For the reaction : N2(g)+3H2(g)⇔2NH3(g), ΔH=−ve, the correct statement is :
ΔH=ΔU=0
|ΔH|<|ΔU|
|ΔH|>|ΔU|
ΔH=ΔU≠0
The correct Answer is:C
To solve the question regarding the reaction N2(g)+3H2(g)⇌2NH3(g) with ΔH<0, we will analyze the thermodynamic properties of the reaction step by step.
1. Identify the Reaction and Its Enthalpy Change:
- The reaction given is N2(g)+3H2(g)⇌2NH3(g).
- It is stated that the enthalpy change ΔH for this reaction is negative, indicating that the reaction is exothermic.
2. Calculate the Change in Moles of Gas (ΔN):
- We need to calculate ΔN, which is the change in the number of moles of gas during the reaction.
- Moles of products = 2 (from 2NH3)
- Moles of reactants = 1 (from N2) + 3 (from 3H2) = 4
- Therefore, ΔN=Moles of products−Moles of reactants=2−4=−2.
3. Relate Enthalpy Change to Internal Energy Change:
- The relationship between enthalpy change (ΔH) and internal energy change (ΔU) can be expressed as:
ΔH=ΔU+PΔV
- For ideal gases, PΔV can be expressed in terms of ΔN:
PΔV=ΔNRT
- Hence, we can rewrite the equation as:
ΔH=ΔU+ΔNRT
4. Substitute the Value of ΔN:
- Since ΔN=−2:
ΔH=ΔU−2RT
5. Analyze the Sign of ΔH and ΔU:
- Given ΔH<0 (since the reaction is exothermic), we can infer that:
ΔU−2RT<0
- This implies that:
ΔU<2RT
- Since R (universal gas constant) and T (temperature) are positive, 2RT is positive, meaning ΔU must also be a negative value but less than 2RT.
6. Conclusion:
- The correct statement regarding the relationship between ΔH and ΔU is that ΔH<ΔU because ΔH is negative and ΔU is less negative (or more positive) than 2RT.
Final Answer:
The correct statement is that ΔH<ΔU.
- The reaction given is N2(g)+3H2(g)⇌2NH3(g).
- It is stated that the enthalpy change ΔH for this reaction is negative, indicating that the reaction is exothermic.
- We need to calculate ΔN, which is the change in the number of moles of gas during the reaction.
- Moles of products = 2 (from 2NH3)
- Moles of reactants = 1 (from N2) + 3 (from 3H2) = 4
- Therefore, ΔN=Moles of products−Moles of reactants=2−4=−2.
- The relationship between enthalpy change (ΔH) and internal energy change (ΔU) can be expressed as:
ΔH=ΔU+PΔV
- For ideal gases, PΔV can be expressed in terms of ΔN:
PΔV=ΔNRT
- Hence, we can rewrite the equation as:
ΔH=ΔU+ΔNRT
- Since ΔN=−2:
ΔH=ΔU−2RT
- Given ΔH<0 (since the reaction is exothermic), we can infer that:
ΔU−2RT<0
- This implies that:
ΔU<2RT
- Since R (universal gas constant) and T (temperature) are positive, 2RT is positive, meaning ΔU must also be a negative value but less than 2RT.
- The correct statement regarding the relationship between ΔH and ΔU is that ΔH<ΔU because ΔH is negative and ΔU is less negative (or more positive) than 2RT.
The correct statement is that ΔH<ΔU.
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Calculate ΔfH∘(inkJmol) for C2H6(g), if ΔcH∘ [C(graphite)]=–393.5kJmol, ΔcH∘[(H2)g]=–286kJmol and ΔcH∘[C2H6(g)] = –1560kJmol
View SolutionE∘Cu2+/Cu=0.34V
E∘Cu+/Cu=0.522V
E∘Cu2+/Cu+=
View SolutionThe correct statement with respect to dinitrogen is :
View SolutionFor the chemical reaction
N2(g)+3H2(g)⇔2NH3(g)
The correct option is:
View SolutionWhich statement about the given reaction is incorrect?
N2+3H2⇔2NH3, ΔH=−ve
View SolutionFor the reaction : N_(2(g))+3H_(2(g))hArr2NH_(3(g)) , DeltaH=-ve , the correct statement is :
View SolutionFor N2+3H2⇔2NH3,ΔH=-ve then :-
View SolutionFor the reaction N_(2)(g)+3H_(2)(g)to2NH_(3)(g) , which of the following is correct regarding DeltaH ?
View SolutionIncreased pressure shifts the equilibrium of the reaction: N2(g)+3H2(g)↔2NH3(g) so as to
View SolutionIn reaction N2(g)+3H2(g)⇔2NH3(g),ΔH=−93.6kJ/mole, the yield of ammonia does not increase when
View Solution(K_(c))/(K_(p)) for the reaction, N_(2)(g)+3H_(2)(g)hArr2NH_(3(g)) is
View SolutionFor the reversible reaction N_(2(g))+3H_(2(g))hArr2NH_(3(g))+"Heat" . The equilibrium shifts in forward direction.
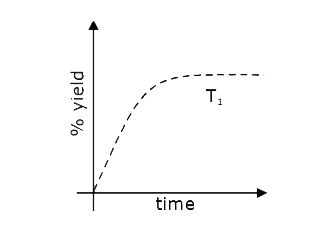
View SolutionThe % yield of ammonia as a function of time in the reaction N2(g)+3H2(g)⇔2NH3(g),(g)ΔH<0 at (P,T1) is given below
View SolutionWhich of the following is correct for the reaction? N_(2)(g)+3H_(2)(g)hArr2NH_(3)(g)
View SolutionConsider the following reactions .In which case the formation of product is favoured by decreasein pressure?
(1)CO2(g)+C(s)⇔2CO(g),ΔH∘=+172.5Kj
(2)N2(g)+3H2(g)⇔2NH3(g)⇔2NH3(g),ΔH∘=−91.8KJ
(3) N2(g)+O2(g)⇔2NO(g),ΔH∘=181KJ
(4) 2H2O(g)⇔2H2(g)+O2(g),ΔH∘=484.6KJ
View Solution
