The E∘ at 25∘C for the following reaction at the indicated concentrations is 1.50 V. Calculate the ΔG in kJ/mol 25∘C :
−140.94
−295
−212
−422.83
The correct Answer is:D
To calculate the Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) for the given electrochemical reaction at 25°C, we can follow these steps:
Step 1: Write down the reaction
The reaction is:
Cr (s)+3Ag+(aq)→3Ag (s)+Cr3+(aq)
Step 2: Identify the number of electrons transferred (n)
In this reaction, chromium (Cr) is oxidized from an oxidation state of 0 to +3, losing 3 electrons. Silver ions (Ag⁺) are reduced from +1 to 0, gaining 3 electrons. Therefore, the number of electrons transferred (n) is:
n=3
Step 3: Use the Nernst equation
The Nernst equation relates the standard cell potential (E°) to the cell potential (E) under non-standard conditions:
E=E°−0.059nlog((Cr3+)(Ag+)3)
Given:
- E°=1.50V
- (Cr3+)=0.1M
- (Ag+)=0.1M
Step 4: Substitute values into the Nernst equation
Substituting the known values into the Nernst equation:
E=1.50−0.0593log(0.1(0.1)3)
Step 5: Simplify the logarithm
The logarithm simplifies as follows:
log(0.1(0.1)3)=log(0.1)−log(0.13)=log(0.1)−3log(0.1)=−1+3=2
Step 6: Calculate E
Now substituting back into the equation:
E=1.50−0.0593×2
E=1.50−0.059×23
E=1.50−0.03933
E≈1.46067V
Step 7: Calculate ΔG using the formula
The Gibbs free energy change can be calculated using the formula:
ΔG=−nFE
Where:
- F (Faraday's constant) = 96500 C/mol
Substituting the values:
ΔG=−3×96500×1.46067
Step 8: Calculate ΔG
Calculating this gives:
ΔG=−3×96500×1.46067≈−422843.7J/mol
Step 9: Convert to kJ/mol
To convert from joules to kilojoules:
ΔG≈−422.8437kJ/mol
Final Answer
Thus, the Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) is approximately:
ΔG≈−422.84kJ/mol
The reaction is:
Cr (s)+3Ag+(aq)→3Ag (s)+Cr3+(aq)
In this reaction, chromium (Cr) is oxidized from an oxidation state of 0 to +3, losing 3 electrons. Silver ions (Ag⁺) are reduced from +1 to 0, gaining 3 electrons. Therefore, the number of electrons transferred (n) is:
n=3
The Nernst equation relates the standard cell potential (E°) to the cell potential (E) under non-standard conditions:
E=E°−0.059nlog((Cr3+)(Ag+)3)
- E°=1.50V
- (Cr3+)=0.1M
- (Ag+)=0.1M
Substituting the known values into the Nernst equation:
E=1.50−0.0593log(0.1(0.1)3)
The logarithm simplifies as follows:
log(0.1(0.1)3)=log(0.1)−log(0.13)=log(0.1)−3log(0.1)=−1+3=2
Now substituting back into the equation:
E=1.50−0.0593×2
E=1.50−0.059×23
E=1.50−0.03933
E≈1.46067V
The Gibbs free energy change can be calculated using the formula:
ΔG=−nFE
Where:
- F (Faraday's constant) = 96500 C/mol
ΔG=−3×96500×1.46067
Calculating this gives:
ΔG=−3×96500×1.46067≈−422843.7J/mol
To convert from joules to kilojoules:
ΔG≈−422.8437kJ/mol
Thus, the Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) is approximately:
ΔG≈−422.84kJ/mol
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYBOOK - NARENDRA AWASTHI ENGLISHCHAPTER - ELECTROCHEMISTRYEXERCISE - LEVEL-2
28 Videos
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYBOOK - NARENDRA AWASTHI ENGLISHCHAPTER - ELECTROCHEMISTRYEXERCISE - LEVEL-3
37 Videos
- DILUTE SOLUTIONBOOK - NARENDRA AWASTHI ENGLISHCHAPTER - DILUTE SOLUTIONEXERCISE - leval-03
23 Videos
- GASEOUS STATEBOOK - NARENDRA AWASTHI ENGLISHCHAPTER - GASEOUS STATEEXERCISE - Subjective problems
15 Videos
Similar Questions
In the Hall process, aluminium is produced by the electrolysis of molten Al2O3. How many second would it take to produce enough aluminium by the Hall process to make a case of 24 cans of auminium soft-drink, if each can uses 5.0g of Al, a current of 9650amp is employed and the current efficiency of the cell is 90%:
View Solution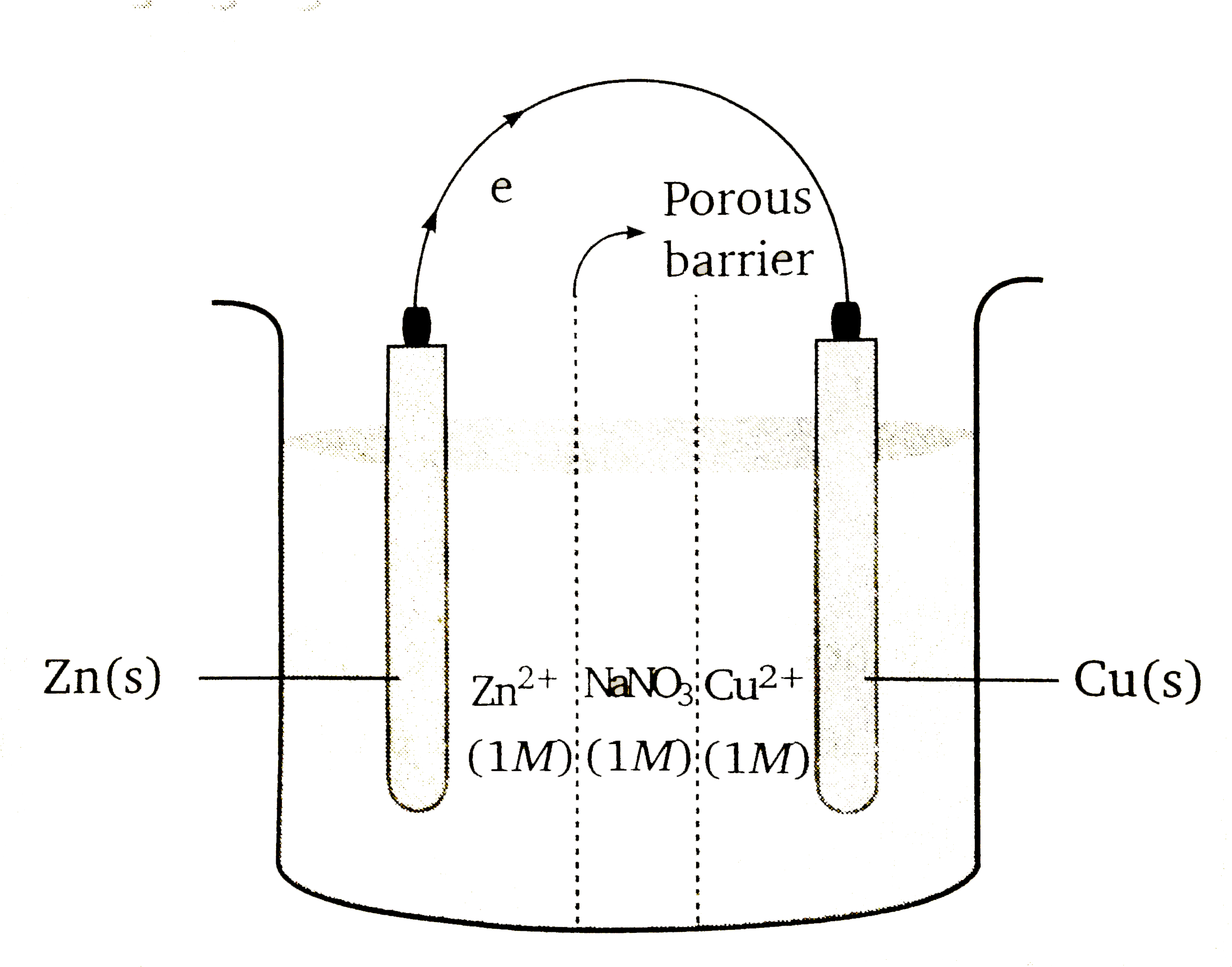
A Galvanic cell consits of three compartment as shown in figure. The first compartment contain ZnSO4(1M) and III compartment contain CuSO4(1M). The mid compartment contain NaNO3 (1M). Each compartment contain 1L solution:
E∘Zn2+/Zn=−0.76, E∘Cu2+/Cu=+0.34,
The concertation of Zn2+ in first compartment after passage of 0.1 F charge will be:
View SolutionLowering in vapour pressure is determined by Ostwald and Walker dynamic methed. It is based on the prinicipal , that when air is allowed to pass through a solvent or solution, it takes up solventvapour with it to get itself saturated at that temperature
I and II are weighted separately before and after passing dry air. Loss in mass of each set, gives the lowing of vapour pressure. The temperature of air, the solution and the solvent is kept constant.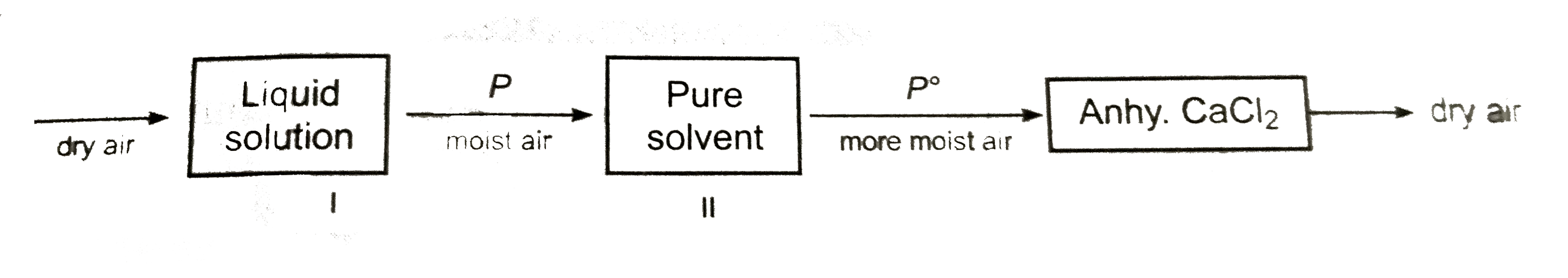
Loss in masss of solvent (wII)will be proportional to :
View SolutionA bubble of gas released at the bottom of a lake increases to four times its original volume when it reaches the surface. Assuming that atmospheric pressure is equivalent to the pressure exerted by a column of water 10 m high, what is the depth of the lake?
View SolutionThe EMF of Westron standard cell is 1.0153 at 20^(@)C and 1.01807 at 25^(@)C . Calculate DeltaG,DeltaH, and Delta S for the cell reaction at 25^(@)C .
View SolutionFor the cell Zn|ZnCl2(m)|AgCl,E is 1.24V at 25∘C and 1.260V at 35∘C of m=10−3. Write down the cell reaction and calculate ΔG,ΔH, and ΔS at 25∘C.
View SolutionThe E^(@) at 25^(@) C for the following reaction is 0.55 V. Calculate the DeltaG^(@) in kJ // mol : 4BiO^(+)(aq)+3N_(2)H_(5)^(+)to4Bi(s)+3N_(2)(g)+4H_(2)O(l)+7H^(+)
View SolutionThe E∘ at 25∘C for the following reaction at the indicated concentrations is 1.50 V. Calculate the ΔG in kJ/mol 25∘C :
View SolutionThe E^(@) at 25^(@) for the following reaction at the indicated concentration is 1.50 V. Calculate the DeltaG in kJ at 25^(@) C: Cr(s)+3Ag^(+)(aq,0.1M) rarrAg(s)+Cr^(3+)(aq,0.1M)
View SolutionThe value of ΔG∘ in the Daniell cell has been found to be -212.3 kJ at 25∘C. Calculate equilibrium constant for the reaction.
View Solution25∘C पर अभिक्रिया NH4Cl(s)→NH2(g)+HCl(g) के लिए ΔH तथा ΔS के मान क्रमश : +177kJmol−1 तथा +285Jmol−1K−1 हैं । इस ताप पर अभिक्रिया के लिए ΔG की मान की गणना कीजिए तथा यह स्पष्ट कीजिए की अभिक्रिया 25∘C पर स्वतः प्रवर्तित है अथवा नहीं ।
View SolutionFor the reaction, bond energies are given as under – (i) C—C, 346 kJ/mol (ii) C—H, 413 kJ/mol (iii) H—H, 437 kJ/mol and (iv) C = C, 611 kJ/mol What will be the value of Delta H at 25^(@) C for the above reaction ?
View SolutionStandard enthalpy change for combustion of methane is –890 kJ mol−1 and standard entropy change for the same combustive reaction is -242.98 J.K−1 at 25∘C. Calculate ΔG∘ of the reaction.
View SolutionStandard enthalpy change for combustion of methane is –890 kJ mol−1 and standard entropy change for the same combustive reaction is -242.98 J.K−1 at 25∘C. Calculate ΔG∘ of the reaction.
View SolutionStandard enthalpy change for combustion of methane is –890 kJ mol−1 and standard entropy change for the same combustive reaction is -242.98 J.K−1 at 25∘C. Calculate ΔG∘ of the reaction.
View Solution

