Figure 22-8c is identical to Fig. 22-8a except that particle 3 now lies on the x axis between particles 1 and 2. Particle 3 has charge q2=−3.20×10−19C and is at a distance (3/4)R from particle 1. What is the net electrostatic force →F1.net on particle 1 due to particles 2 and 3?
KEY IDEA
The presence of particle 3 does not alter the electrostatic force on particle 1 from particle 2. Thus, force →F12 still acts on particle 1. Similarly, the force →F13 that acts on particle 1 due to particle 3 is not affected by the presence of particle 2. Because particles 1 and 3 have charge of opposite signs, particle 1 is attracted to particle 3. Thus, force →F13 is directed toward particle 3, as indicated in the free-body diagram of Fig. 22-8d.
Three particles : To find the magnitude of →F13, we can rewrite Eq. 22-4 as
F13=14πε0|q1||q3|(34R)2
=(8.99×109N⋅m2/C2)×(1.60×10−19C)(3.20×10−19C)(34)2(0.0200m)2
=2.05×10−24N.
We can also write →F13 in unit-vector notation:
→F13=(2.05×10−24N)ˆi.
The net force →F1,net on particle 1 is the vector sum of →F12, and →F13, that is, from Eq. 22-7, we can write the net force →F1,net on particle 1 in unit-vector notation as
→F1,net=→F12+→F13
=−(1.15×10−24N)ˆi+(2.05×10−24N)ˆi
=(9.00×10−25N)ˆi. (Answer)
Thus, →F1, net has the following magnitude and direction (relative to the positive direction of the x axis):
9.00×10−25Nand0∘. (Answer)
Similar Questions
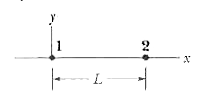
In Fig., particle 1 of charge +6.0μC and particle 2 of charge −2.0μC are held at separation L=10.0cm on an x axis. If particle 3 of unknown charge q3 is to be located such that the net electrostatic force on it from particles 1 and 2 is zero, what must be the (a) x and (b) y coordinates of particle 3 ?
View SolutionThree particles are fixed on an x axis. Particle 1 of charge q1 is at x = -a, and particle 2 charge q2 is at x = +a. If their net electrostatic force on particle 3 of charge +Q is to be zero, what must be the ratio q1/q2 when particle 3 is at (a) x = +0.750 a and (b) x = +1.50 a ?
View SolutionIn Fig., particles 1 and 2 are fixed in place on an axis, at a separation of L = 6.00 cm. Their charges are q_(1) = +e and q_(2) = -27e . Particle 3 with charge q_(3) = +4e is to be placed on the line between particles 1 and 2 , so that they produce a net electrostatic force vec(F)_("3,net") on it. (a) At what coordinate should particle 3 be placed to minimize the magnitude of that force ? (b) What is that minimum magnitude ?
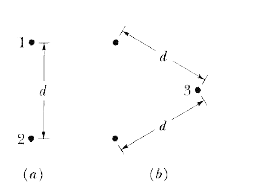
View SolutionIn Fig., particles 1 and 2 have charge 20.0μC each and are held at separation distance d = 0.75 m. (a) What is the magnitude of the electrostatic force on particle 1 due to particle 2? In Fig., particle 3 of charge 20.0μC is positioned so as to complete an equilateral triangle. (b) What is the magnitude of the net electrostatic force on particle 1 due to particles 2 and 3 ?
View SolutionThe charges and coordinates of two charged particles held fixed in an xy plane are q_(1) = +3.0 mu C, x_(1) = 3.5 cm, y_(1) = 0.50 cm , and q_(2) = -4.0 mu C, x_(2) =-2.0 cm, y_(2) = 1.5 cm . Find the (a) magnitude and (b) direction of the electrostatic force on particle 1 due to particle 2. At what (c ) x and (d) y coordinates should a third particle of charge q_(3) = +6.0 mu C be placed such that the net electrostatic force on particle 1 due to particles 2 and 3 is zero ?
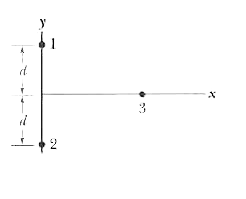
View SolutionIn Fig., particles 1 and 2 of charge q1=q2=+4e are on a y axis at distance d = 1.70 m from the origin. Particle 3 of charge q3=+8e is moved gradually along the x axis from x = 0 to x = +5.0 m. At what values of x will the magnitude of the electrostatic force on the third particle from the other two particles be (a) minimum and (b) maximum ? What are the (c ) minimum and (d) maximum magnitudes ?
View SolutionFigure shows an arrangement of four charged particles, with angle theta = 35.0^(@) and distance d = 2.00 cm. Particle 2 has charge q_(2) = +8.00 xx 10^(-19) C , particle 3 and 4 have charges q_(3) = q_(4) = -1.60 xx 10^(-19)C , (a) What is distance D between the origin and particle 2 if the net electrostatic force on particle 1 due to the other particles is zero ? (b) If particles 3 and 4 were moved closer to the x axis but maintained their symmetry about that axis, would the required value of D be greater than, less than, or the same as the part (a) ?
View SolutionIn Fig., three charged particles lie on an x axis. Particles 1 and 2 are fixed in place. Particle 3 is free to move, but the net electrostatic force on it from particles 1 and 2 happens to be zero. If 2.0L23=L12, what is the ratio q1/q2 ?
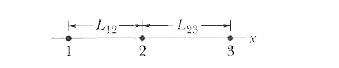
View Solution

