Can the potential difference across a battery be greater than its emf?
To determine whether the potential difference across a battery can be greater than its electromotive force (emf), we can analyze the relationship between the potential difference (V), emf (E), current (I), and internal resistance (R) of the battery. Here’s the step-by-step solution:
Step 1: Understand the Definitions
- Electromotive Force (emf, E): This is the maximum potential difference that a battery can provide when no current is flowing.
- Potential Difference (V): This is the voltage across the terminals of the battery when it is connected in a circuit and current is flowing.
Step 2: Use the Formula
The relationship between the potential difference (V), emf (E), current (I), and internal resistance (R) of the battery is given by the formula:
V=E−I⋅R
Step 3: Analyze the Formula
From the formula:
- When there is no current flowing (I = 0), the potential difference (V) equals the emf (E).
- When current flows (I > 0), the term I⋅R (which represents the voltage drop due to internal resistance) is subtracted from the emf.
Step 4: Conclusion
Since I⋅R is always a positive value when current is flowing, it follows that:
V=E−I⋅R<E
This means that the potential difference (V) across the battery cannot exceed the emf (E) when current is flowing.
Final Answer
Thus, the potential difference across a battery cannot be greater than its emf. The answer to the question is No.
---
- Electromotive Force (emf, E): This is the maximum potential difference that a battery can provide when no current is flowing.
- Potential Difference (V): This is the voltage across the terminals of the battery when it is connected in a circuit and current is flowing.
The relationship between the potential difference (V), emf (E), current (I), and internal resistance (R) of the battery is given by the formula:
V=E−I⋅R
From the formula:
- When there is no current flowing (I = 0), the potential difference (V) equals the emf (E).
- When current flows (I > 0), the term I⋅R (which represents the voltage drop due to internal resistance) is subtracted from the emf.
Since I⋅R is always a positive value when current is flowing, it follows that:
V=E−I⋅R<E
This means that the potential difference (V) across the battery cannot exceed the emf (E) when current is flowing.
Thus, the potential difference across a battery cannot be greater than its emf. The answer to the question is No.
Similar Questions
In the simple L-R circuit, can the emf induced across the inductor ever be greater than the emf of the battery used to produce the current?
View SolutionIn the circuit shown the ammeter 'A' reads 2A. XY is a circuit which can either be a resistance of a battery. In the direction of the current there will always be a potential drop across the resistance. Reagarding battery you have to remember that the potential difference across its terminals can be more than its emf or less depending upon whether the battery is delivering the current, or is being charged in the circuit
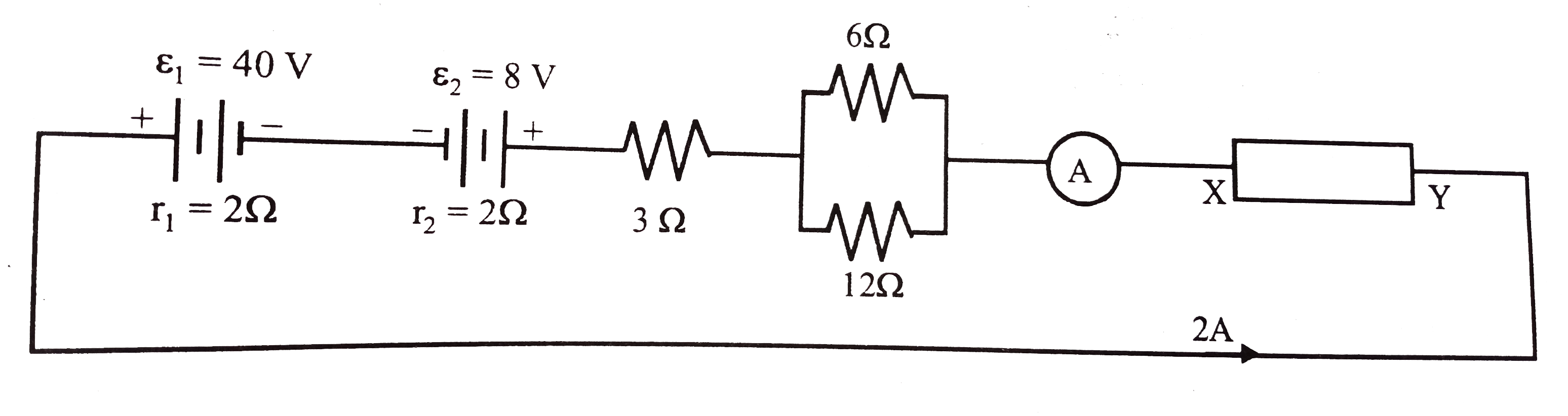
Assuming XY to be a battery with 2Ω internal resistance which is being charged, its emf is:
View SolutionIn the circuit shown the ammeter 'A' reads 2A . XY is a circuit which can either be a resistance of a battery. In the direction of the current there will always be a potential drop across the resistance. Reagarding battery you have to remember that the potential difference across its terminals can be more than its emf or less depending upon whether the battery is delivering the current, or is being charged in the circuit The potential difference as you move from Y to X while considering it to be a battery is :
View SolutionA battery of emf E and internal resistance r is connected across a resistance R. Resistance R can be adjusted to any value greater than or equal to zero. A graph is plotted between the current passing through the resistance (I) and potential difference across the termainals of the battery (V). Maximum power developed across the resistance R is
View SolutionAssertion : Potential difference across the terminals of a battery is always less than the emf of the battery. Reason : During discharging of a battery potential differnce across to terminals of a battery is V = E -ir therefore V lt E
View SolutionThe terminal voltage across a battery of emf E can be
View Solutionक्या बैटरी के टर्मिनलो के मध्य विभवांतर का मान उसके वि वा बल से अधिक हो सकता है ?
View SolutionState the condition under which the terminal potential difference across a battery and its emf are equal.
View SolutionThe terminal potential difference of a cell is greater than its emf when it is
View SolutionPotential difference across the terminals of a cell is always less than its emf.
View SolutionInternal resistance of battery of emf 2E is R_1 and battery of emf E is R_2 . If the potential difference across the cell of emf 2E is zero, then value of R is
View SolutionIn the simple L-R circuit, can the emf induced across the inductor ever be greater than the emf of the battery used to produce the current?
View SolutionA battery of emf E and internal resistance r is connected across a resistance R. Resistance R can be adjusted to any value greater than or equal to zero. A graph is plotted between the current passing through the resistance (I) and potential difference across the termainals of the battery (V). Maximum power developed across the resistance R is
View SolutionAssertion : Potential difference across the terminals of a battery is always less than the emf of the battery. Reason : During discharging of a battery potential differnce across to terminals of a battery is V = E -ir therefore V lt E
View SolutionIf the potential difference across the internal resistance r1 is equal to the emf E of the battery, then
View SolutionAssertion : Potential difference across the terminals of battery can be greater than its emf. Reason : When current is taken from battery, V = in - Ir (Symbols have their usual meaning).
View Solution
