If 0.1 mole H3POx is completely neutralised by 5.6g KOH then select the true statement.
(a) x=3 and given acid is diabasic
(b) x=4 and given acid has no P=H linkage
(c) x=2 and given acid does not form acid salt
(d) all of these
The correct Answer is:C
To solve the problem, we need to determine the value of x in the compound H3POx based on the neutralization reaction with KOH. Here are the steps to arrive at the solution:
Step 1: Calculate the moles of KOH
First, we need to calculate the number of moles of KOH from the given mass.
Given:
- Mass of KOH = 5.6 g
- Molar mass of KOH = 39 (K) + 16 (O) + 1 (H) = 56 g/mol
Calculation:
Moles of KOH=MassMolar mass=5.6 g56 g/mol=0.1 moles
Step 2: Determine the possible acids
The acid H3POx can take three different forms based on the value of x:
1. H3PO4 (x = 4)
2. H3PO3 (x = 3)
3. H3PO2 (x = 2)
Step 3: Analyze the neutralization reactions
Next, we will analyze how many moles of KOH are required for each acid:
1. For H3PO4:
- Reaction: H3PO4+3KOH→K3PO4+3H2O
- Moles of KOH required for 0.1 moles of H3PO4:
0.1 moles of H3PO4×3=0.3 moles of KOH
2. For H3PO3:
- Reaction: H3PO3+2KOH→K2HPO3+2H2O
- Moles of KOH required for 0.1 moles of H3PO3:
0.1 moles of H3PO3×2=0.2 moles of KOH
3. For H3PO2:
- Reaction: H3PO2+KOH→KH2PO2+H2O
- Moles of KOH required for 0.1 moles of H3PO2:
0.1 moles of H3PO2×1=0.1 moles of KOH
Step 4: Compare required moles of KOH with available moles
- From the calculations:
- H3PO4 requires 0.3 moles of KOH (not possible with 0.1 moles available).
- H3PO3 requires 0.2 moles of KOH (not possible with 0.1 moles available).
- H3PO2 requires 0.1 moles of KOH (this is possible with the available moles).
Step 5: Conclusion
Since only H3PO2 can react with the available 0.1 moles of KOH, we conclude that:
- x=2 and the acid is H3PO2.
Step 6: Identify the true statement
Among the given statements:
- The correct statement is: "X is equal to 2 and the given acid does not form acidic salt."
First, we need to calculate the number of moles of KOH from the given mass.
- Mass of KOH = 5.6 g
- Molar mass of KOH = 39 (K) + 16 (O) + 1 (H) = 56 g/mol
Moles of KOH=MassMolar mass=5.6 g56 g/mol=0.1 moles
The acid H3POx can take three different forms based on the value of x:
1. H3PO4 (x = 4)
2. H3PO3 (x = 3)
3. H3PO2 (x = 2)
Next, we will analyze how many moles of KOH are required for each acid:
- Reaction: H3PO4+3KOH→K3PO4+3H2O
- Moles of KOH required for 0.1 moles of H3PO4:
0.1 moles of H3PO4×3=0.3 moles of KOH
- Reaction: H3PO3+2KOH→K2HPO3+2H2O
- Moles of KOH required for 0.1 moles of H3PO3:
0.1 moles of H3PO3×2=0.2 moles of KOH
- Reaction: H3PO2+KOH→KH2PO2+H2O
- Moles of KOH required for 0.1 moles of H3PO2:
0.1 moles of H3PO2×1=0.1 moles of KOH
- From the calculations:
- H3PO4 requires 0.3 moles of KOH (not possible with 0.1 moles available).
- H3PO3 requires 0.2 moles of KOH (not possible with 0.1 moles available).
- H3PO2 requires 0.1 moles of KOH (this is possible with the available moles).
Since only H3PO2 can react with the available 0.1 moles of KOH, we conclude that:
- x=2 and the acid is H3PO2.
Among the given statements:
- The correct statement is: "X is equal to 2 and the given acid does not form acidic salt."
Topper's Solved these Questions
- STOICHIOMETRYBOOK - NARENDRA AWASTHI ENGLISHCHAPTER - STOICHIOMETRYEXERCISE - Match the Colum-II
6 Videos
- STOICHIOMETRYBOOK - NARENDRA AWASTHI ENGLISHCHAPTER - STOICHIOMETRYEXERCISE - Subjective Problems
20 Videos
- SOLID STATEBOOK - NARENDRA AWASTHI ENGLISHCHAPTER - SOLID STATEEXERCISE - Subjective Problems
13 Videos
- THERMODYNAMICSBOOK - NARENDRA AWASTHI ENGLISHCHAPTER - THERMODYNAMICSEXERCISE - Level 3
89 Videos
Similar Questions
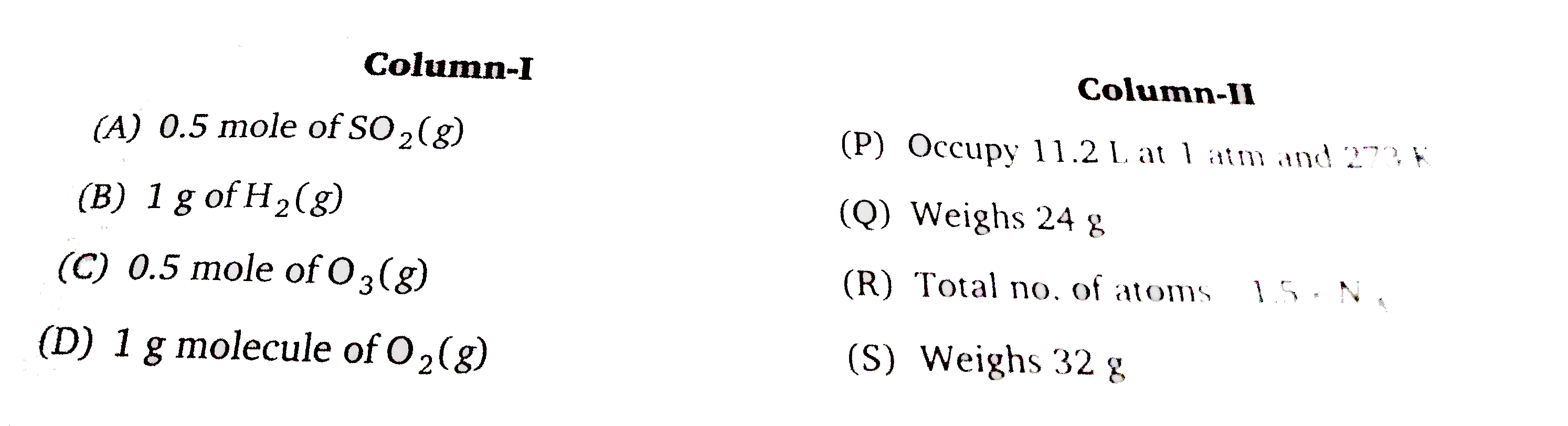
View SolutionWhat volume of a liquid (in L) will contain 10 mole ? If molar mass of liquid is 280 and its density is 1.4 g/mL.
View SolutionIn seven possible crystal system how many crystal system have more than one Bravais lattice ?
View SolutionThe first law of thermodynamics for a closed system is dU = dq + dw, where dw = dwpv+dwnon-pv. The most common type of wnon-pv is electrical work. As per IUPAC convention work done on the system is positive.
A system generates 50 J electrical energy, has 150 J of pressure-volume work done on it by the surroundings while releasing 300 J of heat energy. What is the change in the internal energy of the sytem?
View SolutionThe true statement for the acids of phosphorus. H_(3)PO_(2) H_(3)PO_(3) and H_(3)PO_(4) is:
View SolutionIf 0.1 mole H_(3)PO_(x) is completely neutralised by 5.6g KOH then select the true statement.
View SolutionThe true statement of the oxoacids of phosphorus H_(3)PO_(2),H_(3)PO_(3) and H_(3)PO_(4) is
View Solution0.12 mole H_(3)PO_(x) is compeltely neutralized by 5.6 g KOH then the true statement is :-
View SolutionTo neutralise completely 20 mL of 0.1 M aqueous solution of phosphorus acid (H3PO3), the volume of 0.1 M aqueous KOH solution required is :
View SolutionThe true statement for the acids of phosphorus H_(3)PO_(2), H_(3)PO_(3) and H_(3)PO_(4) is
View SolutionTo neutralise completely 20 mL ofO. I M aqueous solution of phosphorous acid (H_(3)PO_(3)), the value of 0.1 M aqueous KOH solution required is
View SolutionThe true statement for the acids of phosphorus. H3PO2,H3PO3andH3PO4 is :
View Solution0.01 mole H_(3)PO_(x) is completely neutralised by 0.56 gram of KOH hence :
View SolutionTo neutralise completely 20 mL of 0.1 M aqueous solution of phosphorous acid (H_(3)PO_(3)) , the volume of 0.1 M aqeous KOH solution required is
View SolutionThe true statement for the acids of phosphorus, H3PO2,H3PO3 and H3PO4 is -
View Solution

