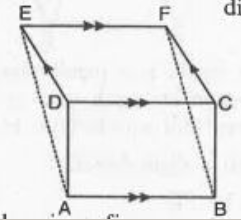
In the adjoing figure, two parallelograms ABCD and AEFB are drawn on opposite sides of AB. Prove that
ar(||gm ABCD)+ar(||gm AEFB)
=ar(||gm EFCD).
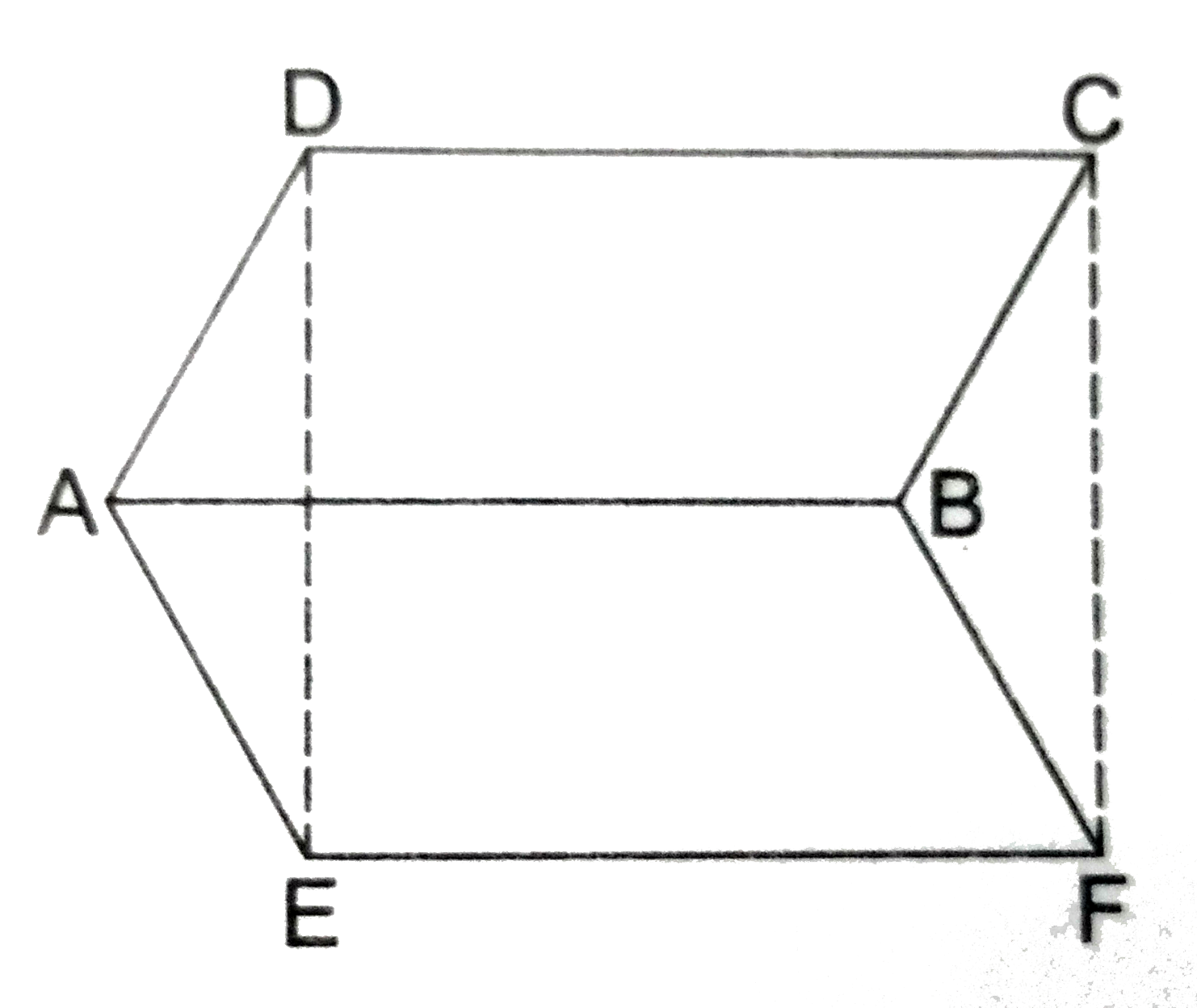
In △AED and △BFC, we have
AD = BC, AE = BF and DE = CF (opp. Sides of a ||gm).
∴△AED≅△BFC.
So, ar(△AED)=ar(△BFC). ...(i)
ar(||gm ABCD)+ar(||gm AEFB)
=ar(||gm DEFC)+ar(△AED)−ar(△BFC)
=ar(||gm EFCD) [ using (i)].
Similar Questions
चित्र में , ABCD एक समान्तर चतुर्भुज है तथा EFCD एक आयत है। साथ ही AL⊥DC, तो सिद्ध कीजिए कि
(i)ar(ABCD)=ar(EFCD)
(ii)ar(ABCD)=DC×AL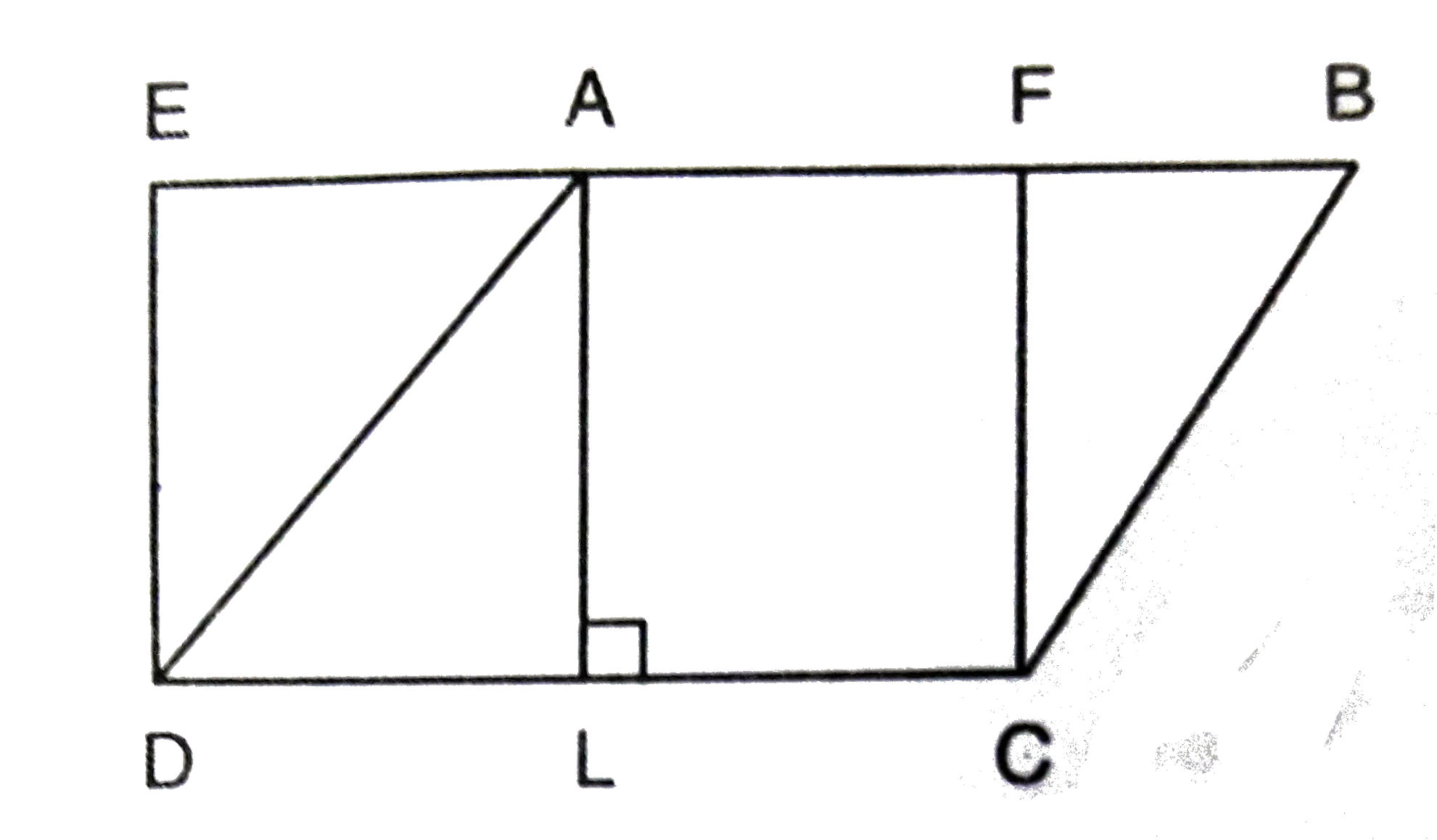
View Solutionचित्र में PQRS तथा ABRS समान्तर चतुर्भुज है तथा X भुजा BR पर स्थित कोई बिंदु है। दर्शाए कि
(i)ar(||gmPQRS)=ar(||gmABRS) (ii)ar(ΔAXS)=12ar(||gmPQRS)
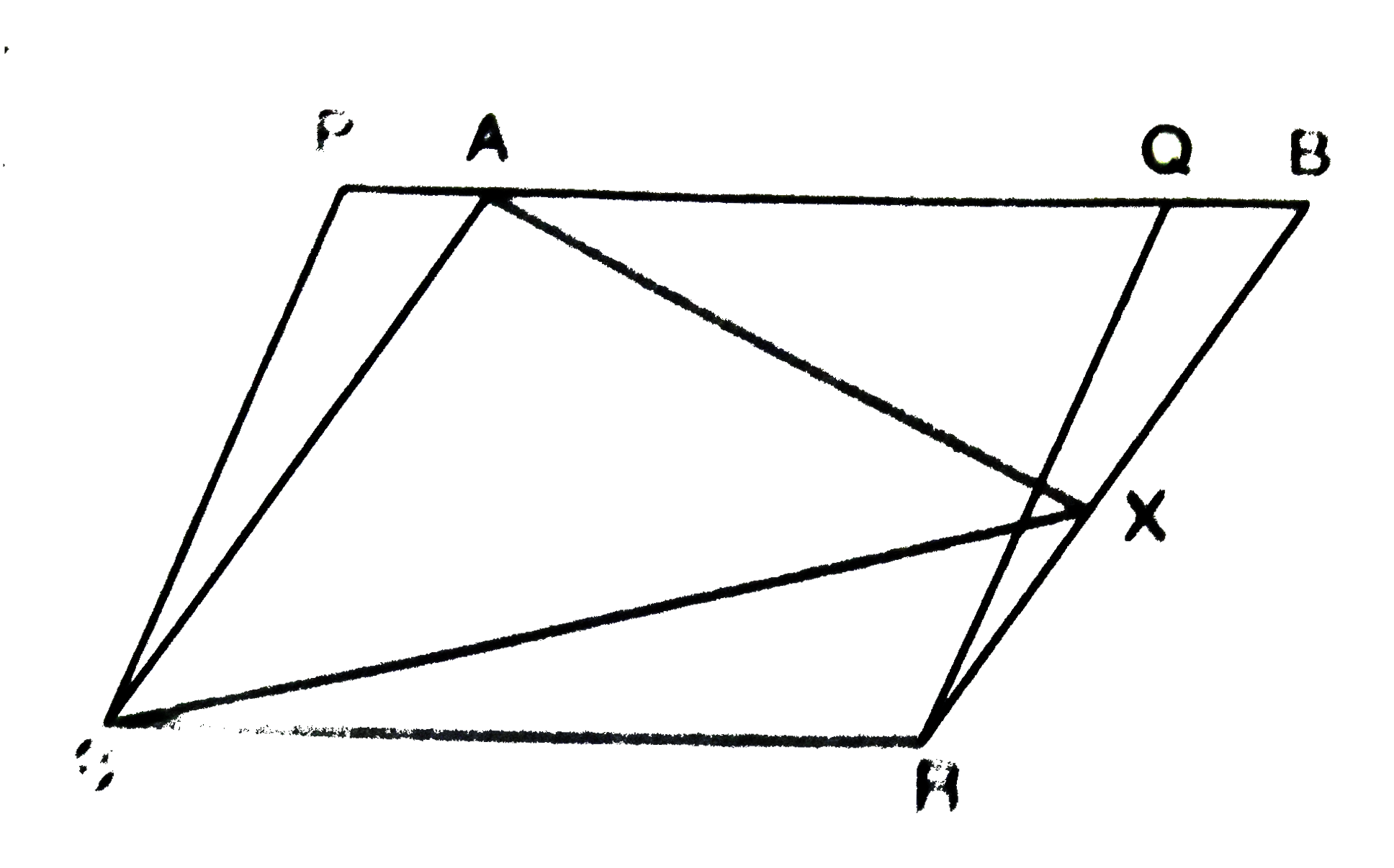
View SolutionABCD एक समांतर चतुर्भुज है तथा O इसके अन्तः क्षेत्र में स्थित कोई बिंदु है सिद्ध कीजिए कि
(i) ar(ΔAOB)+ar(ΔCOD)=ar(ΔBOC)+ar(ΔAOD)
(ii) ar(ΔAOB)+ar(ΔCOD)=12ar(।।gmABCD)
View Solutionसमांतर चतुर्भुज ABCD की भुजा AB को किसी बिंदु P तक बढ़ाया गया है। बिंदु A से CP के समांतर खींची गयी रेखा CB के आगे बढ़ाये गये भाग को Q पर मिलती है। और समांतर चतुर्भुज PBQR को पूरा करती है। सिद्ध कीजिए कि
ar(।।gmABCD)=ar(।।gmBPRQ)
View Solutionयदि ABCD एक समांतर चतुर्भुज है, तो सिद्ध कीजिए कि
ar(ΔABD)=ar(ΔBCD)=ar(ΔABC)=ar(ΔACD)=12ar(||gmABCD)
View Solutionचित्र में, ABCD एक समान्तर चतुर्भुज है। AC पर कोई बिंदु O है। यदि PQ ।। AB तथा LM ।। AD तो सिद्ध कीजिए कि ar(।।gmDLOP)=ar(।।gmBMOQ)
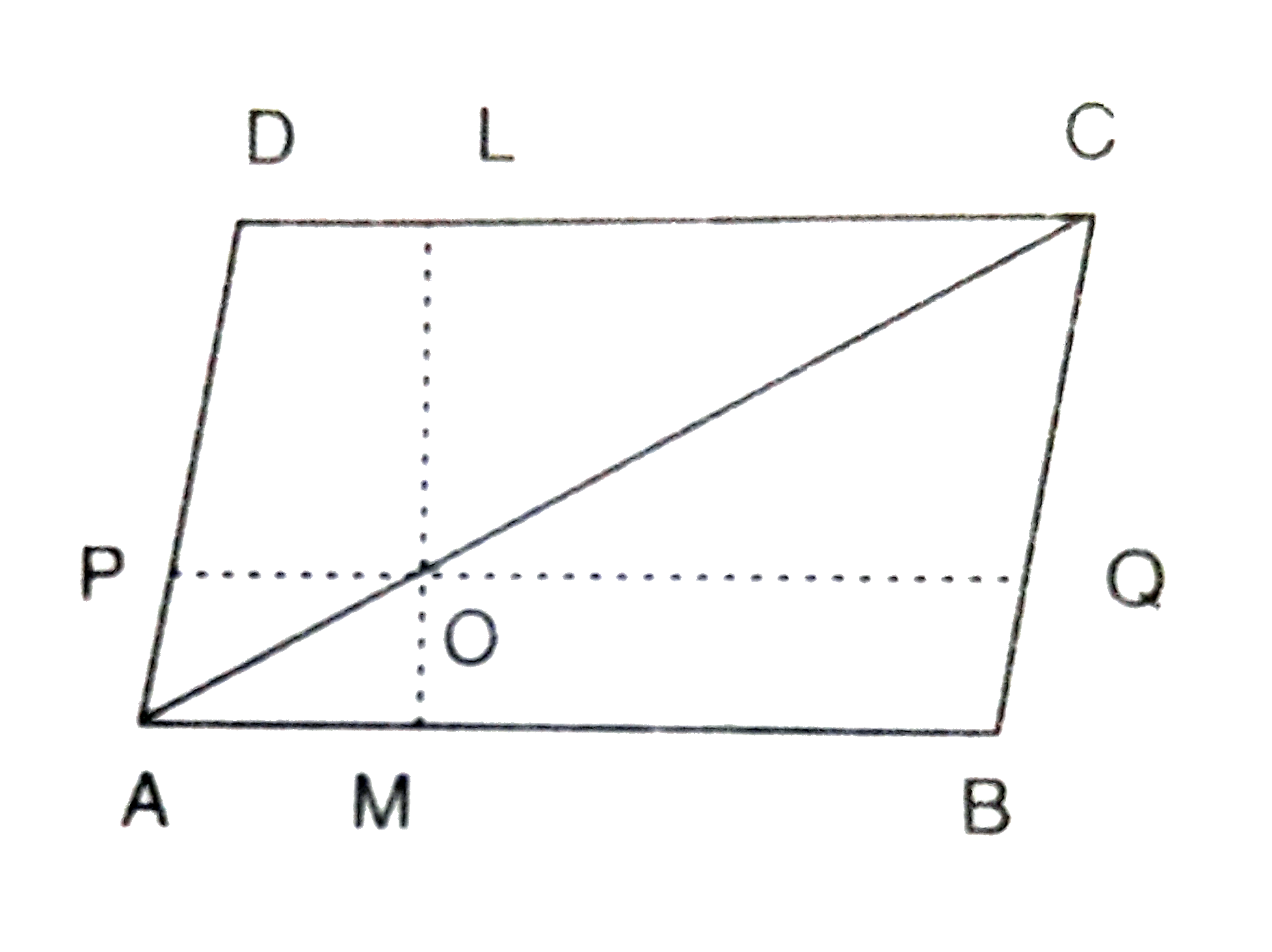
View SolutionThe side AB of a parallelogram ABCD is produced to any point P. A line through A and parallel to CP meets CB produced at Q and then parallelogram PBQR is completed as shown in Figure. Show that ar(∣∣gmABCD)=ar(∣∣gmPBQR)
View SolutionIn the given figure
 ABCD is a rectangle and a parallelogram CDEF drawn on opposite side of CD. If ar(∣∣gmABFE)=60cm2 and ar(∣∣gmCDEF)=32cm2, find ar(rect ABCD).
ABCD is a rectangle and a parallelogram CDEF drawn on opposite side of CD. If ar(∣∣gmABFE)=60cm2 and ar(∣∣gmCDEF)=32cm2, find ar(rect ABCD).
View Solution
