The random variable X can take only the values 0,1,2. If
P(X=0)=P(X=1)=pandE(X2)=E[X],
then find valu of p.
Since, X=0,1,2 and P(X) at X =0 and 1 is p, let at X=2,P(X) is x.
⇒P+P+x=1
⇒x=1−2p
We get, the following distribution.
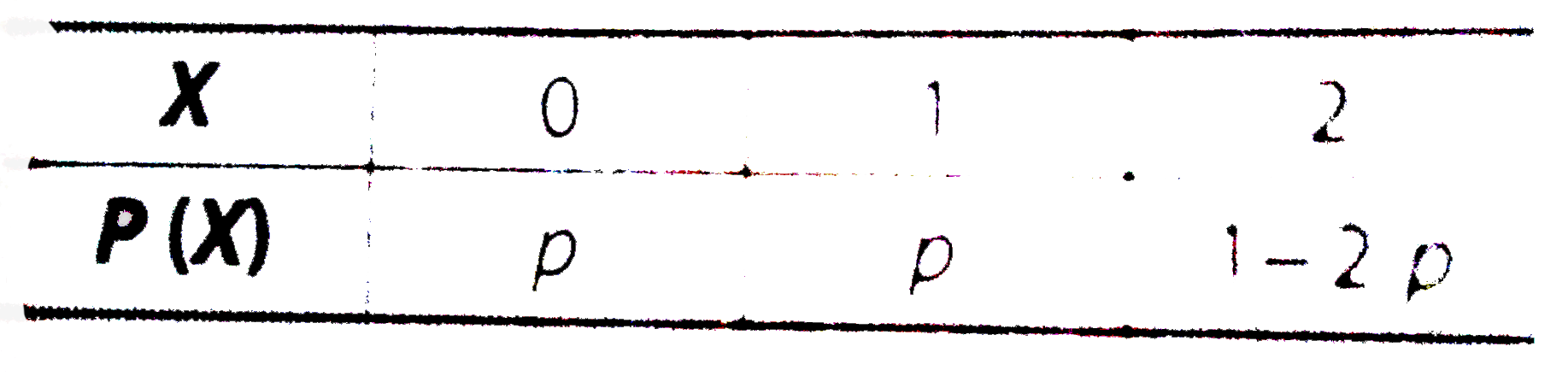
∴E[X]=∑XP(X)
=0⋅p+1⋅p+2(1−2p)
and E(X2)=∑X2P(X)
=0⋅P+1⋅p+4⋅(1−2p)
=p+4−8p=4=−7p
Also, given thatE(X2)=E[X]
⇒4−7p=2−3p
⇒4p=2⇒p=12
Topper's Solved these Questions
- PROBABILITYBook:NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISHChapter:PROBABILITYExercise:Long Answer Type Questions
Explore 15 Videos
- PROBABILITYBook:NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISHChapter:PROBABILITYExercise:Objective Type Questions
Explore 38 Videos
- MATRICESBook:NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISHChapter:MATRICESExercise:Solved example
Explore 101 Videos
- RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONSBook:NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISHChapter:RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONSExercise:Fillers
Explore 15 Videos
Similar Questions
Knowledge Check
A random variable X takes the values 0,1,2,3 and its mean = 1,3 .If P(X=3) =2P(X=1) and P(X=2) = 0.3 then P(X=0) is
A0.4B0.3C0.2D0.1
The random variable X can the values 0, 1, 2, 3, Give P(X = 0) = P(X = 1)= p and P(X = 2) = P(X = 3) such that ∑pix2i=2∑pixi then find the value of p
View SolutionThe random variable takes the values 1,2,3,…….m. If P(X=n)=1m to each n, then the variance of X is
View SolutionA randomm variable X takes the value -1,0,1. It's mean is 0.6. If (X=0)=0.2 then P(X=1)=
View SolutionA random variate X takes the values 0, 1, 2, 3 and its mean is 1.3. If P(X=3)=2P(X=1) and P(X=2)=0.3, then P(X=0) is equal to
View SolutionA random variable X takes the values 0,1,2,3,..., with prbability PX(=x)=k(x+1)(15)x, where k is a constant, then P(X=0) is.
View SolutionThe range of a random variable X is {0, 1, 2}. Given that P(X=0)=3c3,P(X=1)=4c−10c2,P(X=2)=5c−1 where c is constant.
Find (i) the value of c (ii) P(X<1)
(iii) P(1<X≤2) (iv) P(0<X≤3)
View SolutionIf X is a random variable with probability distribution P(X=k)=(k+1)C2k,K=0,1,2,…. then find C.
View Solution
