A sphere of mass 3 kg moving with a velocity of 2 ms- collides head-on with another sphere of mass 4 kg moving in opposite direction with a velocity of 1 ms. After collision if they stick together and move with a velocity v, find
(i) the total initial momentum and (ii) the value of velocity v.
The correct Answer is:2kgms−1;2/7ms−1
Topper's Solved these Questions
- COLLISIONS BOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - COLLISIONS EXERCISE - NUMERICAL EXERCISE ( LEVEL 2)
23 Videos
- COLLISIONS BOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - COLLISIONS EXERCISE - QUESTIONS FOR DESCRIPTIVE ANSWERS
4 Videos
- COLLISIONS BOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - COLLISIONS EXERCISE - VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
12 Videos
- CENTRE OF MASSBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - CENTRE OF MASSEXERCISE - ADDITIONAL PRACTICE EXERCISE (PRACTICE SHEET (ADVANCED))
3 Videos
- ELASTICITYBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - ELASTICITYEXERCISE - Questions for Descriptive Answers
10 Videos
Similar Questions
A bullet of mass 0.04kg travelling horizontally at 100 m/s hits a stationary block of wood of mass 8kg, passes through it and emerges horizontally with a speed of 40 m/s. If the block is free to move on a smooth horizontal plane, what is the speed with which it moves after the bullet had passed through it?
View SolutionFour identical balls A,B,C and D are placed in a line on a frictionless horizontal surface. A and D are moved with same speed .u. towards the middle as shown. Assuming elastic collisions, find the final velocities.
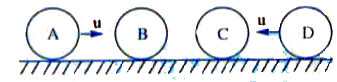
View SolutionWhat is a collision ? Mention the types of collisions
View SolutionA man (m1) with a bag (m2) in hand falls freely vertically from a height h above the ground. After falling through a height y0, man throws bag horizontally with a velocity u0 towards his right.
View SolutionA steel wire of area of cross-section A and length 2L is clamped firmly between two points seperated by a distance .2L.. A body is hung from the middle point of the wire such that the middle point sags by a distance X. Calculate the mass of the body and the angle made by the string with the horizontal. (Young.s modulus of Steel = y)
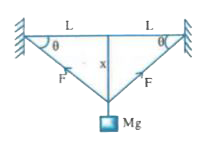
View SolutionA ball of mass M moving with a velocity v collides perfectly inelastically with another ball of same mass but moving with a velocity v in the opposite direction. After collision
View SolutionA body of mass 2 kg moving with a velocity of 3 m/sec collides head on with a body of mass 1 kg moving in opposite direction with a velocity of 4 m/sec. After collision, two bodies stick together and move with a common velocity which in m/sec is equal to
View SolutionA sphere of mass 'm' moving with velocity 'v' collides head-on on another sphere of same mass which is at rest. The ratio of final velocity of second sphere to the initial velocity of the first sphere is (e is coefficient of restitution and collision is inelastic)
View SolutionA ball of mass 1 kg moving with a velocity of "0.4 ms"^(-1) collides with another stationary ball. After the collision, the first ball moves with a velocity of 0.3ms^(1) in a direction making an angle of 90^(@) with its initial direction. The momentum of the second ball after the collision will be (in kg ms^(-1) )
View SolutionA spere of mass 20 kg moving with a velocity 40ms−1 collides with another sphere of mass 15 kg which is at rest . After collision they move with the same velocity . Find the velocity .
View SolutionA sphere of mass M moving with velocity w collides elastically with another of mass m at rest. After collision their final velocities are V and v. The value of vis:
View SolutionA sphere of mass M moving with velocity u collides elastically with another of mass mat rest. After collision their final velocities are V and v. The value of v is:
View SolutionTwo perfectly elastic spheres of masses 2 kg and 3 kg moving in opposite directions with velocities 8ms−1and6ms−1 respectively collide with each other. Find their velocities after the impact.
View SolutionA sphere of mass 50xx10^(-3) kg moving with a velocity of 2ms^(-1) hits another sphere which is at rest. Assuming the collision to be head - on collision and if they stick together after collision and move in the same direction with a velocity of 0.5 ms^(-1) , find the mass of the second sphere.
View SolutionTwo perfectly elastic spheres of masses 2 kg and 3 kg moving in opposite directions with velocities 8 ms^(-1) and 6 ms^(-1) respectively collide with each other. Find their velocities after the impact.
View Solution

