Obtain the first Bohr's radius and the ground state energy of muonic hydrogen atom [i.e., an atom in which a negatively charged (μ−) of mass about 207 me orbits around a proton].
According to Bohr.s theory of hydrogen atom radius of nth orbit will be
rn=∈0n2h2πme2⇒rn∞1m
∴ Radius of first Bohr.s orbit for a muonic hydrogen atom .
rm=re.memm=5.3×10−11.me207me=2.56×10−13m
Similarly expression for energy En=−me48∈20n2h2 suggests that En∝m
∴ Energy in 1 st orbit of muonic hydrogen atom will be
Em=Ee.mmme=(−13.6eV).207meme=−2.8×103eV=−2.8KeV
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ATOMSBOOK - U-LIKE SERIESCHAPTER - ATOMSEXERCISE - CASE BASED/SOURCE - BASED INTERGRATED QUESTIONS
10 Videos
- ATOMSBOOK - U-LIKE SERIESCHAPTER - ATOMSEXERCISE - MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
30 Videos
- ATOMSBOOK - U-LIKE SERIESCHAPTER - ATOMSEXERCISE - SELF ASSESSMENT TEST (SECTION C)
2 Videos
- ALTERNATING CURRENT BOOK - U-LIKE SERIESCHAPTER - ALTERNATING CURRENT EXERCISE - SELF ASSESSMENT TEST (SECTION -C)
2 Videos
- CBSE EXAMINATION PAPER 2020 BOOK - U-LIKE SERIESCHAPTER - CBSE EXAMINATION PAPER 2020 EXERCISE - SECTION D
12 Videos
Similar Questions
Read the pasage given below as well as the adjoining energy level diagram and then answer the questions given after the passage .
As per Bohr's theory og hydrogen atom the energy of an atom in a state corresponding to principal quantum number n is given as :
En=−13.6n2eV
The energy of an atom is the least when its electron is revolving in an orbit closets to the nucleus i.e., the one for which n =1. This state is called the ground state. When a hydrogen atom receives energy by processes such as electron collision , the atom may acquire sufficient energy to raise the electron to higher energy states and the atom is then said to be in an excited state . From these excited states the electron can then fall back to a state of lower energy , emitting a photon in the process.
The energy level diagram for the stationary states of a hydrogen atom , compouted from Bohr's relation for energy , is given in Fig.12.02. The principal quantum number n labels the stationary states in the ascending order of energy . Obviously , the highest energy corresponds to n=∞ and has an energy of 0 eV. This is the energy of the atom when the electron is completely removed (r=∞) from the nucleus and is at rest.
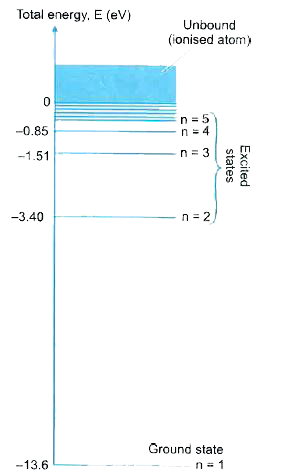
Now answer the follwoing questions:
What does negative value of atomic energy signify?
View SolutionThe Rutherford α - particle experiment shows that most of the α - particle pass through almost unscattered while some are scattered though large angles. What information does it gives about the structure of the atom ?
View SolutionA monochromatic radiation of wavelength 975Å excites the hydrogen atom from its ground state to a higher state . How many different spectral lines are possivle in the resulting spectrum ? Which transition corresponds to the longest wavelenght amongst them ?
View SolutionA capacitor (C) and resistor (R) are connected in series with an a.c. source of voltage of frequency 50 Hz. The potential difference across C and R are respectively 120 V, 90 V, and the current in the circuit is 3 A. Calculate (i) the impedance of the circuit (ii) the value of the inductance, which when connected in series with C and R will make the power factor of the circuit unity.
View SolutionUse Gauss's law to show that due to uniformly charged spherical shell of radius R, the electric field at any point situated outside the shell at a distance r from its centre is equal to the electric field at the same point, when the entire charge on the shell were concentrated at its centre. Also plot the graph showing the variation of electric field with r, for r≤R and r≥R.
View SolutionObtain the first Bohr radius and the ground state energy of a muonic hydrogen atom (i.e., an atom in which a negatively charged muon (mu) of mass about 207m_e revolves around a proton).
View Solutionif muonic hydrogen atom is an atom in which a negatively charged muon (mu) of mass about 207m_e revolves around a proton, then first bohr radius of this atom is (r_e=0.53xx10^(-10)m)
View Solutionप्रथम बोहर-त्रिज्या और म्यूओनिक हाइड्रोजन परमाणु [अर्थात कोई परमाणु जिसमें लगभग 207 me द्रव्यमान का ऋणावेशित म्यूऑन (μ−) प्रोटॉन के चारों ओर घूमता है] कि निम्नतम अवस्था ऊर्जा तो प्राप्त करने का परिकलन कीजिए।
View Solutionम्युऑनिक हाइड्रोजन परमाणु में ऋणावेशित म्यूऑन (μ−) जिसका द्रव्यमान इलेक्ट्रॉन के द्रव्यमान का 207 गुना होता है, प्रोटॉन के चारो ओर परिक्रमण करता है। इस परमाणु के लिए प्रथम बोर त्रिज्या तथा निम्नतम ऊर्जा के मान प्राप्त करे। सामान्य हाइड्रोजन की निम्नतम कक्षा की त्रिज्या 5.3×10−11m और निम्नतम ऊर्जा −13.6eV ले ।
View SolutionObtain the first Bohr radius and the ground state energy of a muonic hydrogen atom (I.e ., an atom in which negatively charged muon ( mu^(-)) of mass about 207 m_e orbits around a proton).
View Solutionप्रथम बोर-त्रिज्या ओर म्यूओनिक हाइड्रोजन परमाणु अर्थात कोई परमाणु जिसमे लगभग 207me द्रव्यमान का ऋणावेशित म्यूऑन (μ−) प्रोटॉन के चारो ओर घूमता है की निम्नतम अवस्था ऊर्जा को प्राप्त करने का परिकलन कीजिए।
View SolutionObtain the first Bohr’s radius and the ground state energy of a muonic hydrogen atom [i.e., an atom in which a negatively charged muon (μ–) of mass about 207me orbits around a proton].
View Solutionএকটি মিউয়নিক হাইড্রোজেনের (একটি পরমাণু যাতে 207me ভর বিশিষ্ট একটি ঋণাত্মক মিউয়ন কণা একটি প্রোটনের চারিদিকে আবর্তন করছে)প্রথম বোর কক্ষপথের ব্যাসার্ধ এবং ভূমিস্তরের শক্তি নির্ণয় করো|
View SolutionObtain the first Bohr’s radius and the ground state energy of a muonic hydrogen atom [i.e., an atom in which a negatively charged muon (mu^(–)) of mass about 207m_e orbits around a proton].
View SolutionObtain the first Bohr’s radius and the ground state energy of a muonic hydrogen atom [i.e., an atom in which a negatively charged muon (μ–) of mass about 207me orbits around a proton].
View Solution

