When an object is placed normally on the principal axis of a spherial mirror at a distance 'a' from its pole, its image is formed at a distance 'v' from the pole of mirror such that 1v+1u=1f, where f = focal length of given mirror.
The relation is called mirror formula and is true for all types of mirrors under all conditions. However, values of u, v and f must be put with proper signs are per the sign convention followed. If 'h' be the height of the linear object and h' the height of image, then ratio h'h is called linear magnification or lateral magnification and its value m is given as :
m=h'h=−vu
(e) Find an expression for longitudinal magnification of a small object placed linearly along the axis of a spherical mirror.
Let linear size of object be du andlinear size of its image be dv.
As per mirror formula, we have
1v+1u=1f
On differentiation, we get
−dvv2−duu2=0
⇒ dvv2=−duu2
∴ Longitudinal magnification =dvdy=−v2u2
Similar Questions
When an object is placed normally on the principal axis of a spherial mirror at a distance 'a' from its pole, its image is formed at a distance 'v' from the pole of mirror such that 1v+1u=1f, where f = focal length of given mirror.
The relation is called mirror formula and is true for all types of mirrors under all conditions. However, values of u, v and f must be put with proper signs are per the sign convention followed. If 'h' be the height of the linear object and h' the height of image, then ratio h'h is called linear magnification or lateral magnification and its value m is given as :
m=h'h=−vu
(d) Define longitudinal magnification.
View SolutionWhen an object is placed normally on the principal axis of a spherial mirror at a distance 'a' from its pole, its image is formed at a distance 'v' from the pole of mirror such that 1v+1u=1f, where f = focal length of given mirror.
The relation is called mirror formula and is true for all types of mirrors under all conditions. However, values of u, v and f must be put with proper signs are per the sign convention followed. If 'h' be the height of the linear object and h' the height of image, then ratio h'h is called linear magnification or lateral magnification and its value m is given as :
m=h'h=−vu
What is the surface area of image of linear object formed by the given concave mirror?
View Solution
Knowledge Check
An object is placed on the principal axis of a concave mirror at a distance of 1.5 f(f is the focal length). The image will be at,
A1.5fB−1.5fC3fD−3fWhat is f in mirror formula 1u+1v=1f ?
Adistance of objectBdistance of imageCfocal lengthDNone.An object is present on the principal axis of a concave mirror at a distance 30cm from it. Focal length of mirror is 20cm.
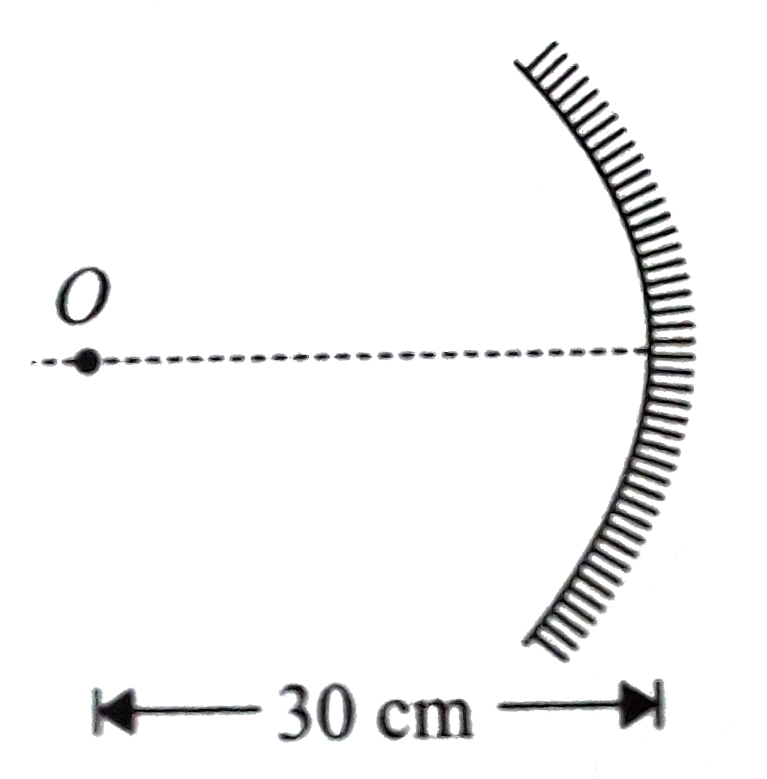
Q. Image formed by mirror isAAt a distance of 60cm in front of mirrorBAt a distance 60cm behind the mirrorCAt a distance 12 cm in front of mirrorDAt a distance 12cm behind the mirror
When an object is placed normally on the principal axis of a spherial mirror at a distance 'a' from its pole, its image is formed at a distance 'v' from the pole of mirror such that 1v+1u=1f, where f = focal length of given mirror.
The relation is called mirror formula and is true for all types of mirrors under all conditions. However, values of u, v and f must be put with proper signs are per the sign convention followed. If 'h' be the height of the linear object and h' the height of image, then ratio h'h is called linear magnification or lateral magnification and its value m is given as :
m=h'h=−vu
(a) A planer object of length 3 cm and breadth 2 cm is held normal to the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm at a distance of 30 cm from its pole. Where is its image formed?
View SolutionWhen an object is placed normally on the principal axis of a spherial mirror at a distance 'a' from its pole, its image is formed at a distance 'v' from the pole of mirror such that 1v+1u=1f, where f = focal length of given mirror.
The relation is called mirror formula and is true for all types of mirrors under all conditions. However, values of u, v and f must be put with proper signs are per the sign convention followed. If 'h' be the height of the linear object and h' the height of image, then ratio h'h is called linear magnification or lateral magnification and its value m is given as :
m=h'h=−vu
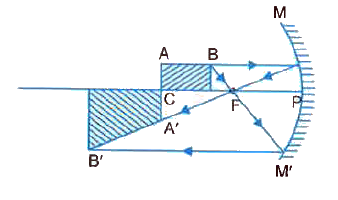
A small match box lies along the principal axis of a concave mirror and one end of match box is at centre of curvature of the mirror. Draw a ray diagram to show its image. Is its magnetification uniform?
View SolutionAn object is present on the principal axis of a concave mirror at a distance 30cm from it. Focal length of mirror is 20cm.

Q. Image formed by mirror is
View SolutionAn object is present on the principal axis of a concave mirror at a distance 30cmfrom it.Focal length of mirror is20cm
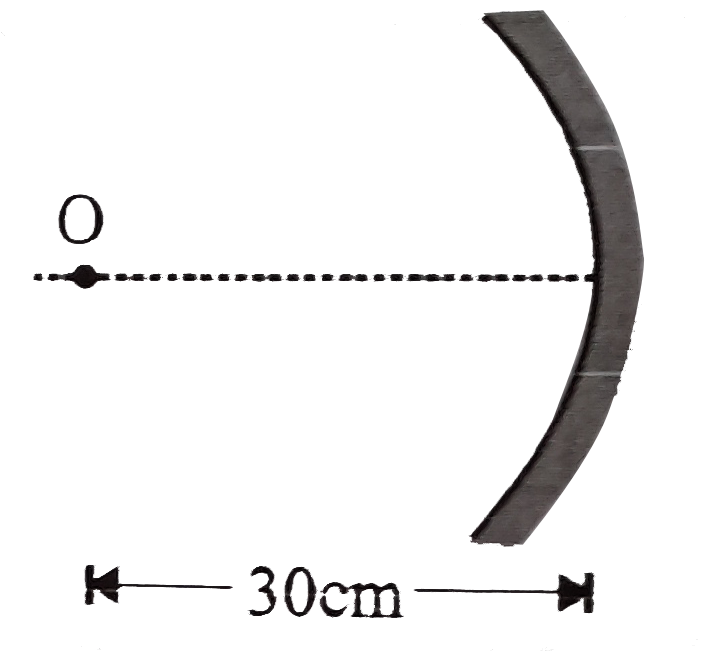
Image formed by mirror is
View SolutionAn object is kept on the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 10cm, at a distance of 15 cm from its pole. The image formed by the mirror is:
View Solution

