The reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is gives below-
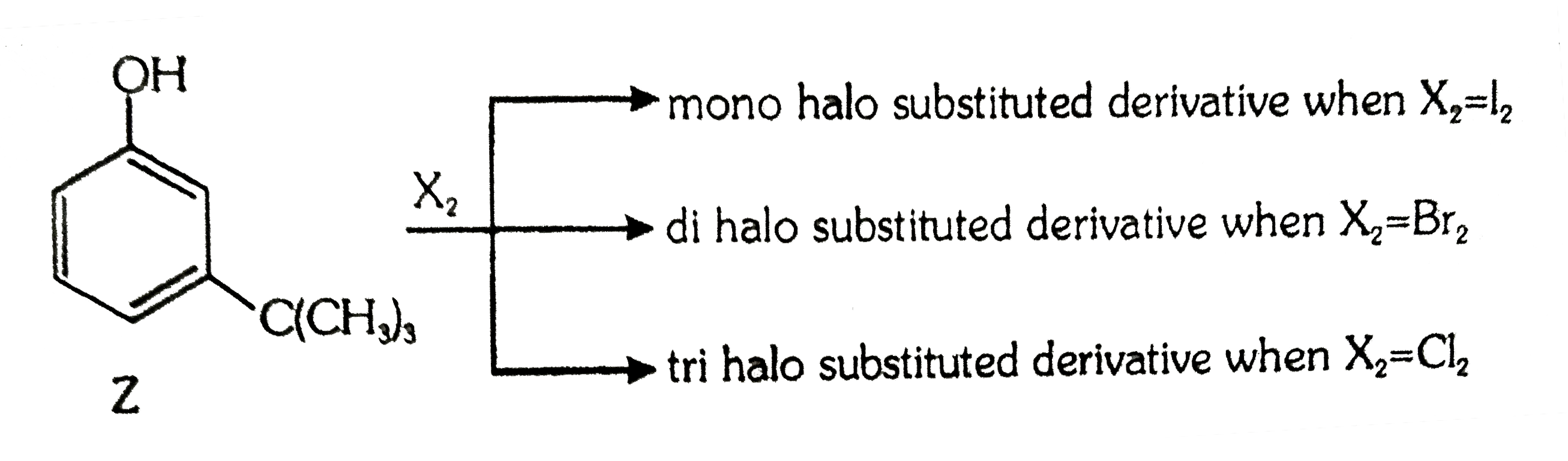
The observed pattern of electrophilic substitution can be explained by-
The steric effect of the halogen
The steric effect of the tert-butyl group
The electronic effect of the phenolic group
The electronic effect of the tert-butyl group
The correct Answer is:A, B, C
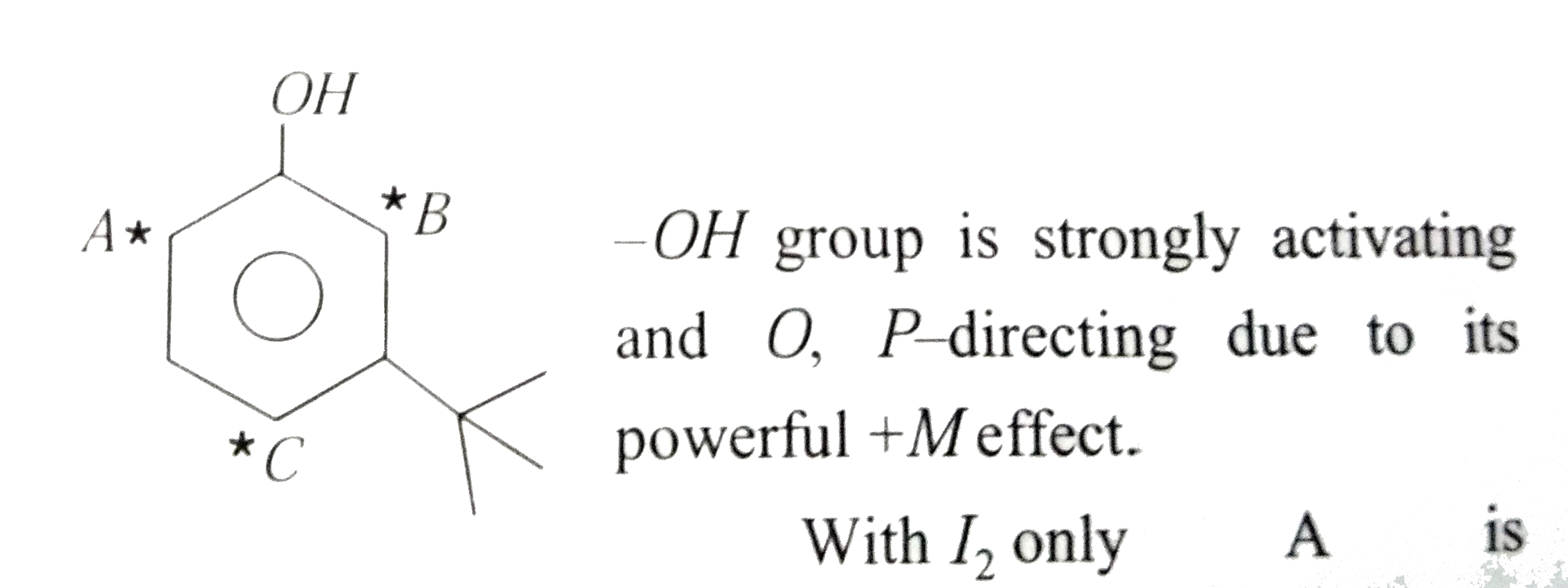
−OH group is strongly activating and O, P-directing due to its powerful +M effect.
With I2 only A is substituted, since -I is large, steric inhibition by large −CMe3 group forbids substitution at B or C.
-Br and -Cl become progressively more reactive, due to (a) Increasing electrophilic nature of X⊕ (not mentioned is any option).
(b) Smaller size most sterically hindered location is B which is substituted only by -Cl.
Similar Questions
Explain the following observations giving appropriate reasons : Halogens are strong oxidising agents.
View Solutionऐसा यौगिक, जो इलेक्ट्रोफिलिक प्रतिस्थापन के प्रति क्रियाशील नहीं है
View SolutionThe most reactive compound towards electrophilic substitution is
View SolutionInterhalogen compounds are compounds formed by combination of different halogen atoms. Which are more reactive, halogens or interhalogen compounds? Give reason
View SolutionReactivity OF Aromatic Compounds|| Electrophilic Addition, Electrophilic Substitution || Examples OF EAS, Niration, Nitrosoation, Halogenation, Chloromethylation and Examples
View SolutionThe reactivity of compound Z with different halogens under appropriate conditions is given below (1)the steric effect of the halogen (2)the steric effect of tert-butyl group (3)the electronic effect of the phenolic group (4)the electronic effect of the tert-butyl group
View SolutionWhich of the following is most reactive towards electrophillic aromatic substitution for halogen ?
View SolutionGive the increasing order of reactivity towards electrophilic substitution.
View Solution

