The stability of complex ion depend upon charge, size electronegativity of metal ion. Greater the charge of metal ion greater would be the stability. As size of metal ion decreases stability of metal ion increases complex ion more stable if chelating ligand present.
Fe+3+6CN−⇔[Fe(CN)6]−3,K1
Fe+2+6CN−⇔[Fe(CN)6]−4,K2 : the value of K1 and K2 are Solution in Telugu
1.8×106,1.2×1031
1.8×106,1.8×106
1.2×1031,1.2×1031
1.2×1031,1.8×106
The correct Answer is:D
Stability of complex ion, α Charge of metal ion α=1size of metal ion
Hence, order of stability [Fe..(CN)6]4−<[Fe..(CN)6]3−⇒K2<K1
Topper's Solved these Questions
- CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDSBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDSEXERCISE - LEVEL-II LECTURE SHEET EXERCISE-II (Linked Comprehension type questions ) Passage-VI
3 Videos
- CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDSBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDSEXERCISE - LEVEL-II EXERCISE-III (Match the following questions)
13 Videos
- CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDSBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDSEXERCISE - LEVEL-II LECTURE SHEET EXERCISE-II (Linked Comprehension type questions ) Passage-IV
3 Videos
- CHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE BOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - CHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE EXERCISE - PRACTICE SHEET - 2 (PRACTICE SHEET -2 (INTEGER ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS))
7 Videos
- COMPLEX COMPOUNDS BOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - COMPLEX COMPOUNDS EXERCISE - PRACTICE EXERCISE
45 Videos
Similar Questions
The d-orbitals participating in hybridisation of metal atom may be from the n & (n-1) shell. This depends on the nature of metal and nature of ligand. The complexes involving the inner d-level (inner orbital complexes) results when the ligand is a powerful (or) strong ligand results in a diamagnetic (or) low spin complexes. A weak ligand usually results in the formation of outer orbital complex (or) high spin complex.
The hybridisation of Cu in [CuCl4]2−&[Cu(NH3)4]2+ are respectivly
View SolutionMatch Column-I (Compounds) with Column - II (Oxidation states of Co) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the Columns
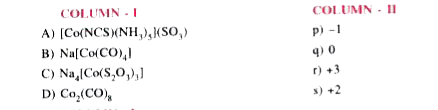
View SolutionThe central metal ion in the complex makes available a number of empty orbitals for the formation of co-ordinate bonds with suitable ligands. The inner d-orbitals or outer d-orbitals are involved. The empty hybrid orbitals of metal ion overlap with the filled orbitals of ligand to from metal ligand co-ordinate bonds. For co-ordination number 6 octahedral geometry and sp3,d2ord2sp2 hybridisation involved and for cordiantion number 4 tetrahedral geometry, square planar geometry and sp3.dsp2 hybridisation involved.
Hybridisation present in [Cr(NH3)6]+3
View SolutionOne mole Benzene in presence of light on reaction with 'x' moles of Cl2 forms B.H.C. what is 'x' ?
View SolutionThe primary and secondary valencies of the central metal ion in the complex [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 respectively are
View SolutionWith K4[Fe(CN)6],Cu2+ ion gives
View SolutionA metal ion give chocolate coloured ppt with K_(4)[Fe(CN)_(6)] What is the oxidation state of that metal in its ion ?
View Solutionक्या K4[Fe(CN)6] के विलयन में Fe2+ आयन उपस्थित होते हैं ?
View SolutionOxidation state of the metal ion in the complex [Fe(CN)6]3− is
View SolutionThe complex ions [Fe(CN)_(6)]^(3-) and [Fe(CN)_(6)]^(4-) __________.
View SolutionThe complex ions [Fe(CN)_(6)]^(3-) and [Fe(CN)_(6)]^(4-) :
View SolutionK3[Fe(CN)6]में केन्द्रीय धातु आयन का ऑक्सीकरण संख्या व उपसहसंयोजक संख्या बताइये?
View Solutionनिम्नलिखित संकुलों में केंद्रीय धातु आयन की ऑक्सीकरण अवस्था एवं उपसहसंयोजन संख्या दीजिए।
K4[Fe(CN)6]
View SolutionThe complex ion in k4[Fe(CN)6] is ……… .
View SolutionThe number of ions present in K3[Fe(CN)6] are:
View Solution

