Let g(x)=√x−2k,∀2k≤x<2(k+1), where k∈ integer. Check whether g(x) is periodic or not.
g(x)=√x−2k,∀2k≤x<2(k+1), where k∈Z.
=⎧⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪⎨⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
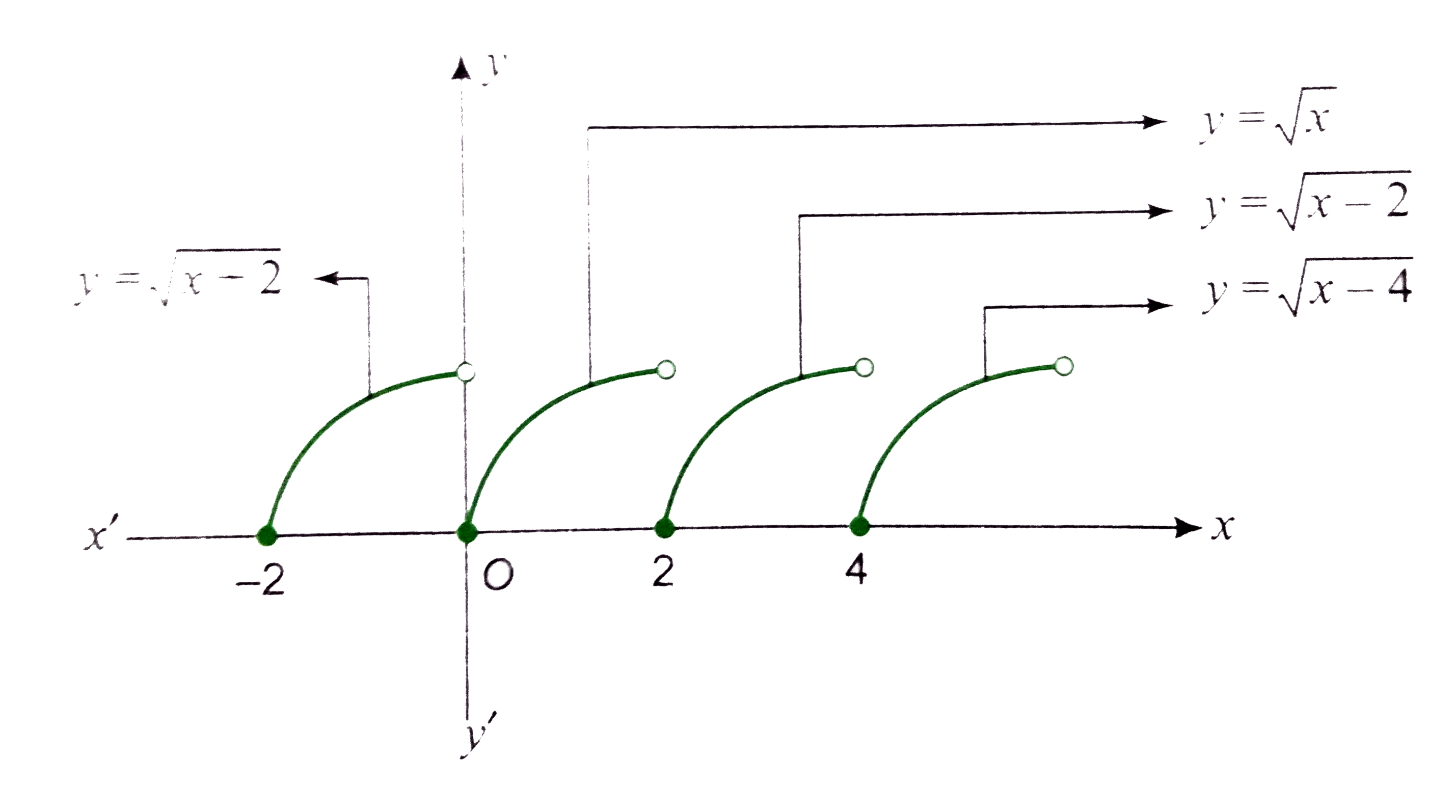
⎪⎩......√x+2,−2≤x<0√x,0≤x<2√x−2,2≤x<4√x−44≤x<6......
Graph of the function is as shown in the figure.
Similar Questions
Let g be a function defined by g(x)=√{x}+√1−{x} .where {.} is fractional part function, then g is
View SolutionLet g(x)=√x−2k,∀2k≤x<2(k+1), where k∈ integer. Check whether g(x) is periodic or not.
View SolutionLet g(x)=√x−2K,∀2K≤x<2(k+1), wherek∈ integer . If g(x) is periodic then period of g(x) is
View Solutionϕ(x)=f(x)g(x)andf'(x)g'(x)=k, then 2kf(x)g(x) =
View SolutionCheck whether following pairs of function are identical or not?
f(x)=√x2 and g(x)=(√x)2
View SolutionLet a function f be even and integrable everywhere and periodic with period 2. Let g(x)=∫x0f(t)dt and g(t)=kThe value of g(2) in terms of k is equal to (A) k (B) 2k (C) 3k (D) 5k
View SolutionFind the domain of f(x)=√([x]−1)+√(4−[x]) (where [ ] represents the greatest integer function).
View SolutionLet g(x)=√x−2k,∀2k≤x<2(k+1), where k∈ integer. Check whether g(x) is periodic or not.
View Solution

