Two rods of different metals, having the same area of cross-section A, are placed end to end between two massive walls as shown in fig. If the temperature of both the rods are now raised by Δt0C then
(a) Find the force with which the rods acts on cach other at higher temperature.
(b) Find the lengths of the rods at the higher temperature.
Assume that there is no change in the cross-sectional area of the rods and the rods do not bend. There is no deformation of walls.

(a) Due to heating the increases in length of the composite rod will be (Δl)1=l1α1Δt+l2α2Δt=(l1α1+l2α2)Δt...(1)
due to compressive force .F from the walls, due to elasticity, the decrease in length will be
(Δl)D=Fl1AY1+Fl2AY2=FA(l1Y1+l2Y2)....(2)
As the length of the composite rod remains unchanged the increase in length due to heating must be equal to decrease in length due to compression.
(l1α1+l2α2)Δ=FA(l1Y1+l2Y2)⇒(##AKSELTAIPHYXIV01C_C01SLV023_S01.png width=80%><br>As∈itiallythe≤n>hofo≠rod∈L,anddue→heat∈gits≤n>h∈creasesby(Deltal_(1))_(H)=alpha_(1) l_(1)Deltat.<br>whi≤due→compressionits≤n>hdecreasesby(Deltal_(1_(C))=(Fl_(1))/(AY_(1))<br>soitsf∈al≤n>hl_(1)^(1)=l_(1)+(Deltal_(1))_(H)-(Deltal_(1))_(C)=l_(1)+l_(1)alpha_(1) Deltat-(Fl_(1))/(AY_(1))<br>fortheotherfordl_(1)^(2)=l_(2)+(Deltal_(2))_(H)-(Deltal_(2))_(C), l_(2)^(1)=l_(2)+l_(2)alpha_(2)Deltat-(Fl_(2))/(AY_(2))
Topper's Solved these Questions
- ELASTICITYBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - ELASTICITYEXERCISE - TEST YOUR SELF
11 Videos
- ELASTICITYBOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - ELASTICITYEXERCISE - Very Short Answer Type Questions
15 Videos
- COLLISIONS BOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - COLLISIONS EXERCISE - QUESTIONS FOR DESCRIPTIVE ANSWERS
4 Videos
- ELEMENTS OF VECTORS BOOK - AAKASH SERIESCHAPTER - ELEMENTS OF VECTORS EXERCISE - QUESTIONS FOR DESCRIPTIVE ANSWER
10 Videos
Similar Questions
A spring made of steel not copper. Why?
View SolutionThe increase of length of a wire under a load is equal to its initial length. What is the stress in the wire equal to?
View SolutionFour identical balls A,B,C and D are placed in a line on a frictionless horizontal surface. A and D are moved with same speed .u. towards the middle as shown. Assuming elastic collisions, find the final velocities.
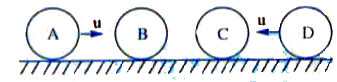
View SolutionFind the components of vector →A=2ˆi+3ˆj along the directions of ˆi+ˆj and ˆi−ˆj.
View SolutionTwo rods of different metals having the same area of cross section A are placed between the two massive walls as shown is Fig. The first rod has a length l1, coefficient of linear expansion α1 and Young's modulus Y1. The correcsponding quantities for second rod are l2,α2 and Y2. The temperature of both the rods is now raised by t∘C.
i. Find the force with which the rods act on each other (at higher temperature) in terms of given quantities.
ii. Also find the length of the rods at higher temperature.

View SolutionTwo rods of different materials having differnet lengths and same cross sectional areas are joined end to end in a straight line. The free ends of this compound rod are maintained at different temperatures The temperature gradient in each rod will be .
View SolutionTwo rods A and B of same metal and of same cross-section have length in the ratio 1:2 One end of each rod is at O∘C and temperature of other ends are 30∘C and 40∘C respectively Which of the rod will have higher flow of heat ? .
View SolutionTwo rods of the same length and areas of cross-section A_1 and A_2 have their ends at the same temperature. K_1 and K_2 are the thermal conductivities of the two rods. The rate of flow of heat is same in both the rods if-
View SolutionTwo rods are connected as shown. The rods are of same length and same cross sectional area. In steady state, the temperature (θ) of the interface will be -
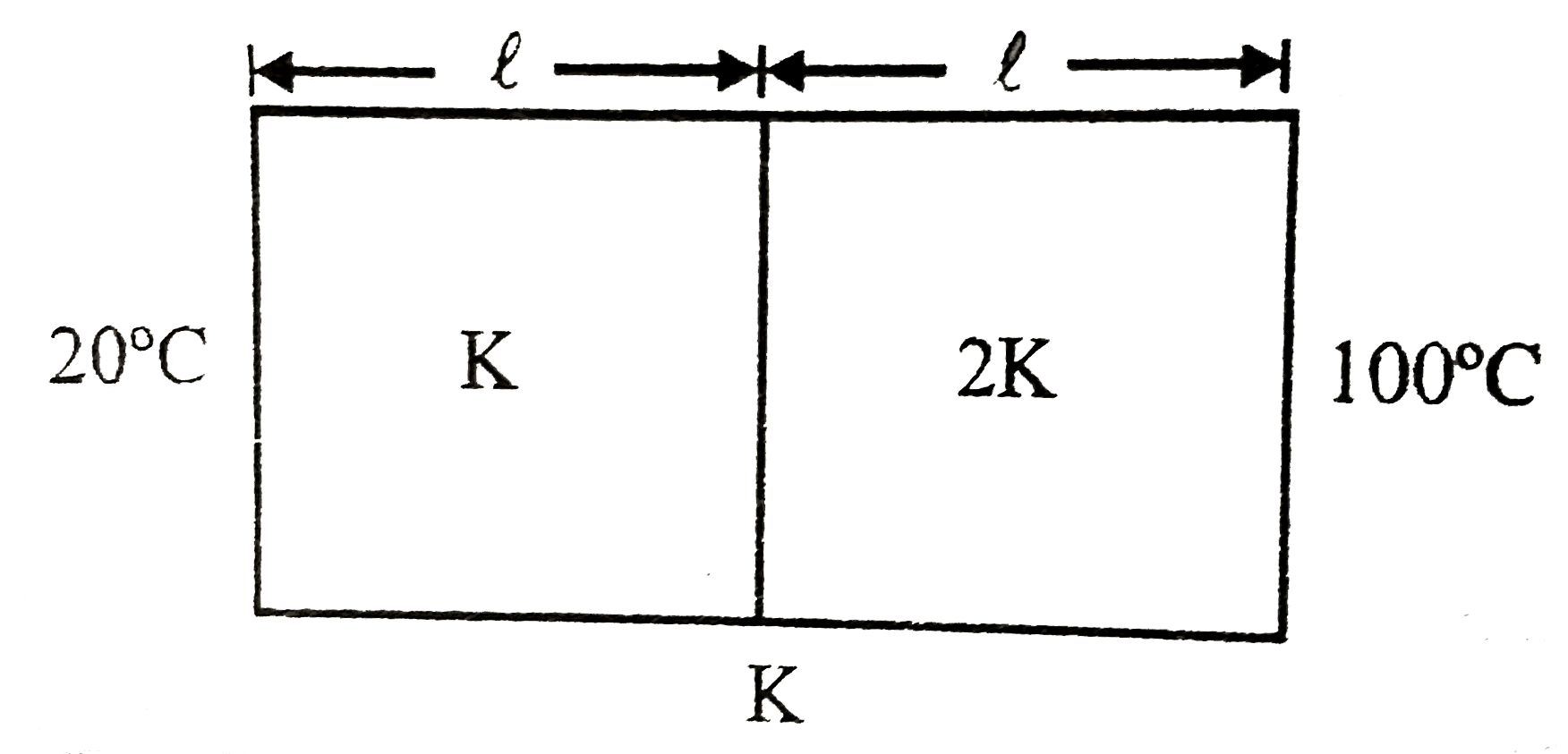
View SolutionTwo rods of equal cross sections area are joined end the end as shown in figure. These are supported between two rigid vertical walls. Initially the rods are unstrained . If temperature of system is increased by DeltaT then junction will not shift if -
View Solutionएक धातु की बनी दो छड़ो के अनुप्रस्थ-काट के क्षेत्रफल परस्पर समान है। एक छड़ की लम्बाई 40 सेमि एवं उसके सिरों का तापांतर 100∘C तथा दूसरी छड़ की लम्बाई 60 सेमि एवं उसके सिरों का तापांतर 120∘C है। आवश्यक गणना देते हुए बताइये की किस छड़ में ऊष्मा-चालकता की दर अधिक होगी?
View Solutionएक ही धातु की बनी तथा समान अनुप्रस्थ काट की दो छड़ो की लम्बाइयाँ क्रमश: 0.5 मीटर तथा 0.8 मीटर है | प्रथम छड़ के दोनों सिरों के बीच तापान्तर 40∘C है | दूसरी छड़ के सिरों के बीच तापान्तर ज्ञात कीजिये यदि दोनों छड़ो में ऊष्मा चालन की दर समान हो |
View SolutionTwo rods R and Q of same metal and same cross-section have length in the ratio 1:2 One end of each rod is at 0∘C and temperatures of other are 30∘C and 40∘C respectively. Which of the rod will have higher flow of heat ?
View SolutionTwo rods of different metals, having the same area of cross-section A, are placed end to end between two massive walls as shown in fig. If the temperature of both the rods are now raised by Delta t^@ C then a) Find the force with which the rods acts on each other at higher temperature. b) Find the lengths of the rods at the higher temperature. Assume that there is no change in the cross-sectional area of the rods and the rods do not bend. There is no deformation of walls.
View SolutionPassage - II: Two rods of different metals having the same area of cross section A are placed between the two massive walls as shown in Fig. The first rod has a length l coefficient of linear expansion alpha_(1) and Young's modulus Y_(1) . The corresponding quantities for second rod are l , alpha_2 and Y_2 . The temperature of both the rods is now raised by t^(@) C . Find the force with which the rods act on each other (at higher temperature) in terms of given quantities
View Solution

