The inward and outward electric flux for a closed surface in units of N-m2/C are respectively 8×103and4×103. Then the total charge inside the surface in S.I. units is (where ∈0= permittivity in free space)
4×103
−4×103
(−4×103)∈0
−4×103∈0
The correct Answer is:D
Similar Questions
The inward and outward electric flux for a closed surface unit of N−m2/C are respectively 8×103 and 4×103. Then the total charge inside the surface is [where ε0= permittivity constant]
View SolutionThe suface integral of electrostatic field →E produced by any sources over any closed surface S enclosing a volume V in vacumm, i.e., total electric flux over the closed S in vacumm is 1/∈0 times the total charge (Q) contained inside S, i.e, ϕE=∮→E.→ds=Q∈0
The charge inside S may be point charges or even continous charge distributions.
There is no contribution to total electric flux from the charges outside S. Further, the location at Q inside S does not affect the value of surface integral.
Read the above passage and answer the following questions :
(i) what are the SI unit and dimensions of electric flux ?
(ii) A closed surface in vacumm encloses charge −q,+3qand+5q. Another charge +4q lies outside the surface. What is total electric flux over the surface ?
(iii) A point charge q lies inside a spherical of radius r. How will the electric flux be affected if radius of the sphere is doubled ?
(iv) What values of life do you earn from the theorem ?
View Solution
Knowledge Check
The inward and outward electric flux for a closed surface unit of N−m2/C are respectively 8×103 and 4×103. Then the total charge inside the surface is [where ε0= permittivity constant]
A4×103CB−4×103CC(−4×103)εCD−4×103ε0CThe inward annd outward electric flux from a closed surface are respectively 8×103and4×103 units. Then the net charge inside the closed surface is
A−4×103ε0coulombB−4×103ε0 coulombC4×103 coulombD4×103ε0 coulombIf the electric flux entering and leaving a closed surface are 6×106 and 9×106 SI units respectively, then the net charge inside the surface of permittivity of free space ε0 is
Aε0×106B−ε0×106C−2ε0×106D3ε0×106
Find the flux of the electric field through a spherical surface of radius R due to a charge of 8.85×10−8C at the centre and another equal charge at a point 3R away from the centre (Given : ε0=8.85×10−12 units )
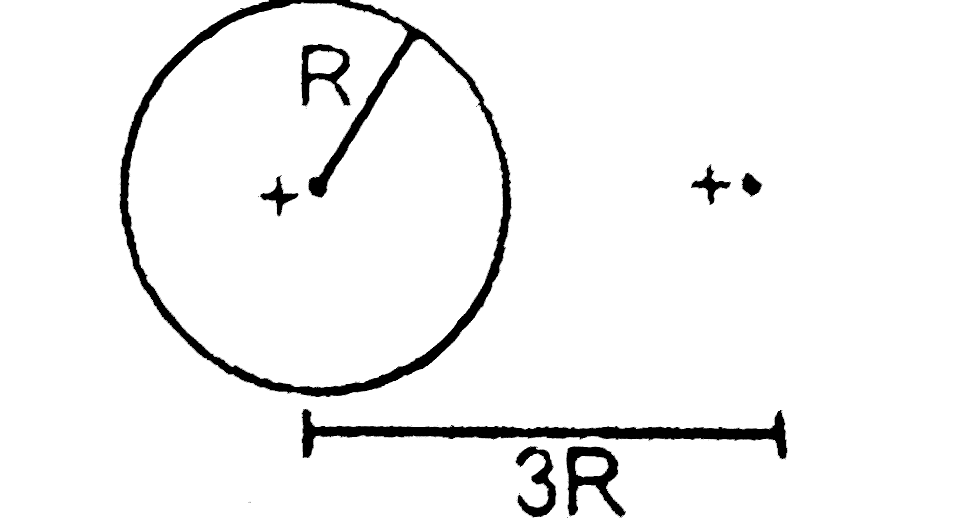
View SolutionFind the flux of the electric field through a spherical surface of radius R due to a charge of 8.85×10−8C at the centre and another equal charge at a point 3R away from the centre (Given : ε0=8.85×10−12 units )

View SolutionCareful measurement of the electric field at the surface of a black box indicates that the net outward flux through the surface of the box is 8.0×103Nm2/C (a) what is the net charge inside the box ? (b) If the net outward flux through the surface of the box were zero, could you conclude that there were no charges inside the box ? Why or why not?
View SolutionA closed surface is vacumm encloses charges −qand+3q. Another charge −2q lies outside the surface. Total electric flux over the surface is
View SolutionA cubical Gaussian surface encloses electric flux of 30C per unit permittively of a charge ,the electric flux through each face of the cube per unit permittivity is
View Solution

