature and high pressure
At low temperature and low pressure
The correct Answer is:C
To determine whether the forward reaction is favored and whether greater products will be obtained in the reaction:
A(g)+2B(g)⇌C(g)+Q kJ
we need to analyze the conditions under which the forward reaction is favored.
Step 1: Identify the nature of the reaction
The given reaction is exothermic, as indicated by the release of heat (Q kJ). In exothermic reactions, heat is released when products are formed.
Hint: Remember that exothermic reactions release heat, which can influence the position of equilibrium.
Step 2: Apply Le Chatelier's Principle
According to Le Chatelier's Principle, if a system at equilibrium is subjected to a change in concentration, temperature, or pressure, the equilibrium will shift to counteract that change.
Hint: Consider how changes in conditions (like temperature and pressure) affect the equilibrium position.
Step 3: Analyze the effect of temperature
For exothermic reactions, lowering the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right (towards the products) to produce more heat. Therefore, lower temperatures favor the formation of products.
Hint: Lower temperatures favor exothermic reactions.
Step 4: Analyze the effect of pressure
In this reaction, we have 3 moles of gas on the reactant side (1 mole of A and 2 moles of B) and 1 mole of gas on the product side (C). Increasing the pressure will favor the side with fewer moles of gas, which is the product side in this case.
Hint: Increasing pressure favors the side with fewer gas moles.
Step 5: Conclusion
To obtain greater products in the reaction A(g)+2B(g)⇌C(g)+Q kJ, the forward reaction is favored by:
- Low Temperature: Shifts equilibrium to the right (towards products).
- High Pressure: Shifts equilibrium to the right (towards products).
Final Answer: Greater product will be obtained if the reaction is conducted at low temperature and high pressure.
The given reaction is exothermic, as indicated by the release of heat (Q kJ). In exothermic reactions, heat is released when products are formed.
According to Le Chatelier's Principle, if a system at equilibrium is subjected to a change in concentration, temperature, or pressure, the equilibrium will shift to counteract that change.
For exothermic reactions, lowering the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right (towards the products) to produce more heat. Therefore, lower temperatures favor the formation of products.
In this reaction, we have 3 moles of gas on the reactant side (1 mole of A and 2 moles of B) and 1 mole of gas on the product side (C). Increasing the pressure will favor the side with fewer moles of gas, which is the product side in this case.
To obtain greater products in the reaction A(g)+2B(g)⇌C(g)+Q kJ, the forward reaction is favored by:
- High Pressure: Shifts equilibrium to the right (towards products).
Topper's Solved these Questions
- CHEMICAL EQULIBRIUMBOOK - ERRORLESS CHAPTER - CHEMICAL EQULIBRIUMEXERCISE - CRITICAL THINKING (OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS)
10 Videos
- CHEMICAL EQULIBRIUMBOOK - ERRORLESS CHAPTER - CHEMICAL EQULIBRIUMEXERCISE - JS JEE SECTION (ONLY ONE CHOICE ANSWER)
35 Videos
- CHEMICAL EQULIBRIUMBOOK - ERRORLESS CHAPTER - CHEMICAL EQULIBRIUMEXERCISE - (ORDINARY THINKING) ACTIVATION ENERGY, STANDARD FREE ENERGY AND DEGREE OF DISSOCIATIN AND VAPOUR DENSITY
12 Videos
- CHEMICAL BONDING BOOK - ERRORLESS CHAPTER - CHEMICAL BONDING EXERCISE - JEE Section (Jee (advanced ) 2018)
1 Video
- CHEMICAL KINETICS BOOK - ERRORLESS CHAPTER - CHEMICAL KINETICS EXERCISE - JEE (Advanced ) 2018
1 Video
Similar Questions
Kp for the following reaction at 700 K is 1.3×10−3atm−1 . The Kc at same temperature for the reaction 2SO2+O2→2SO3 will be
View SolutionThe reaction A+B⇔C+D + heat, has reached equilibrium. The reaction may be made to proceed forward by
View SolutionThe standard state Gibbs's energy change for the isomerisation reaction cis−2−pentence⇔trans−2−pentence is −3.67kJmol−1 at 400K. If more trans−2−pentence is added to the reaction vessel, then:
View SolutionMatch each set of hybrid orbitals from List -I with complex (es) given in List-II
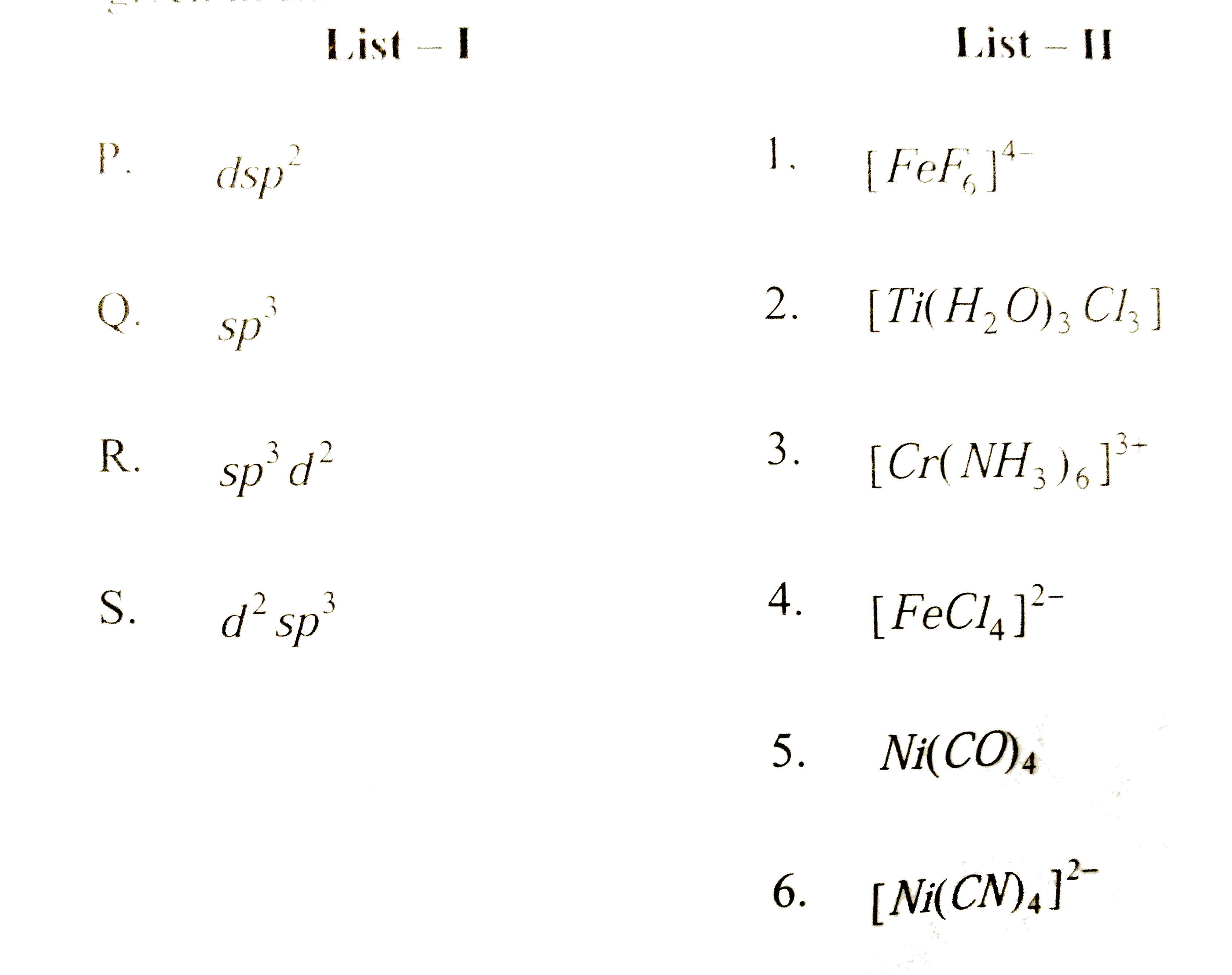
View SolutionFor a first order reaction A(g)→2B(g)+C(g) at constant volume and 300 K, the total pressure at the beginning (t=0) and at time t ae P0andPt respectively. Initially, only A is present with concentration [A]0andt1/3 is the time required for the partial pressure of A to reach 1/3rd of its initial value. The correct options (s) is (are) :
(Assume that all these behave as ideal gases)
View SolutionIn a gases reaction, A_((g))+B_((g))hArrC_((g)) , predict the effect of addition of inert gas, if addition is made at : ( a ) constant volume, ( b ) constant pressure.
View SolutionFor a reaction A_((g)) + B_((g))hArrC_((g)) + D_((g)) the intial concentration of A and B are equals but the equilibrium constant of C is twice that of equilibrium concentration of A. Then K is
View SolutionFor the system A(g)+2B(g)⇔C(g) the equilibrium concentration is
A=0.06molL−1,B=0.12molL−1
C=0.216molL−1 The Keq for the reaction is
View SolutionIn the reaction A (g) + B (g)⇔ C (g), the backward reaction is favoured by (A) Increase in pressure
View SolutionFor the reaction A_((s)) + 2B_((g)) hArr 3C_((g)) . At constant pressure on addition of inert gas, the equilibrium state
View SolutionFor the reaction, A(g)+2B(g)⇔3C(g)+3(g),Kp=0.05 atm at 1000K. The value of Kc is represented by
View SolutionThe Kc for given reaction will be
A2(g)+2B(g)⇔C(g)+2D(g)
View SolutionThe reaction A_((g)) + B_((g))hArrC_((g)) + D_((g)) proceeds to right hand side upto 99.9%. The equilibrium constant K for the reaction will be -
View SolutionFor the reaction 2HI_((g))hArrH_(2(g))+I_(2(g))-QkJ , , the equilibrium constant depends upon
View SolutionThe yield of the products in the reaction,
A2(g)+2B(g)⇔C(g)+Q kJ would be higher at :
View Solution

