The enthalpy change for the reaction, C2H6(g)→2C(g)+6H(g) is X kJ. The bond energy of C-H bond is :
X2
X3
X6
data insufficient
The correct Answer is:D
To solve the problem regarding the enthalpy change for the reaction C2H6(g)→2C(g)+6H(g) and to find the bond energy of the C-H bond, we can follow these steps:
Step 1: Identify the bonds in the reactant
In ethane (C2H6), there are:
- 1 C-C bond
- 6 C-H bonds
Step 2: Write the expression for the total energy required to break these bonds
To break the bonds in C2H6 into individual atoms (2 carbon atoms and 6 hydrogen atoms), we need to account for the energy required to break both the C-C bond and the C-H bonds.
Let:
- z = bond energy of one C-H bond
- y = bond energy of the C-C bond
The total energy required to break all the bonds in C2H6 can be expressed as:
Total energy=6z+y
Step 3: Relate the total energy to the enthalpy change
According to the problem, the enthalpy change for the reaction is given as X kJ. Therefore, we can set up the equation:
6z+y=X
Step 4: Analyze the information given
The problem does not provide the value of y (the bond energy of the C-C bond). Without this information, we cannot isolate z (the bond energy of the C-H bond) because we have two unknowns in our equation.
Conclusion
Since we do not have enough information to determine the bond energy of the C-H bond, we conclude that the data is insufficient to solve for z.
Final Answer
The bond energy of the C-H bond cannot be determined from the given information. Therefore, the answer is that the data is insufficient.
---
In ethane (C2H6), there are:
- 1 C-C bond
- 6 C-H bonds
To break the bonds in C2H6 into individual atoms (2 carbon atoms and 6 hydrogen atoms), we need to account for the energy required to break both the C-C bond and the C-H bonds.
- z = bond energy of one C-H bond
- y = bond energy of the C-C bond
Total energy=6z+y
According to the problem, the enthalpy change for the reaction is given as X kJ. Therefore, we can set up the equation:
6z+y=X
The problem does not provide the value of y (the bond energy of the C-C bond). Without this information, we cannot isolate z (the bond energy of the C-H bond) because we have two unknowns in our equation.
Since we do not have enough information to determine the bond energy of the C-H bond, we conclude that the data is insufficient to solve for z.
The bond energy of the C-H bond cannot be determined from the given information. Therefore, the answer is that the data is insufficient.
Topper's Solved these Questions
- THERMODYNAMICSBook:NARENDRA AWASTHI ENGLISHChapter:THERMODYNAMICSExercise:Level 2
Explore 40 Videos
- THERMODYNAMICSBook:NARENDRA AWASTHI ENGLISHChapter:THERMODYNAMICSExercise:Level 3
Explore 89 Videos
- STOICHIOMETRYBook:NARENDRA AWASTHI ENGLISHChapter:STOICHIOMETRYExercise:Match the Colum-II
Explore 6 Videos
Similar Questions
A heating coil is immersed in a 100 g sample of H2O (l) at a 1 atm and 100∘ C in a closed vessel. In this heating process , 60% of the liquid is converted to the gaseous form at constant pressure of 1 atm . The densities of liquid and gas under these conditions are 1000 kg/m3 and 0.60 kg/m3 respectively . Magnitude of the work done for the process is :
(Take : 1L-atm= 100 J)
View SolutionThe first law of thermodynamics for a closed system is dU = dq + dw, where dw = dwpv+dwnon-pv. The most common type of wnon-pv is electrical work. As per IUPAC convention work done on the system is positive.
A system generates 50 J electrical energy, has 150 J of pressure-volume work done on it by the surroundings while releasing 300 J of heat energy. What is the change in the internal energy of the sytem?
View Solution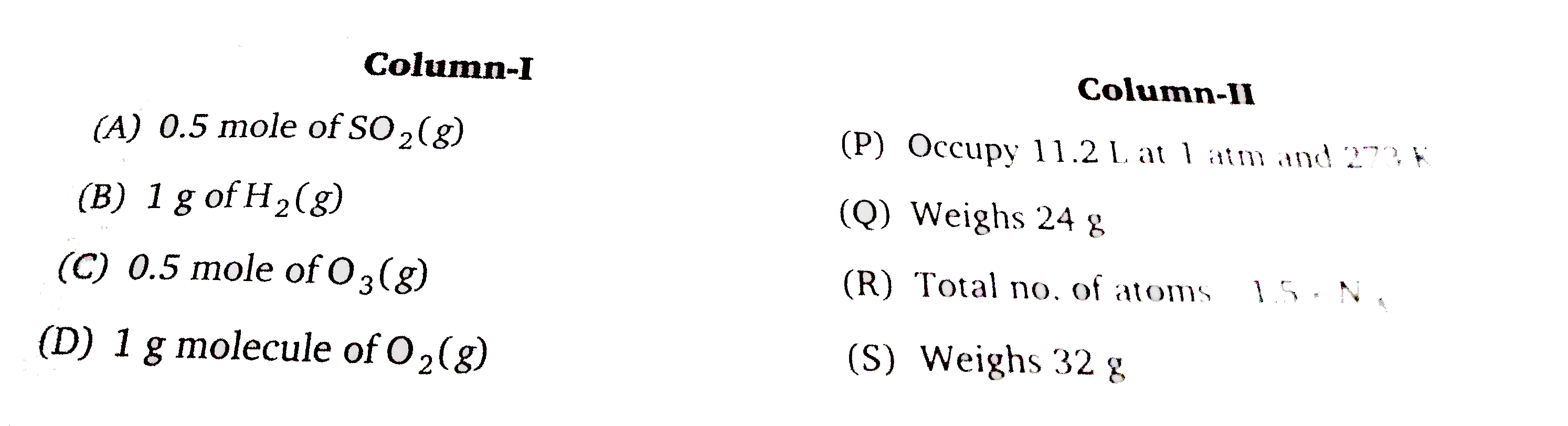
View SolutionGiven that Cu_(4)(g) +360 kJ rarr C(g) +4H(g) C_(2)H_(6)(g) +620 kJ rarr 2C(g) +6H(g) The value of C-C bond enegry is
View SolutionThe enthalpy change for the reaction, C2H6(g)→2C(g)+6H(g) is X kJ. The bond energy of C-H bond is :
View SolutionEnthalpy change of the reaction
2H(g)→H2(g) is −104kcal
The H−H bond dissociation energy is
View SolutionEnthalpy change for the reaction, 4H(g)→2H2(g) is −869.6 kJ
The dissociation energy of H-H bond is :
View SolutionEnthalpy change for the reaction, 4H_((g))rarr2H_(2(g)) is - 869.6 kJ. The dissociation energy of H - H bond is
View SolutionEnthalpy change for the reaction,
4H(g)→2H2(g) is -869.5 kJ.
The dissociation energy of H-H bonds is
View SolutionThe bond enthalpy of C - C, C = C, H - H and C - H bonds are 350,600,400 and 410 kJ · mol-1 respectively. The enthalpy change for reaction
C2H4(g)+H2(g)→C2H6(g) is
View SolutionUsing the bond enthalpy data given below, calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction. C_(2)H_(4) (g) + H_(2) (g) to C_(2) H_(6) (g) Data : {:("Bond" , C- C , C = C) , (, C-H , H - H):} Bond Enthalpy 336.81 kJ/mol 606.68 kJ/mol 410.87 kJ/mol 431.79 kJ/mol
View SolutionCalculate the enthalpy of hydrogenation : C_(2)H_(5)(g) + H_(2)(g) to C_(2)H_(6)(g) Given that the bond enthalpies of H - H , C = C, C- C and C - H bonds are 433, 615, 347 and 413 kJ mol^(-1) respectively.
View SolutionEnthalpy change for the reaction, 4H(g) to 2H_(2)(g) is -869.6 kJ . The dissociation energy of H - H bond is
View SolutionGiven :
C2H6(g)→2C(g)+6H(g):ΔH=712kcal
The C - C bond energy is 112 kcal, what is the C - H bond energy ?
View SolutionThe enthalpy change for the reaction C_(2)H_(6(g)) rarr 2C_((g)) + 6H_((g)) is x kJ. The bond energy of C-H bond is:
View Solution
