What is the conductivity of a semiconductor sample having electron concentration of 5×1018m−3 hole concentration of 5×1019m−3, electron mobility of 2.0m2V−1s−1 and hole mobility of 0.01m2V−1s−1?
(Take charge of electron as 1.6×10−19C)
1.83(Ω−m)−1
1.68(Ω−m)−1
1.20(Ω−m)−1
0.59(W−m)−1
The correct Answer is:B
To find the conductivity of the semiconductor sample, we can use the formula for conductivity (σ) given by:
σ=q⋅(n⋅μe+p⋅μh)
where:
- q is the charge of an electron,
- n is the electron concentration,
- p is the hole concentration,
- μe is the electron mobility,
- μh is the hole mobility.
Step 1: Identify the given values
- Electron concentration (n) = 5×1018m−3
- Hole concentration (p) = 5×1019m−3
- Electron mobility (μe) = 2.0m2V−1s−1
- Hole mobility (μh) = 0.01m2V−1s−1
- Charge of an electron (q) = 1.6×10−19C
Step 2: Substitute the values into the formula
Now, substituting the values into the conductivity formula:
σ=(1.6×10−19)⋅((5×1018)⋅(2.0)+(5×1019)⋅(0.01))
Step 3: Calculate the contributions from electrons and holes
1. Calculate the contribution from electrons:
n⋅μe=(5×1018)⋅(2.0)=10×1018=1.0×1019
2. Calculate the contribution from holes:
p⋅μh=(5×1019)⋅(0.01)=0.05×1019
Step 4: Combine the contributions
Now, combine the contributions:
n⋅μe+p⋅μh=1.0×1019+0.05×1019=1.05×1019
Step 5: Calculate the conductivity
Now, substitute this back into the conductivity formula:
σ=(1.6×10−19)⋅(1.05×1019)
Calculating this gives:
σ=1.68m−1
Final Answer
The conductivity of the semiconductor sample is:
σ=1.68S/m
---
- q is the charge of an electron,
- n is the electron concentration,
- p is the hole concentration,
- μe is the electron mobility,
- μh is the hole mobility.
- Electron concentration (n) = 5×1018m−3
- Hole concentration (p) = 5×1019m−3
- Electron mobility (μe) = 2.0m2V−1s−1
- Hole mobility (μh) = 0.01m2V−1s−1
- Charge of an electron (q) = 1.6×10−19C
Now, substituting the values into the conductivity formula:
1. Calculate the contribution from electrons:
n⋅μe=(5×1018)⋅(2.0)=10×1018=1.0×1019
p⋅μh=(5×1019)⋅(0.01)=0.05×1019
Now, combine the contributions:
n⋅μe+p⋅μh=1.0×1019+0.05×1019=1.05×1019
Now, substitute this back into the conductivity formula:
σ=(1.6×10−19)⋅(1.05×1019)
σ=1.68m−1
The conductivity of the semiconductor sample is:
σ=1.68S/m
Topper's Solved these Questions
- JEE MAINSBook:JEE MAINS PREVIOUS YEAR ENGLISHChapter:JEE MAINSExercise:Chemistry
Explore 1 Video
- JEE MAINBook:JEE MAINS PREVIOUS YEAR ENGLISHChapter:JEE MAINExercise:All Questions
Explore 452 Videos
- JEE MAINS 2020Book:JEE MAINS PREVIOUS YEAR ENGLISHChapter:JEE MAINS 2020Exercise:PHYSICS
Explore 250 Videos
Similar Questions
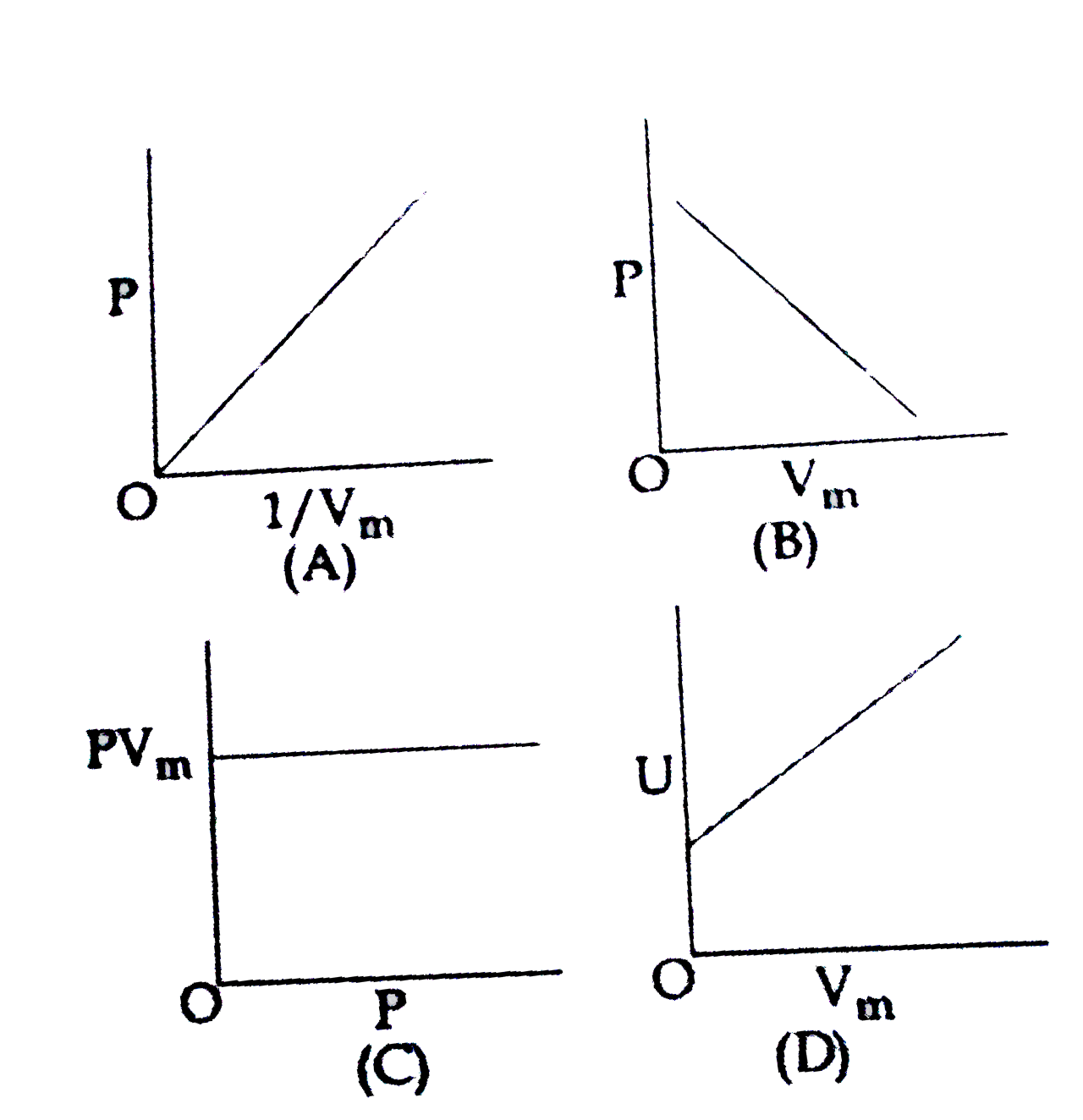
The combination of plots which does not represent isothermal expansion of an ideal gas is :
View SolutionA box weighs 196 N on a spring balance at the noth pole. Its weight recorded on the same balance if it is shifted to the equator is close to (take g=10ms−2 at the north pole and the radius of the earth = 6400 km) :
View SolutionIf x and y are arbitrary intensive variables, then
View SolutionA semiconductor has an electron concentration of 0.45×1012m−3 and a hole concentration of 5.0×1020m−3. Calculate its conductivity. Given electron mobility =0.135m2V−1s−1, hole mobility =0.048m2V−1s−1,
View SolutionDetermine the conductivity of pure germanium at 27^(@)C . The concentration of the carriers at this temperature is 2.2 xx 10^(19)m^(-3) . The mobility of electrons = 0.36 and that of holes = 0.17
View SolutionWhat is the conductivity of a semiconductor sample having electron concentration of 5×1018m−3 hole concentration of 5×1019m−3, electron mobility of 2.0m2V−1s−1 and hole mobility of 0.01m2V−1s−1?
(Take charge of electron as 1.6×10−19C)
View SolutionAn extrinsic semiconductor has the concentration of holes as charge carriers 5×1020m−3 . The electron concentration is negligible as compared to hole concentration . If mobility of holes is 0.05 m2.V−1.s−1 then find the conductivity (in mho. m−1) of the semiconductor ?
View Solutionशुद्ध जर्मेनियम में इलेक्ट्रॉन - होल जोड़ो (electron -hole pair ) की संख्या 3×1019m−3 है । यदि इलेक्ट्रॉन तथा होल की गतिशीलता ( mobility ) क्रमशः 0.39×m2V−1s−1 तथा 0.19m2V−1s−1 हो , तो इसकी प्रतिरोधकता (resistivity) ज्ञात करे ।
View Solutionकिसी अपद्रव्यी या बाह्य अर्धचालक (extrinsic semiconductor ) में इलेक्ट्रॉन तथा होल के संख्या घनत्व (number density ) क्रमशः 8×1019m−3 तथा 5×1018m−3 है । यदि इलेक्ट्रॉन तथा होल की गतिशीलता क्रमशः 2.3m2V−1s−1 तथा 0.01m2V−1s−1 , हो , तो इस अर्धचालक की चालकता तथा प्रतिरोधकता ज्ञात करे । यह अर्धचालक टाइप का ही या इस अर्धचालक की चालकता तथा प्रतिरोधकता ज्ञात करे । यह अर्धचालक n- टाइप का है या p- टाइप का ?
View Solutionनैज सिलिकॉन में कक्ष ताप पर आवेश वाहकों की प्रति एकांक आयतन संख्या 1.6×1016/m3 है| यदि इलेक्ट्रान की गतिशीलता 0.150m2V−1S−1 तथा हॉल गतिशीलता 0.05m2V−1S−1 है तब सिलिकॉन की चालकता (Ω−1m−1) में है-
View Solutionकिसी अर्थ-चालकों में इलेक्ट्रान सांद्रता 0.45×1012m−3 तथा हॉल सांद्रता 5×1020m−3 है| इसकी विशिष्ट चालकता ज्ञात कीजिये| दिया है,
हॉल गतिशीलता (hole mobility) =0.048m2V−1s−1 तथा इलेक्ट्रान गतिशीलता =0.135m2V−1s−1 |
View Solutionकमरे के ताप पर किसी नाइज अर्धचालक (जर्मेनियम) (Intrinsic semiconductor) में इलेक्ट्रान व होल की गतिशीलता क्रमश: 0.36 m2V−1s−1 एवं 0.17m2V−1s−1 है| एलेक्ट्रोंन व होल प्रत्येक का घनत्व 2.5×1019m3 है| जर्मेनियम की विघुत चालकता क्या है?
View SolutionA type semiconductor sample has electron and hole concentration of 1.6×1019 the electron and hole mobility in the sample is 1.2m2v−1s−1 and 0.001 m2v−1s−1 respectively calculate the value of resistivity of the sample
View SolutionA semiconductor is known to have an electron concentration of 8×1013cm−3 and a hole concentration of 5×1012cm−3 .
a . Is the semiconductor n- type of p-type ?
b. What is the resistitivity of the simple , if the electron mobility is 23,000 cm2V−1s−1 and hole mobility is 100cm2V−1s−1 ? Take charge on electron , e=1.6×10−19 C .
View SolutionA semiconductor has the electron concentration 0.45×1012m−3 and hole concentration 5×1029m−3 . Find its conductivity . Given electron mobility = 0.135m2V−1s−1 and hole mobility = 0.048m2V−1s−1,e=1.6×10−19C
View Solution
