How does current in a pure capacitor vary in terms of phase angle with the voltage across it? Solution in Kannada
If V=V0sinωt
q=CV=CV0sinωt
I=dqdt=ωCV0cosωt
or I=ωCV0sin(ωt+π2)
So, the current leads the applied voltage in phase by π/2.
Similar Questions
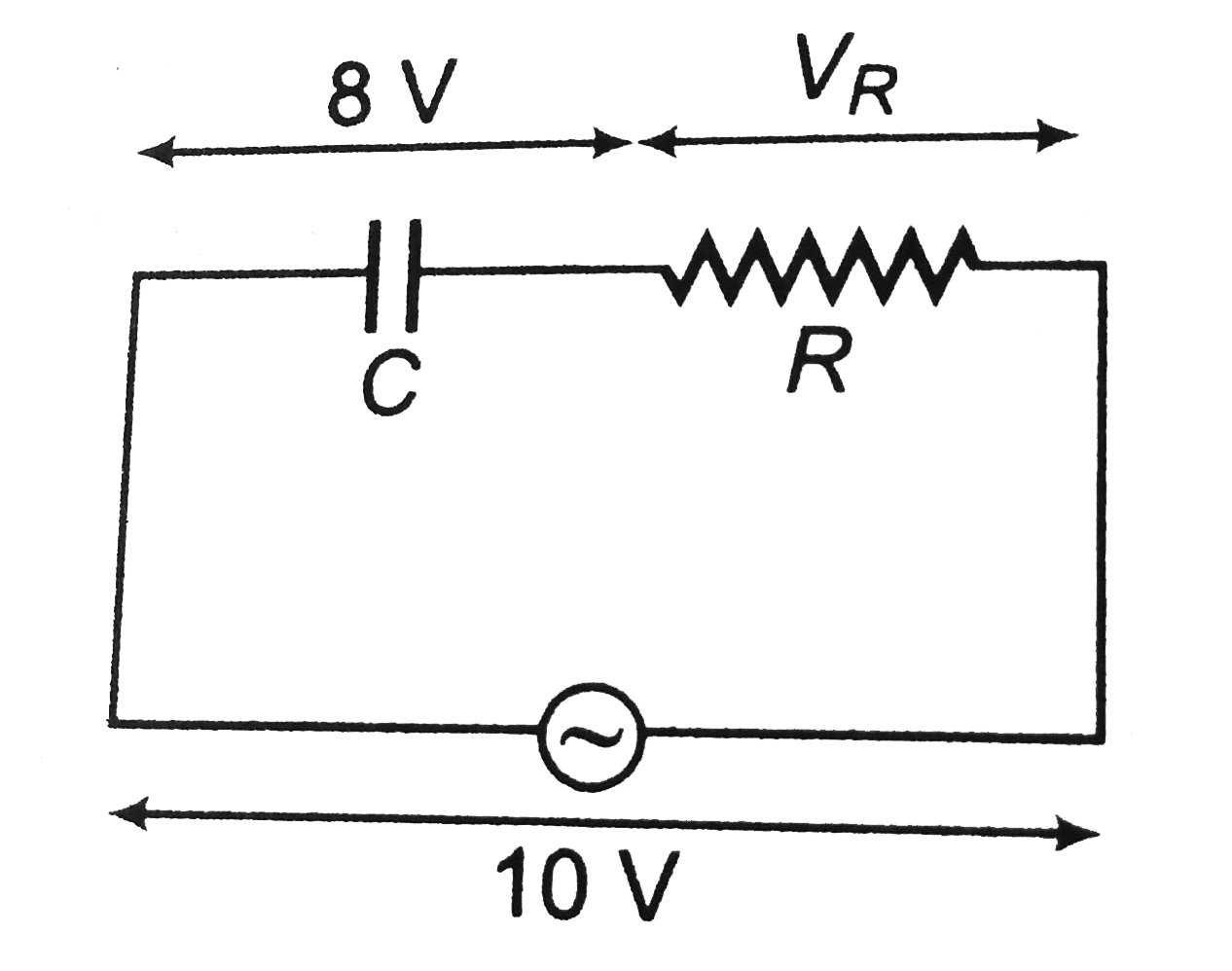
In a series C−R circuit shown in figureure, the applied voltage is 10V and the voltage across capacitor is found to8V. The voltage across R, and the phase difference between current and the applied voltage will respectively be
 .
.
View SolutionIn a series C-R circuit shown in figureure, the applied voltage is 10 V and the voltage across capacitor is found to 8 V . The voltage across R , and the phase difference between current and the applied voltage will respectively be .
View SolutionWhat will be the phase difference between the current and voltage when 240 V, 60 Hz ac source is connected across (a) a pure capacitor (b) a pure inductor?
View SolutionExplain the term 'capacitive reactance'.Show graphically the variation of capacitive reactance with frequency of the applied alternating voltage. An a.c. voltage E=E_(0) sin omegat is applied a across a pure capacitor C .Show mathematically that the current flowing through it leads the applied voltage by a phase angle of pi//2
View SolutionThe phase angle between current and voltage in a purely inductive circuit is
View SolutionVoltage across a capacitor varies as shown in the diagram. Which diagram correctly represents the current time curve?

View SolutionWhat is the phase difference between voltage across the inductance and a capacitor in an a.c. circuit?
View SolutionIn a series LCR circuit the voltage across an inductor, a capacitor and a resistor are 30V, 30V and 60V respectively. What is the phase difference between the applied voltage and current in the circuit?
View Solution
